








Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
Various principles and techniques related to ultrasound imaging, including topics such as aperture, penetration depth, imaging modes, doppler shift, pulse repetition frequency, beam width, spatial resolution, harmonic imaging, and more. A series of multiple-choice questions that test the reader's understanding of these ultrasound concepts. By studying this document, one can gain a comprehensive understanding of the fundamental principles and techniques that underlie ultrasound imaging technology, which is widely used in medical diagnostics and other applications. The questions cover a broad range of topics, allowing the reader to assess their knowledge and identify areas for further learning.
Typology: Exams
1 / 15

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!










What is dynamic aperture? A. Aperture that varies with transmit frequency B. Aperture that decreases as a function of time C. Aperture that increases with increasing focal length D. Aperture that changes as a function of frame rate To which acoustic variable is penetration depth inversely related? A. Frequency B. Wavelength C. Period D. Propagation speed Which imaging mode requires a broadband transducer? A. Continuous wave doppler B. Pulsed wave doppler C. Color flow imaging D. Harmonic imaging What is the doppler shift frequency? A. Received ultrasound frequency multiplied by the transmitted ultrasound frequency B. Difference between the transmitted ultrasound frequency and the received ultrasound frequency C. Sum of the transmitted and received ultrasound frequencies D. Ratio of the transmitted ultrasound frequency to the received ultrasound frequency What is the potential effect of increasing the pulse repetition frequency(PRF)? A. Depth ambiguity B. Decreased frame rate C. Poor spatial resolution D. Decreased penetration
What is an advantage of using pulsed wave doppler compared to continuous wave doppler? A. Higher echo sensitivity B. Ability to select sample depth C. Decreased display of aliasing D. Improved temporal resolution What affects the beam width in the near field? A. Pulse repetition frequency B. Pulse duration C. Frame rate D. Transducer aperture What is the advantage of using pulsed-wave doppler versus continuous-wave doppler? A. Allows measurement of higher velocities B. Increases range ambiguity C. Reduces the potential for aliasing D. Provides depth specificity Which parameter is target group C evaluating based on the image? A. Dead zone B. Dynamic range C. Axial resolution D. Horizontal distance accuracy In this image, which target group is used to evaluate dead zone? A Which ultrasound parameter directly affects an ultrasound beam's intensity?
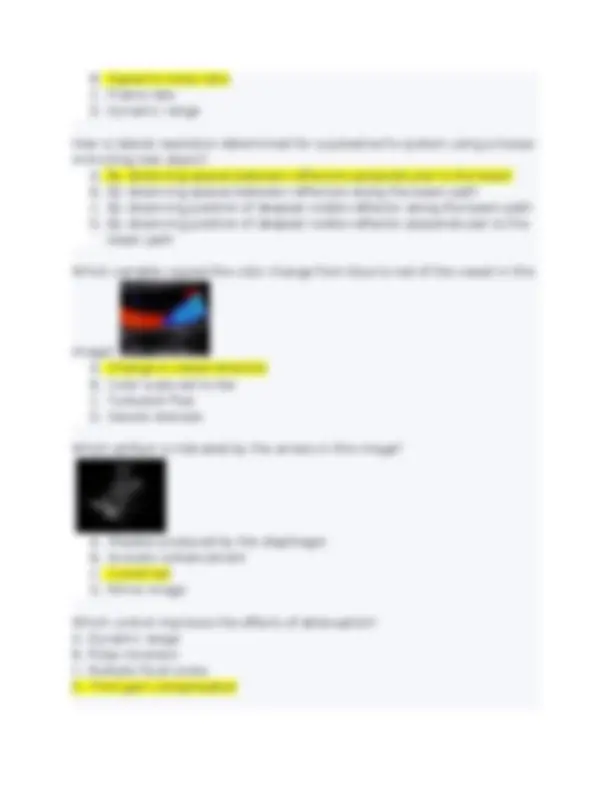
B. Signal-to-noise ratio C. Frame rate D. Dynamic range How is lateral resolution determined for a pulsed-echo system using a tissue- mimicking test object? A. By observing spaces between reflectors perpendicular to the beam B. By observing spaces between reflectors along the beam path C. By observing position of deepest visible reflector along the beam path D. By observing position of deepest visible reflector perpendicular to the beam path Which variable caused the color change from blue to red of the vessel in this image? A. Change in vessel direction B. Color scale set to low C. Turbulent flow D. Severe stenosis Which artifact is indicated by the arrows in this image? A. Shadow produced by the diaphragm B. Acoustic enhancement C. Comet tail D. Mirror image Which control improves the effects of attenuation? A. Dynamic range B. Pulse inversion C. Multiple focal zones D. Time gain compensation
Which doppler angle to flow results in the greatest absolute doppler shift? A. 0 degrees B. 15 degrees C. 45 degrees D. 60 degrees What term describes blood flow changes in response to respiration? A. Phasic B. Parabolic C. Spontaneous D. Pulsatile An increase in which parameter will improve the accuracy of velocity measurements with autocorrelation? A. Color field of view B. Packet size C. Wall filtering D. Transmitted frequency Which harmonic imaging, how does echo frequency relate to transmitted frequency? A. Half the transmitted frequency B. Equal to the transmitted frequency C. Twice the transmitted frequency D. Four times the transmitted frequency Which change would minimize the artifact observed in this image, assuming the pulse repetition frequency is at its maximum limit? A. Adjust the sweep speed B. Adjust the baseline C. Increasing dynamic range D. Increasing the transmitted frequency Which parameter is most likely to affect spatial resolution? A. Dynamic range
Which signals are eliminated by the wall filter in a spectral Doppler display? Low frequency, low amplitude At minimum, what is required when documenting a pathology discovered during an examination? Two images demonstrating the same pathology from different scan planes If the diameter of the sound beam is halved by focusing, what happens to the intensity. Increased by 2 times Which parameter would change on a phantom test if the spatial pulse length were made longer? A. Axial resolution B. Lateral resolution C. Horizontal distance resignation D. Sensitivity If the ultrasound machine comes in contact with a patient’s body fluids, what should be done? A. Remove the machine from use for the day B. Use an approved disinfectant solution to clean it C. Call the manufacturer to see what they would do Which parameter is most related to cavitation tissue? A. Energy B. Pressure C. Duty factor D. Pulse repetition frequency Which interface will cause the maximum reflection of the incident sound beam? A. Fat/muscle B. Soft tissue/bone C. Fat/soft tissue D. Soft tissue/lung Acoustic enhancement occurs distal to what? A. Calcifications B. Near field interface
C. Highly reflecting structure D. Weakly attenuating structure As the pressure amplitude of ultrasound doubles, what happens to the wavelength? A. Quadruples B. Doubles C. Halves D. Unchanged What is the period of a 5 mhz ultrasound wave? A. 0.02 ms B. 0.2 ms C. .5mc D. 5ms What limits diagnostic application at higher frequencies? A. Noise B. Tissue penetration C. Contrast resolution D. Temporal resolution What is the function of a lens on a transducer? A. Focus the beam B. Increase the bandwidth C. Shorten the pulse length D. Provide damping What would improve axial resolution? A. Increase the pulse repetition frequency B. Reduce the receiver gain C. Change the gray scale map D. Increase the transducer frequency What is true of the far field? A. Sound beam converges B. Intensity is highest C. Lateral resolution is best D. Sound beam diverges
B. Duplex imaging C. Pulsed wave doppler D. Continuous wave doppler When employing a tissue mimicking phantom, the depth at which echoes are no longer detected is an indicator of what? A. Dynamic range B. Lateral resolution C. Sensitivity D. Axial resolution What enhances the transmission of ultrasound energy between the transducer and the skin? A. The transducer matching layer B. A lower pulse repetition frequency C. A lower frequency probe D. A narrow active probe aperture Which technique increases the sharpness of high contrast boundaries? A. Edge enhancement B. Interpolation C. Smoothing D. Frame averaging What is the most appropriate action for the sonographer to take when receiving a verbal order for an exam? A. Deny performance of the exam until a written request is received B. Seek approval from supervisor C. Verbally repeat the request back to the referrer to verify correctness D. Document two forms of ID of the patient Which setting of an ultrasound system gives the sonographer the ability to display both strong and week echoes? A. Dynamic range B. Resolution C. Range calibration D. Sensitivity What is a benefit of using contrast agents?
A. Output power can be increased after contrast administration to improve visualization B. Increased amplitude of the returning doppler signals C. Harmonic signals produced by contrast agents are weaker than those produced by tissue D. Frame rate is improved when interrogating contrast with power doppler A sound wave propagates fastest through which substance? A. Bone B. Muscle C. Fat D. Gas When the focal point in a B-mode image is electronically changed, which type of focusing is in use? A. Lens B. Mechanical C. Dynamic D. Curved crystal When a fluid is flowing at a slow and constant rate within a long tube having a uniform diameter, what is the nature of the flow? A. Disturbed B. Turbulent C. Laminar D. Pulsatile What causes range ambiguity artifacts? A. Receiver overload B. Pulser overload C. PRF too high D. PRF too low What is the round trip time in soft tissue for an echo from a reflector at a depth of 1 cm? A. 1.54 usec B. 6.5 usec C. 13 usec D. 26 usec
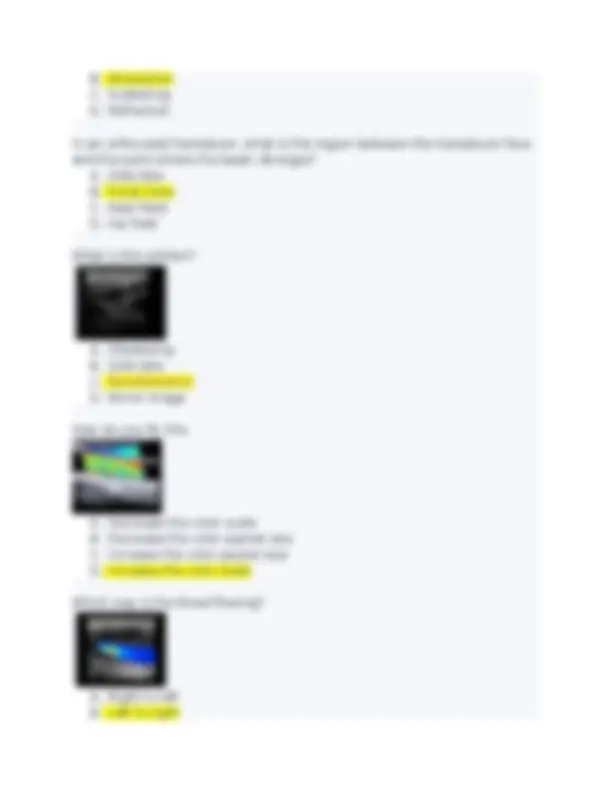
A. 32 khz B. 10 khz C. 8 khz D. 5 khz What caused the color pattern demonstrated in the artery indicated by the arrow in this image? A. Superimposed venous flow B. Aliasing C. Flow reversal D. Color side lobe artifact Which adjustment should be made to avoid the aliasing displayed on this spectral Doppler image seen on spectral analysis? A. Reposition sample volume so it is deeper. B. Decrease acoustic power C. Change the doppler angle from 60 to 45 degrees D. Decrease the transducer freq If red blood cells are approaching a 5 Mhz Doppler transducer at a speed of 75 cm/s, what is the approximate received ultrasound frequency? A. 4,500 khz B. 4,995 khz C. 5,005 khz D. 5,500 khz Which condition must be present for refraction to occur? A. Presence of a strong specular reflector B. Presence of several small reflectors C. Difference in tissue prop speeds D. A change in the angle of reflection The thermal index (TI) is most affected by which type of interaction between sound and tissue? A. Reflection
B. Absorption C. Scattering D. Refraction In an unfocused transducer, what is the region between the transducer face and the point where the beam diverges? A. Side lobe B. Focal Zone C. Near field D. Far field What is this artifact? A. Shadowing B. Side lobe C. Reverberation D. Mirror image How do you fix this A. Decrease the color scale B. Decrease the color packet size C. Increase the color packet size D. Increase the color scale Which way is the blood flowing? A. Right to left B. Left to right