


Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
A list of organic compounds, their acceptable names, characteristic reactions, and examples. It covers hydrocarbons, functional group-containing compounds, and the types of reactions they undergo. useful for students studying organic chemistry and provides a comprehensive overview of the subject.
Typology: Lecture notes
1 / 3

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!


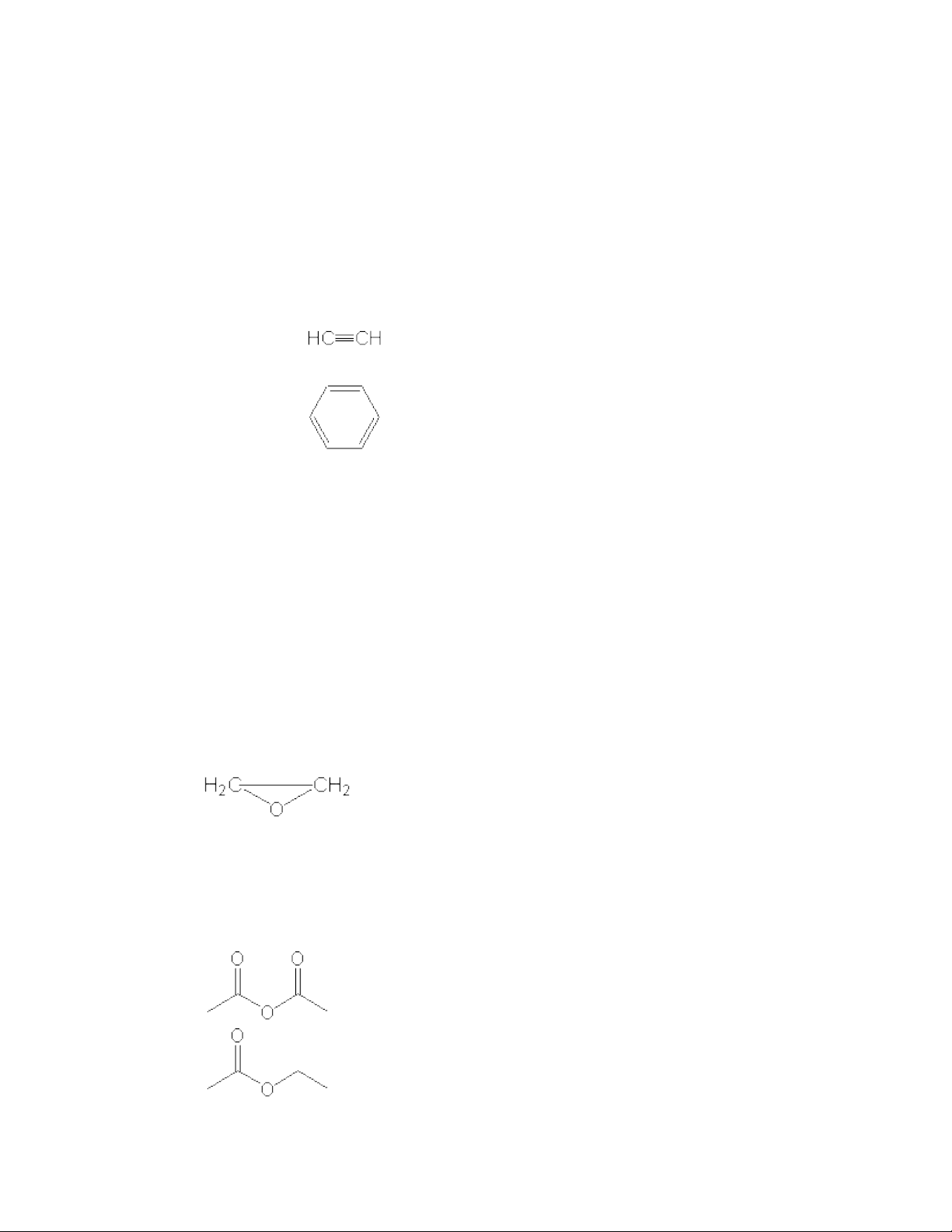
Compound Examples Acceptable Name Characteristic Reactions Alkanes CH 3 CH 3 Ethane Free-radical substitution Alkenes CH 2 =CH 2 Ethene or ethylene Electrophilic addition Alkynes Ethyne or acetylene Electrophilic addition Dienes CH 2 =CHCH=CH 2 1,3-Butadiene Electrophilic addition Arenes Benzene (C 6 H 6 ) Electrophilic subsitution
Compound Examples Acceptable Name Characteristic Reactions Alkyl halides CH 3 CH 2 Cl Chloroethane or ethyl chloride Nucleophilic subsitution; elimination Alkenyl halides CH 2 =CHCl Chloroethene or vinyl chloride Electrophilic addition; elimination Aryl halides C 6 H 5 Cl Chlorobenzene Electrophilic & nucleophilic aromatic substituion Alcohols CH 3 CH 2 OH Ethanol or ethyl alcohol Dehydration; esterification Phenols C 6 H 5 OH Phenol Electrophilic subsitution Epoxides Ethylene oxide or oxirane Nucleophilic ring opening Aldehydes CH 3 CHO Ethanal or acetaldehyde Nucleophilic addition to carbonyl Ketone CH 3 COCH 3 2-Propanone or acetone Nucleophilic addition to carbonyl Carboxylic acids CH 3 COOH Ethanoic (acetic) acid Acid ionization; ester formation Acyl halides CH 3 COCl Ethanoyl (acetyl) chloride Nucleophilic acyl subsitution Acid anhydrides Ethanoic (acetic) anhydride Nucleophilic acyl subsitution Esters Ethyl ethanoate (acetate) Nucleophilic acyl subsitution
Amides CH 3 CONHCH 3 N-Methylethanamide or N- methylacetamide Nucleophilic acyl subsitution Amines CH 3 CH 2 NH 2 Ethanamine or ethylamine Nitrogen (base) as nucleophile Nitriles CH 3 CN Ethanenitrile or acetonitrile Nucleophilic addition Nitro comps. C 6 H 5 NO 2 Nitrobenzene Reduction of nitro to amine Thiols CH 3 CH 2 SH Ethanethiol Oxidation to acids or disulfides Sulfides CH 3 CH 2 SCH 2 CH 3 Diethyl sulfide Alkylation or oxidation
Compound Examples Acceptable Name Characteristic Reactions Alkanes CH 3 CH 3 Ethane Free-radical substitution Alkenes CH 2 =CH 2 Ethene or ethylene Electrophilic addition Alkynes Ethyne or acetylene Electrophilic addition Dienes CH 2 =CHCH=CH 2 1,3-Butadiene Electrophilic addition Arenes Benzene (C 6 H 6 ) Electrophilic subsitution Alkyl halides CH 3 CH 2 Cl Chloroethane or ethyl chloride Nucleophilic subsitution; elimination Alkenyl halides CH 2 =CHCl Chloroethene or vinyl chloride Electrophilic addition; elimination Aryl halides C 6 H 5 Cl Chlorobenzene Electrophilic & nucleophilic aromatic substituion Alcohols CH 3 CH 2 OH Ethanol or ethyl alcohol Dehydration; esterification Phenols C 6 H 5 OH Phenol Electrophilic subsitution Epoxides Ethylene oxide or oxirane Nucleophilic ring opening Aldehydes CH 3 CHO Ethanal or acetaldehyde Nucleophilic addition to carbonyl Ketone CH 3 COCH 3 2-Propanone or acetone Nucleophilic addition to carbonyl Carboxylic acids CH 3 COOH Ethanoic (acetic) acid Acid ionization; ester formation Acyl halides CH 3 COCl Ethanoyl (acetyl) chloride Nucleophilic acyl subsitution Acid anhydrides Ethanoic (acetic) anhydride Nucleophilic acyl subsitution Esters Ethyl ethanoate (acetate) Nucleophilic acyl subsitution