

























Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
This method is useful in drawing the velocity diagram and finding the relative velocities of points on a link. • Let the velocity of B w.r.t A be represented by.
Typology: Study Guides, Projects, Research
1 / 33

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!


























-^ To determine the velocities of different pointson links of a mechanism for a given inputmotion. Determination of the motioncharacteristics of links in a mechanism isrequired for the force analysis •^ Velocities of links and of points of mechanism•^ Velocities of links and of points of mechanism^ can be determined by different methods.^ 1. Relative velocity method or velocity polygonmethod2. Instantaneous centre method.
-^ In order to determine the relative motion ofthe ends of a link, one of the ends isassumed to be moving relative to the otherend. •^ Let a link
-^ Therefore, the direction of relative velocity ofa point w.r.t any other point on a link isalways along perpendicular to the straightline joining the two points.
Velocity of any point on a link: Consider a link
B
A^ V C
A VB
B o^
a b^ c
5
Given the dimensions of al l the links,angular velocity of the crank AB andposition of the crank. Draw configurationdiagram.
D
A
C B θ
Given the dimensions of al l the links, angular velocity ofthe crank OA and position of the crank. Drawconfiguration diagram.
A^ O
B^
ω C
θ
(i)^ Draw a vector
oa^ of length OA X
ω^ (taking a
suitable scale) in a direction perpendicular to OA. (ii) Draw a vector line through a in a directionperpendicular to the link
AB. (draw some length on either side of
a .)
(iii) Draw the vector ob parallel to
OB^ to intersect
the vector
ab^ at^ b. (iv) Divide the ab vector such that
ac : ab^ =^ AC
: AB^8
-^ Since no component of the velocity of the crank pin is used tomove the slider, whole the velocity of the crank at crank pinwill be used to move the lever and hence, the velocity of leverand velocity of tool at these positions (B
Solution:
o 90 A^ O
B
o a
θ
b^90
o
θ θ
3 m 4 m 5 m
m/s
-1) of slider B with
respect to rigid link CD is(A) 0^
(B) 0.
(C) 1.
(D) 2.
Solution: From the dimension given,From the dimension given, angle ABC =
o velocity of crank at B = velocity of slider as AB isperpendicular to CDTherefore velocity of slider along CD =AB x 10 rad/s
=250 mm x10 rad/s = 2500 mm/s = 2.5 m/s
Answer : (D) 2.
-^ A link AB has moved
Bo Bn
B^1
Ao An
A^1
17
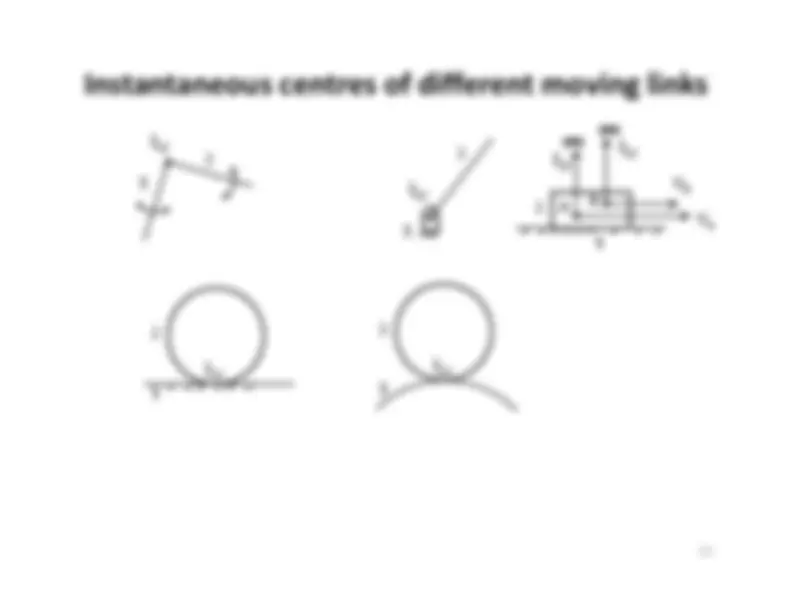
Instantaneous centres of different moving links^1
I^122
(^2) I (^121)
B^ A
VB 2
VA I^12 I^121
2 I^121
2 I^121