








Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
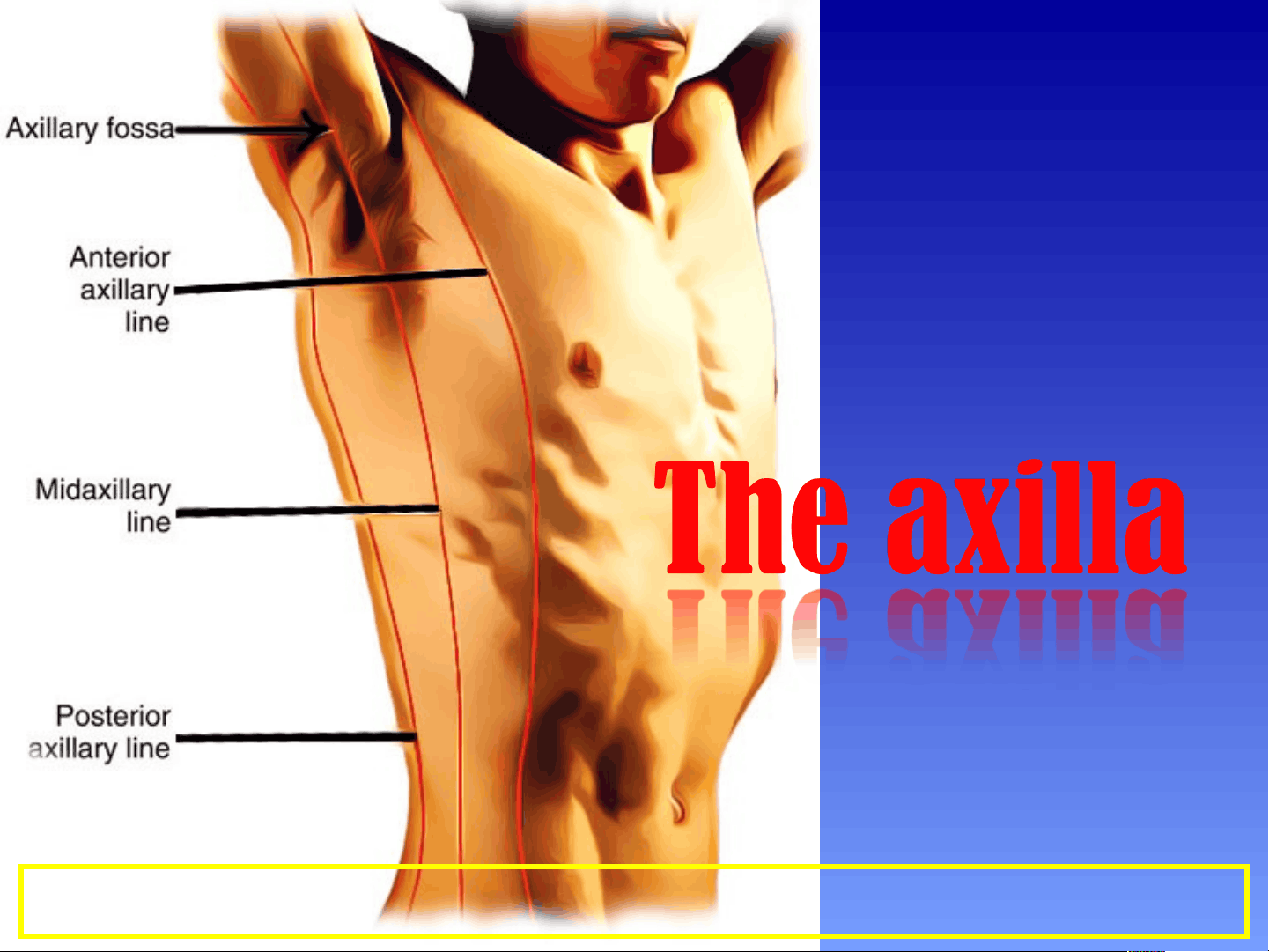
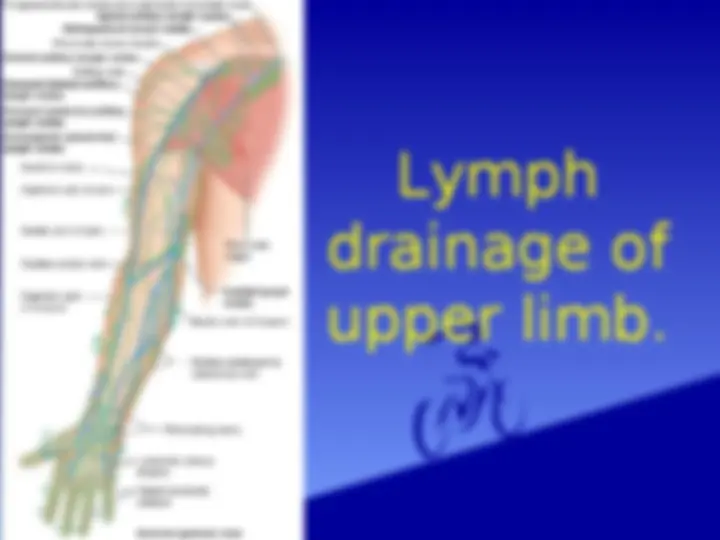
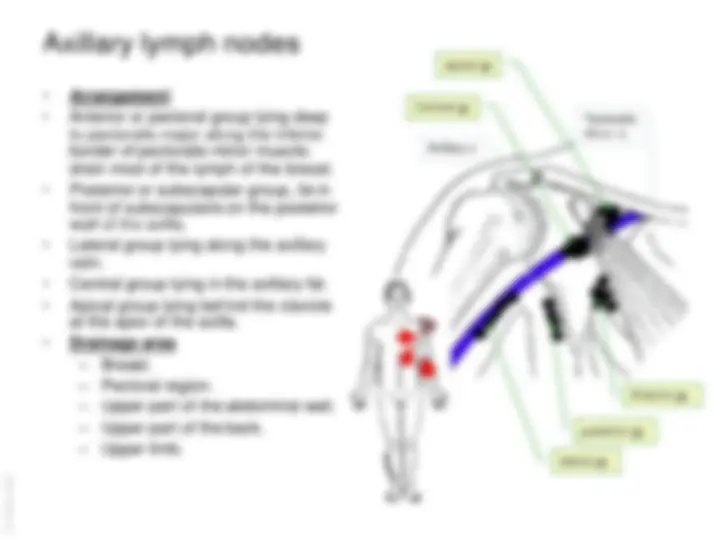
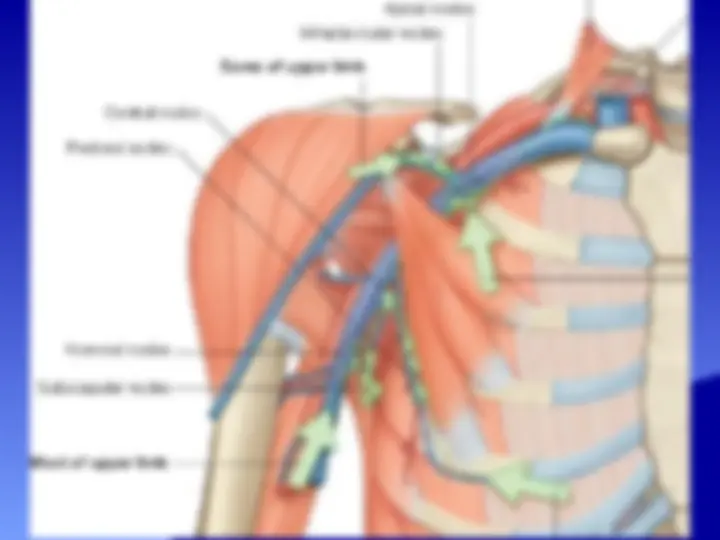
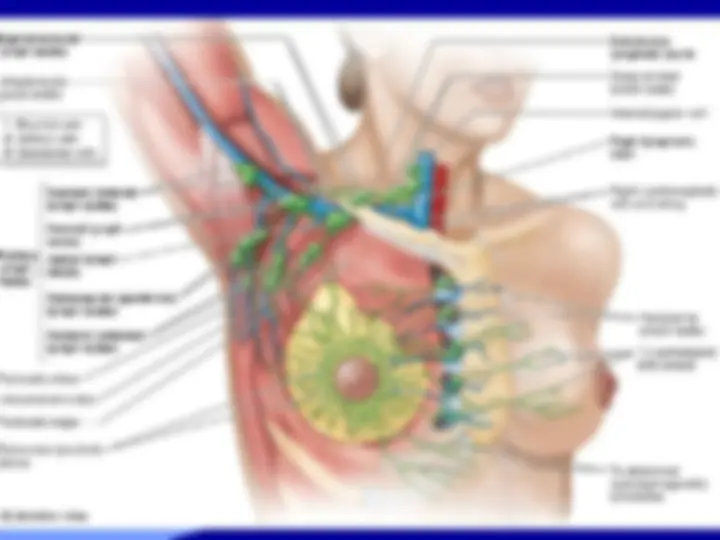
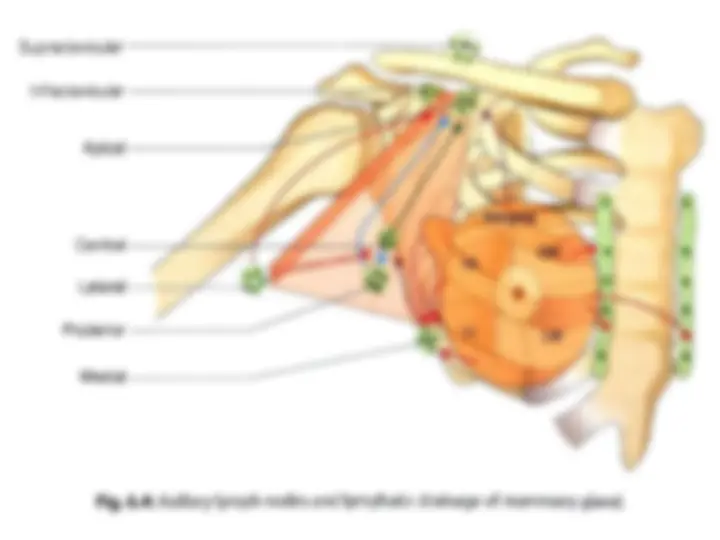
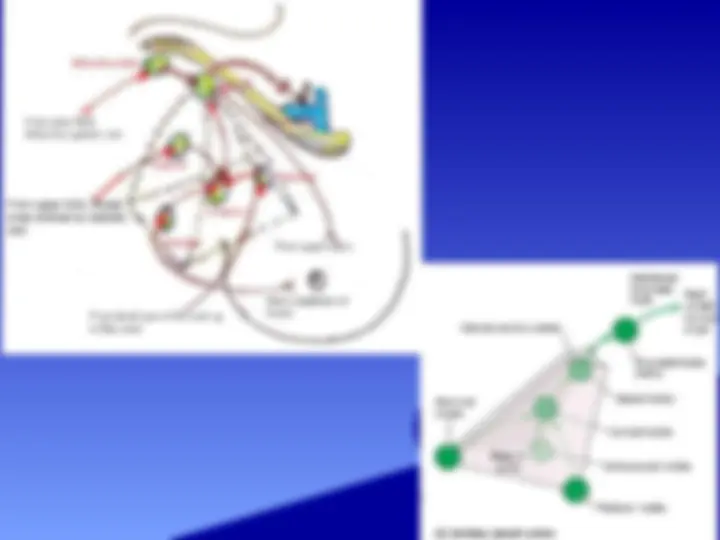
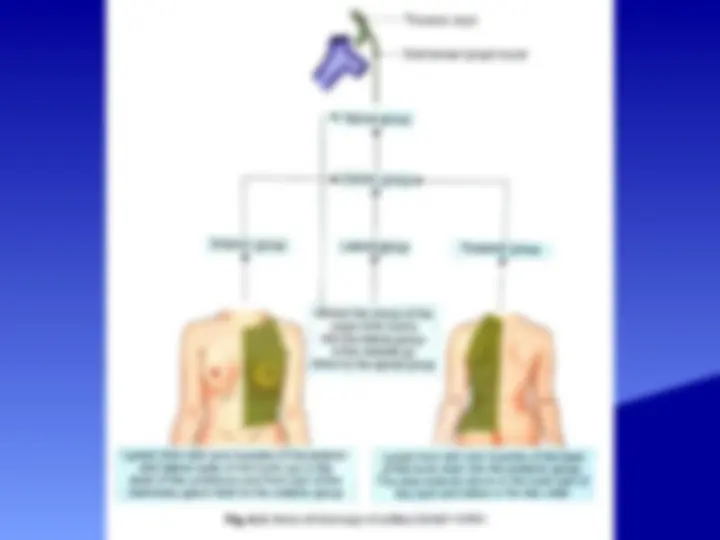
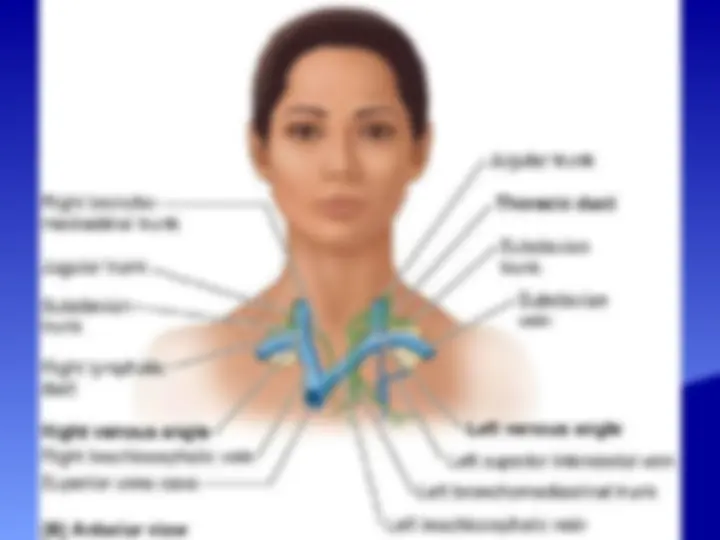
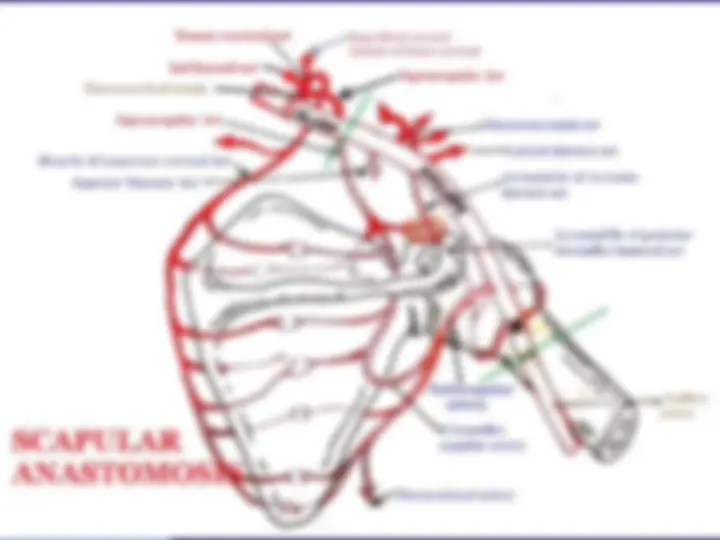
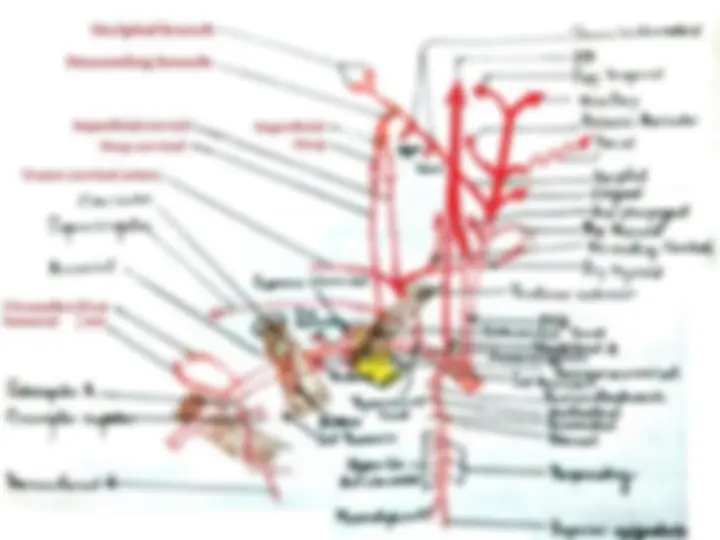
The anatomy and boundaries of the axilla, which is a pyramid-shaped space between the upper part of the arm and the side of the chest. It forms an important passage for nerves, blood, and lymph vessels as they travel from the root of the neck to the upper limb. the boundaries of the cervico-axillary canal, the contents of the axilla, and the axillary artery and vein. It also describes the arrangement and drainage area of the axillary lymph nodes. diagrams and illustrations to aid understanding.
Typology: Study Guides, Projects, Research
1 / 41

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!


































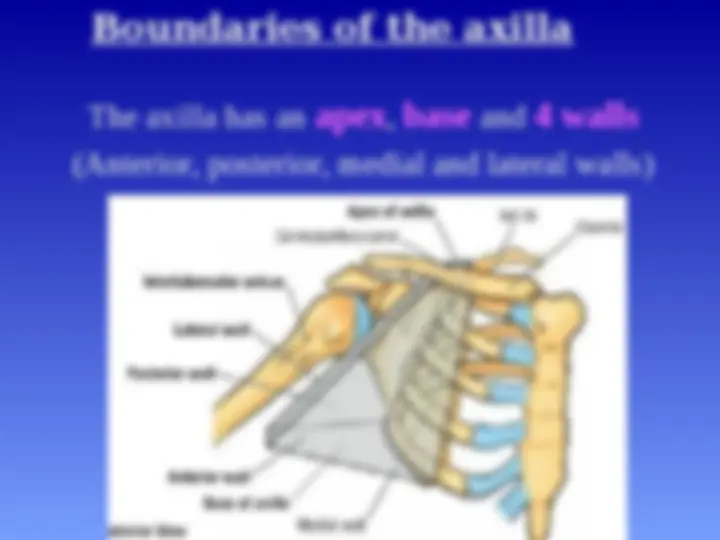
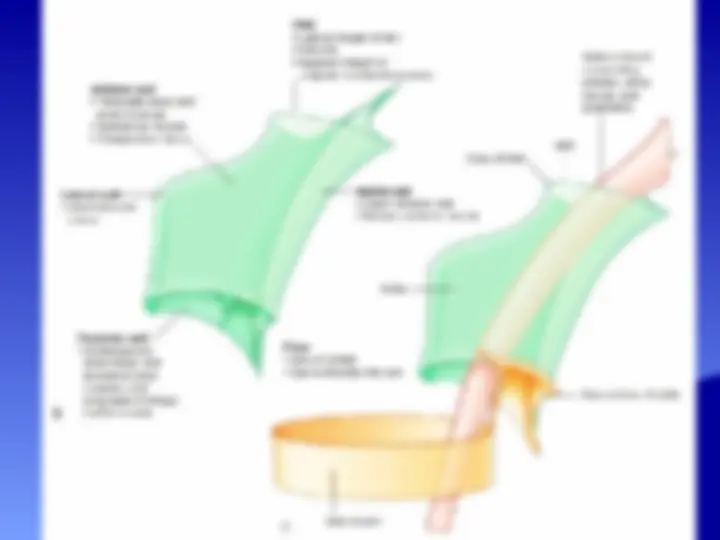
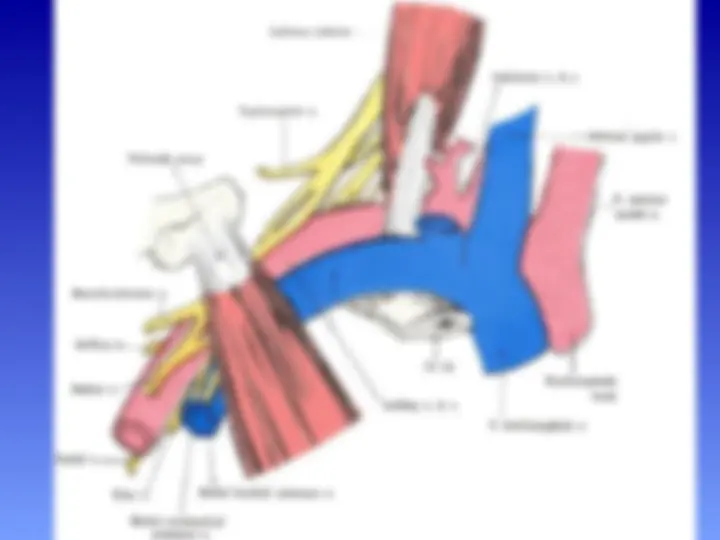
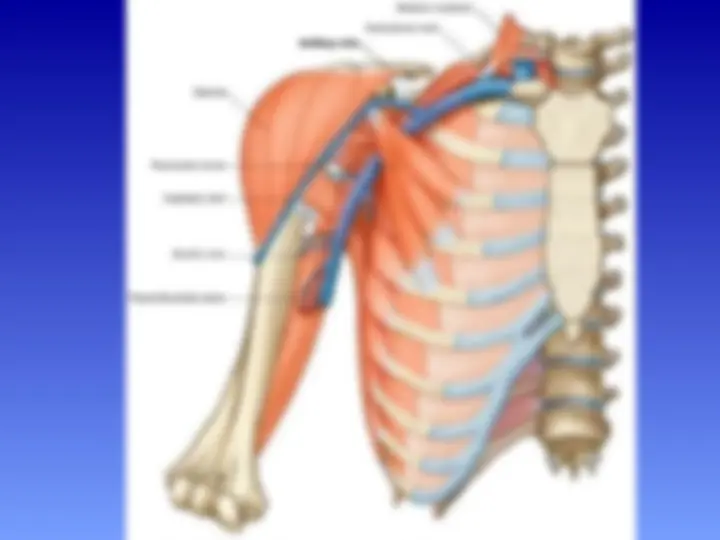
Boundaries of the axilla
The axilla has an apex , base and 4 walls
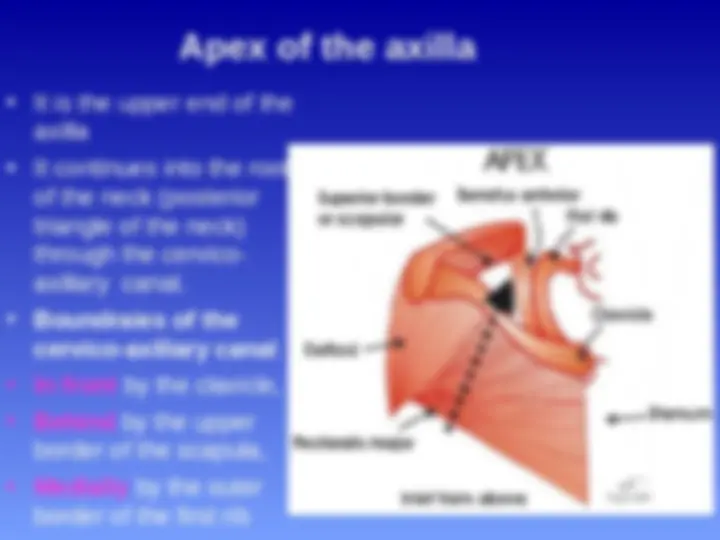
Apex of the axilla
It is the upper end of the
axilla
It continues into the root
of the neck (posterior
triangle of the neck)
through the cervico-
axillary canal.
Boundraies of the
cervico-axillary canal
In front by the clavicle,
Behind by the upper
border of the scapula,
Medially by the outer
border of the first rib
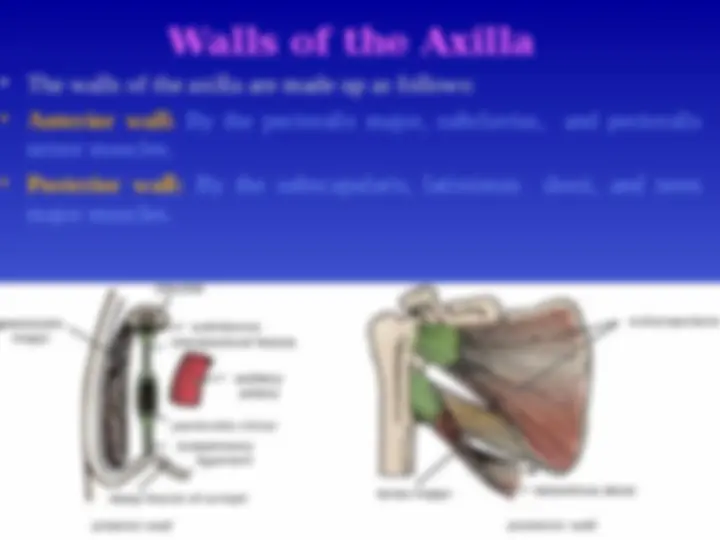
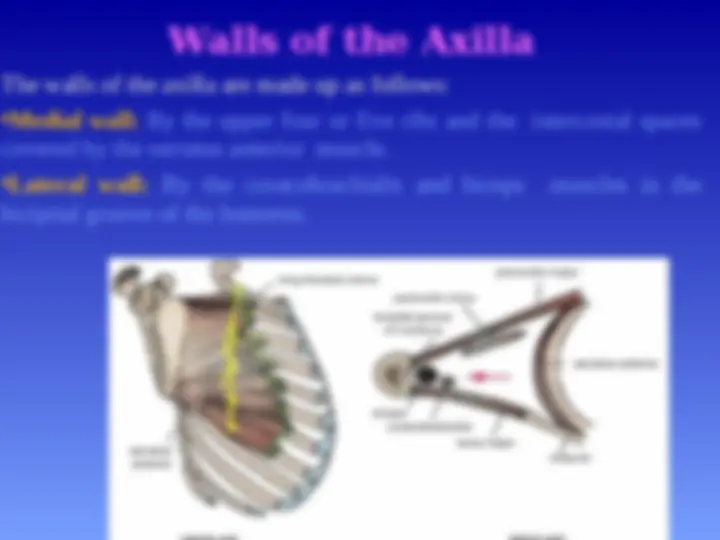
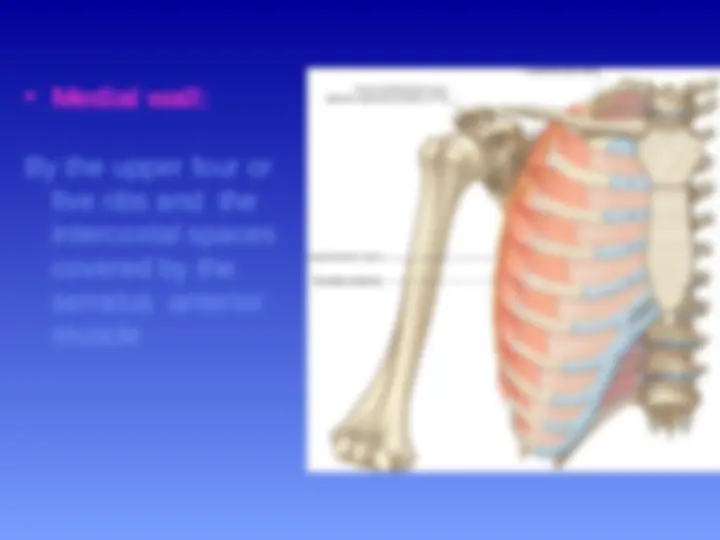
Walls of the Axilla
The walls of the axilla are made up as follows:
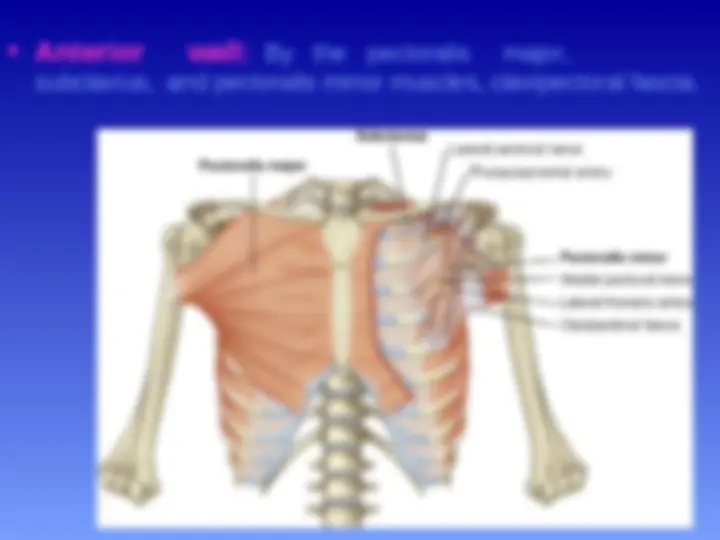
Anterior wall: By the pectoralis major, subclavius, and pectoralis minor muscles.
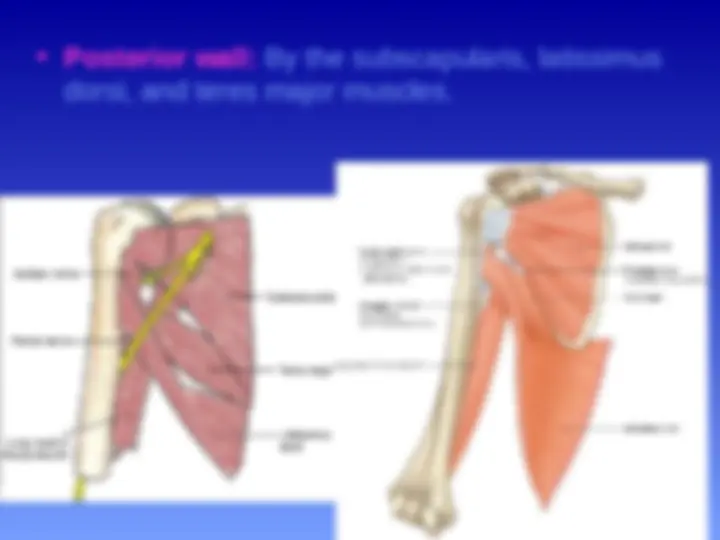
Posterior wall: By the subscapularis, latissimus dorsi, and teres major muscles.
subclavius, and pectoralis minor muscles, clavipectoral fascia.
SP DEPT OF ANATOMY AFMC 9
cervico axillary canal
11
Base
Ant : anterior axillary fold
Post: posterior axillary fold
Medial: Chest wall
Lateral: arm
Major (ant fold) and Lat Dorsi & Teres Major (post fold)
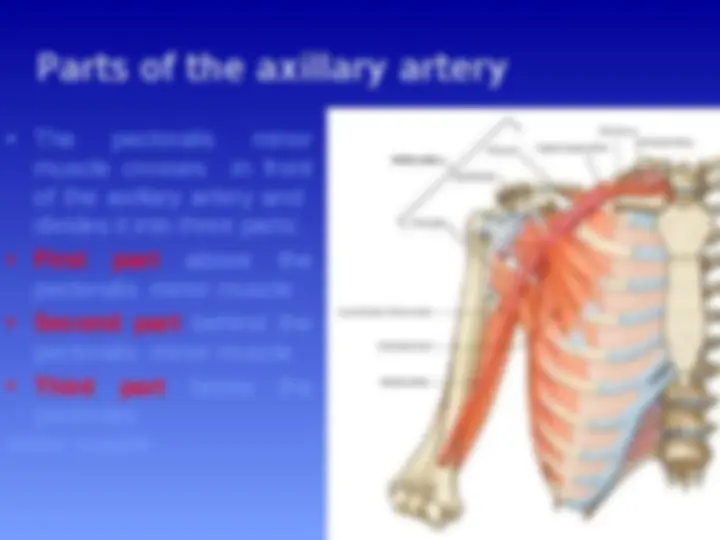
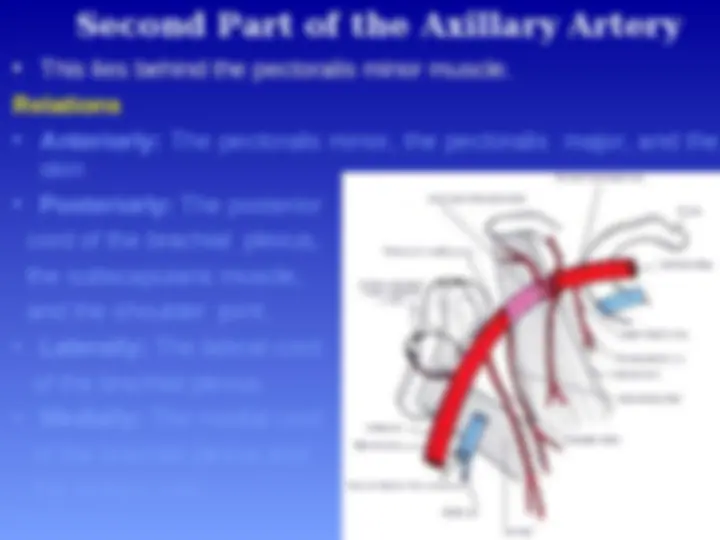
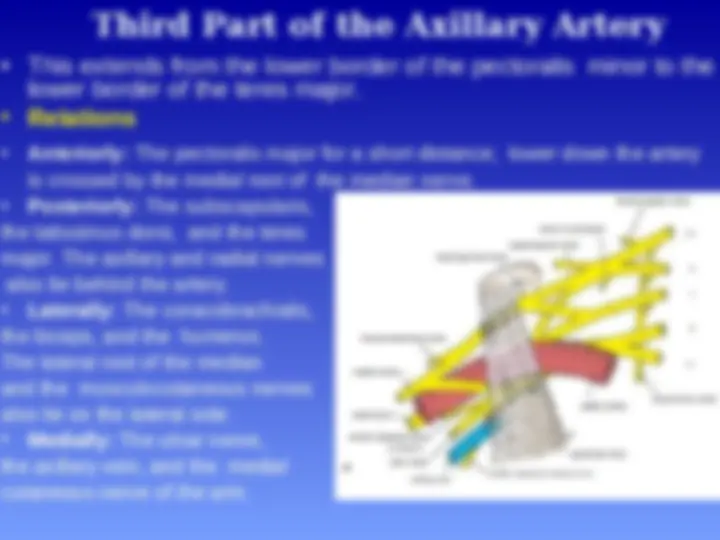
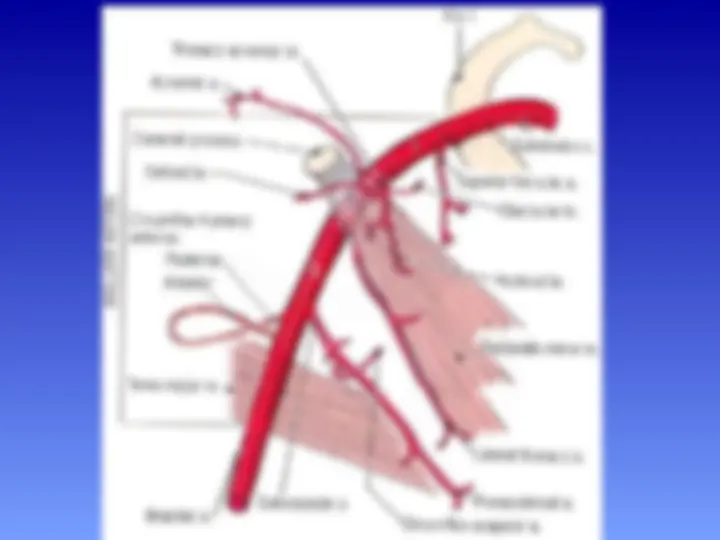
Axillary Artery
Parts of the axillary artery
The pectoralis minor
muscle crosses in front
of the axillary artery and
divides it into three parts:
First part above the
pectoralis minor muscle
Second part behind the
pectoralis minor muscle
Third part below the
pectoralis
minor muscle
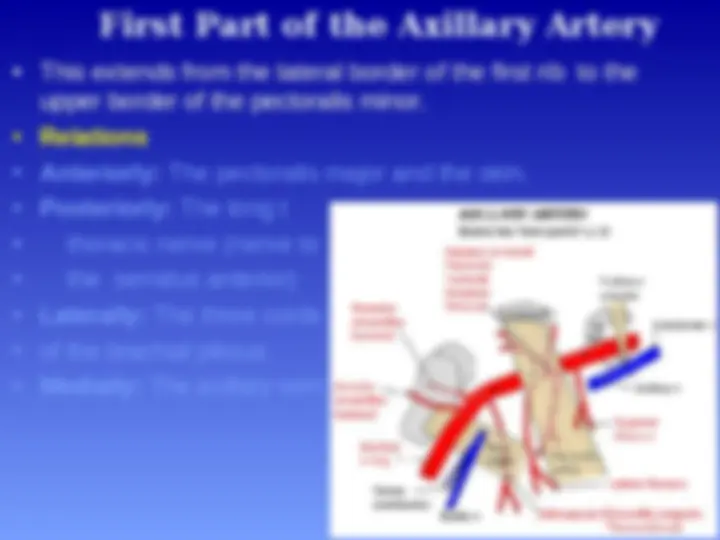
This extends from the lateral border of the first rib to the
upper border of the pectoralis minor.
Relations
Anteriorly: The pectoralis major and the skin.
Posteriorly: The long t
thoracic nerve (nerve to
the serratus anterior)
Laterally: The three cords
of the brachial plexus
Medially: The axillary vein