































Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
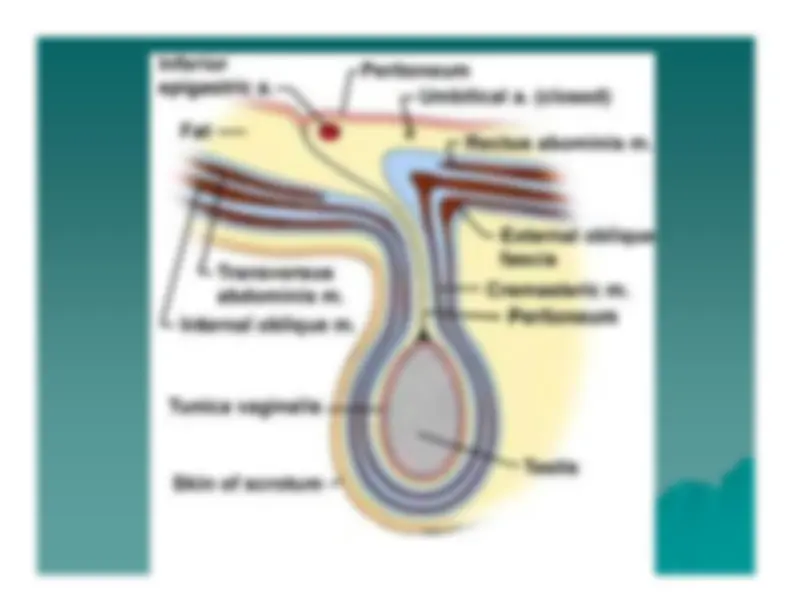
There are three layers, an external, internal and ... External Abdominal Oblique Muscle ... canal passes through the abdominal wall it receives a layer.
Typology: Summaries
1 / 66

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!



























































The Abdominal Wall The Abdominal Wall
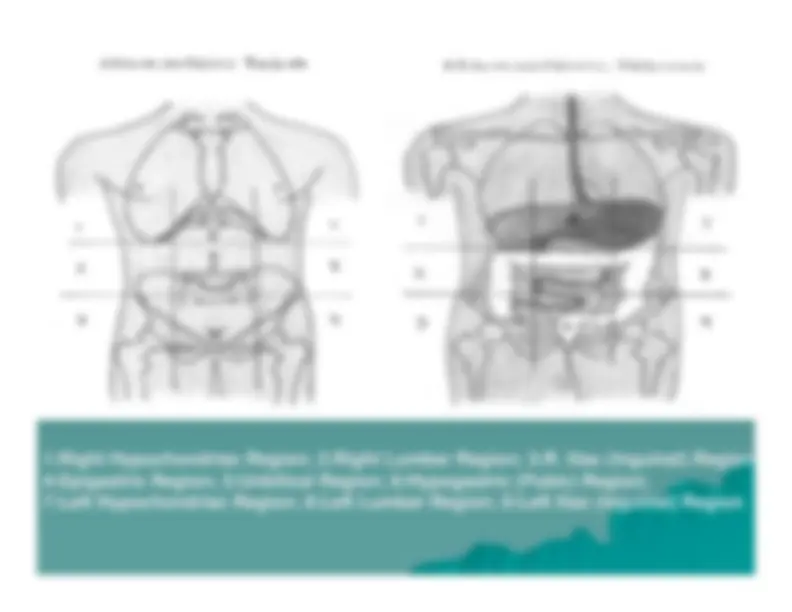
1:Right Hypochondriac Region; 2:Right Lumbar Region; 3:R. Iliac (Inguinal) Region
;
4:Epigastric Region; 5:Unbilical Region; 6:Hypogastric (Pubic) Region;7:Left Hypochondriac Region; 8:Left Lumbar Region; 9:Left Iliac (Inguinal) Region
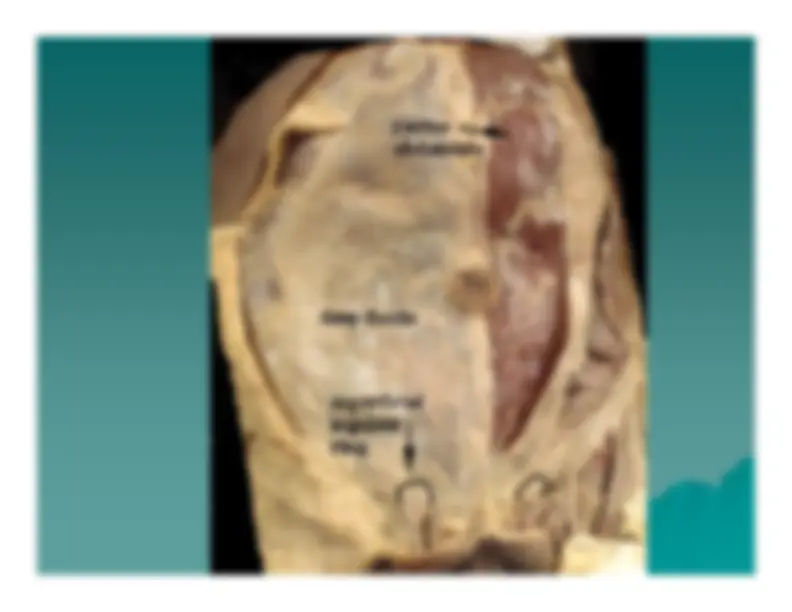
The Fascia The Fascia
Below the skin the superficial fascia is divided into a Below the skin the superficial fascia is divided into a
superficial fatty layer, Camper's fascia, and a deeper superficial fatty layer, Camper's fascia, and a deeper
fibrous layer, fibrous layer,
Scarpa's Scarpa's
fascia.fascia.
The deep fascia lies on the abdominal muscles. Inferiorly The deep fascia lies on the abdominal muscles. Inferiorly
Scarpa's Scarpa's
fascia blends with the deep fascia of the thigh. fascia blends with the deep fascia of the thigh.
This arrangement forms a plane between This arrangement forms a plane between
Scarpa's Scarpa's
fascia fascia
and the deep abdominal fascia extending from the top of and the deep abdominal fascia extending from the top of
the thigh to the upper abdomen. the thigh to the upper abdomen.
Below the innermost layer of muscle, the Below the innermost layer of muscle, the
transversus transversus
abdominis abdominis
muscle, lies the muscle, lies the
transversalis transversalis
fascia. The fascia. The
transversalis transversalis
fascia is separated from the parietalfascia is separated from the parietal
peritoneum by a variable layer of fat. peritoneum by a variable layer of fat.
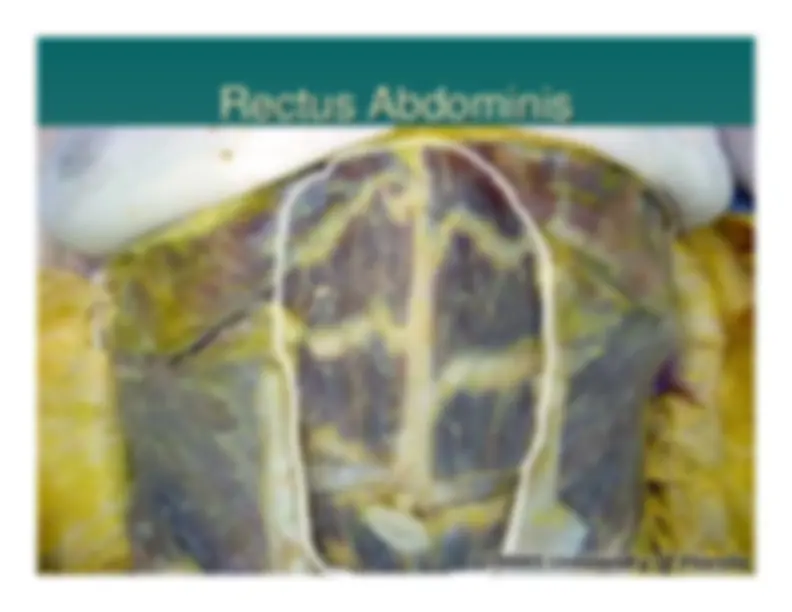
Rectus Rectus Abdominis
Abdominis
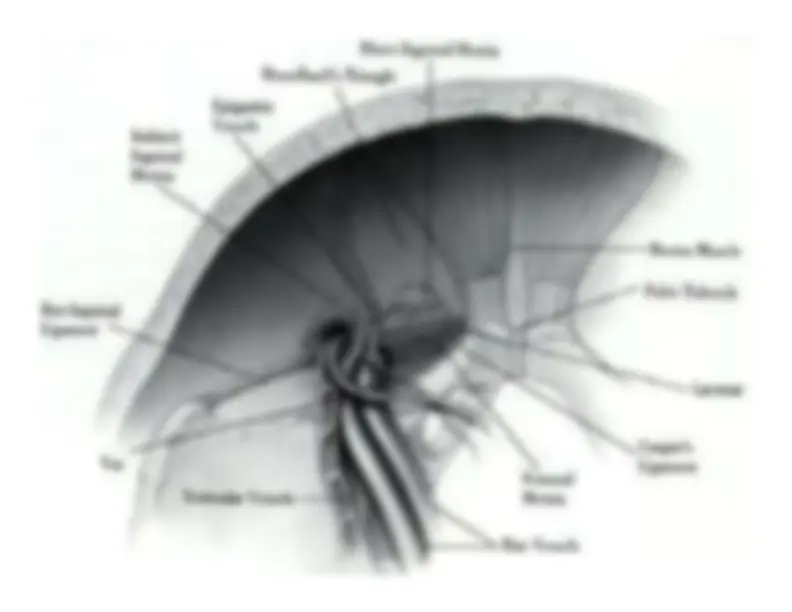
External Abdominal Oblique Muscle External Abdominal Oblique Muscle
The The
external oblique muscle external oblique muscle
arises from the lower eightarises from the lower eight
ribs. ribs.
The fibers run downwards and forwards to form an The fibers run downwards and forwards to form an
aponeurosis aponeurosis
anteriorly anteriorly
The The
aponeurosis aponeurosis
passes passes
anteriorly anteriorly
to the rectus muscle toto the rectus muscle to
insert into the insert into the aponeurosis
aponeurosis
from the other side at the from the other side at the
linea linea
alba. alba.
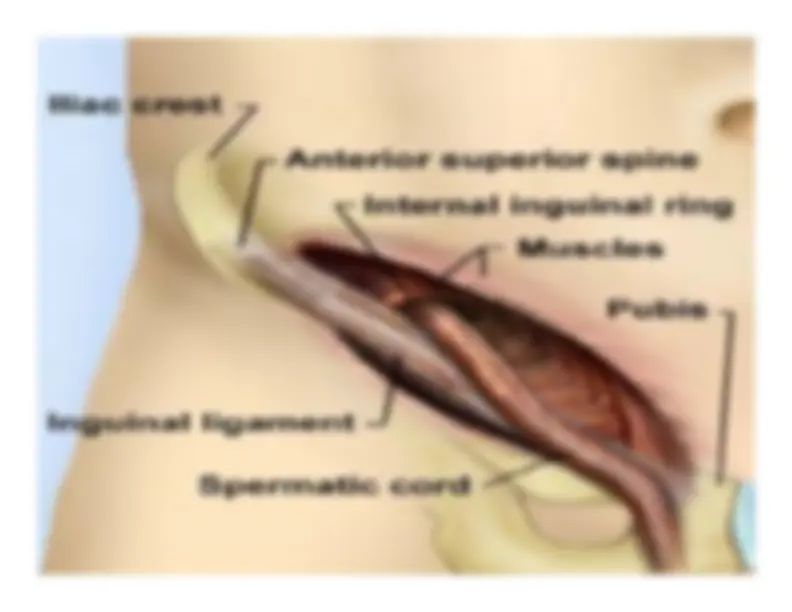
Inferiorly the Inferiorly the
aponeurosisaponeurosis
inserts into the anterior superior inserts into the anterior superior
iliac spine and stretches over to the pubic tubercle, forming iliac spine and stretches over to the pubic tubercle, forming
the the
inguinal ligamentinguinal ligament
. .
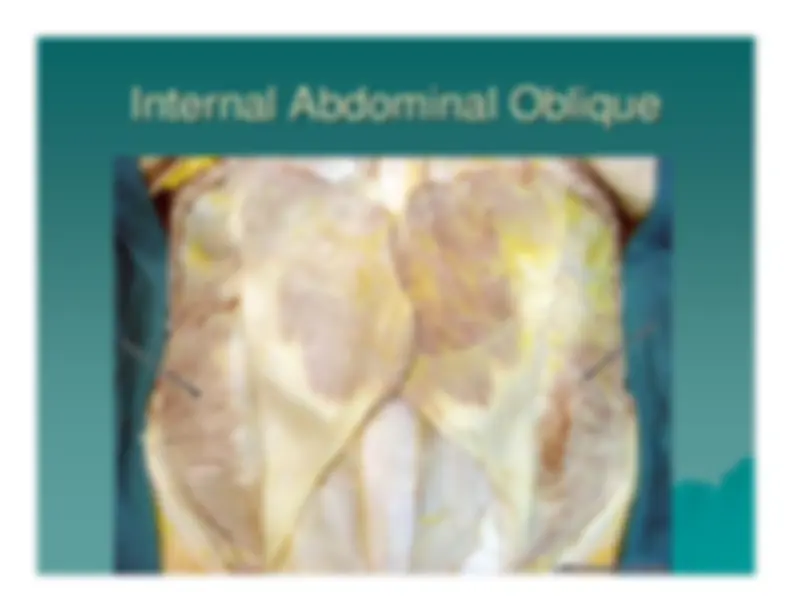
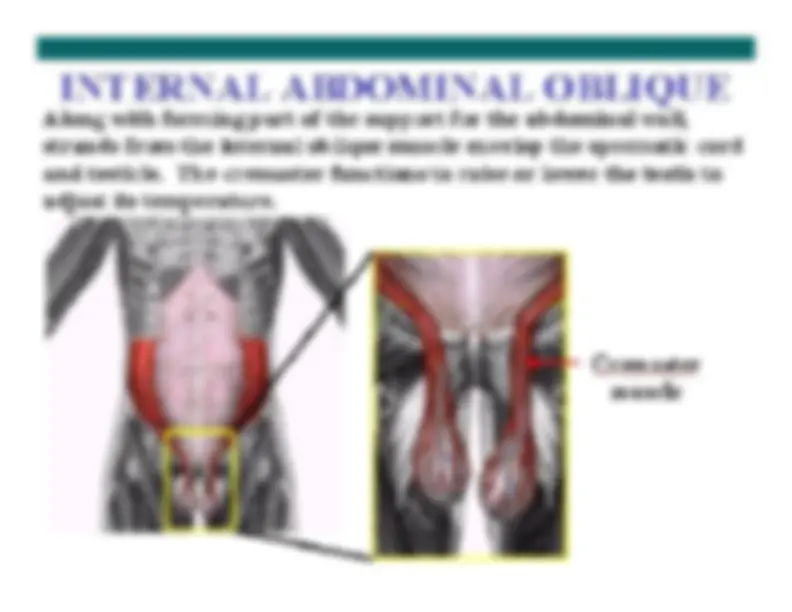
Internal Oblique Muscle Internal Oblique Muscle
The The
internal oblique muscle internal oblique muscle
arises from the lumbar arises from the lumbar
fascia, the iliac crest and the lateral two fascia, the iliac crest and the lateral two
thirds of the thirds of the
inguinal ligament and runs upwards and forwards to form inguinal ligament and runs upwards and forwards to form
an an
aponeurosis aponeurosis
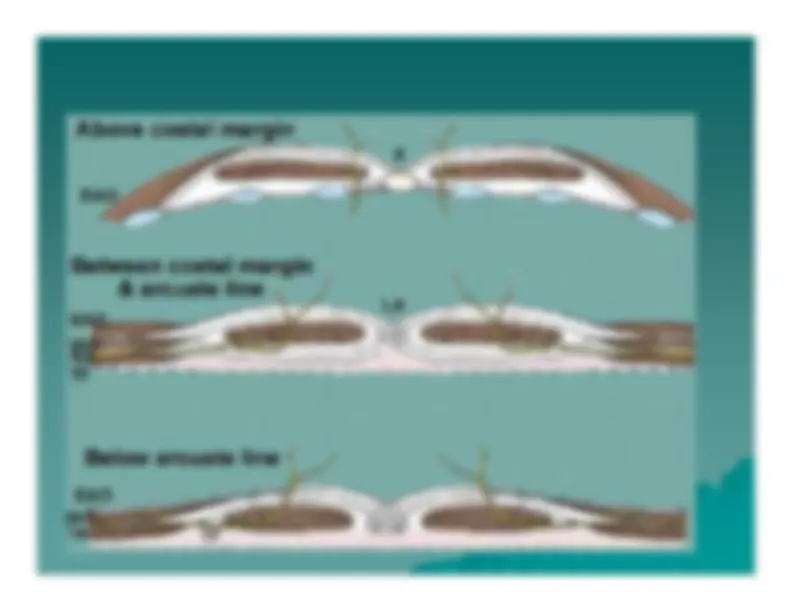
Above the Above the
arcuatearcuate
line the line the
aponeurosis aponeurosis
splits to enclose the splits to enclose the
rectus muscle. rectus muscle.
Below the Below the
arcuate arcuate
line theline the
aponeurosis aponeurosis
passes anterior to passes anterior to
the rectus muscle. the rectus muscle.
The inferior part of the The inferior part of the
aponeurosis aponeurosis
inserts into the inserts into the
symphysis symphysis
pubis. pubis.
At this insertion the At this insertion the
aponeurosisaponeurosis
is fused with the is fused with the
aponeurosis aponeurosis
of the of the
transversus transversus
abdominis abdominis
muscle to form muscle to form
the the
conjoint tendon.conjoint tendon.
Internal Abdominal Oblique Internal Abdominal Oblique
Transversus Transversus
Abdominis Abdominis
The
The
transversus transversus
abdominis
abdominis
muscle muscle
arises from the lower six costal
arises from the lower six costal
cartilages, the lumbar fascia and the
cartilages, the lumbar fascia and the
iliac crest.
iliac crest.
Tranversus Tranversus
Abdominis Abdominis
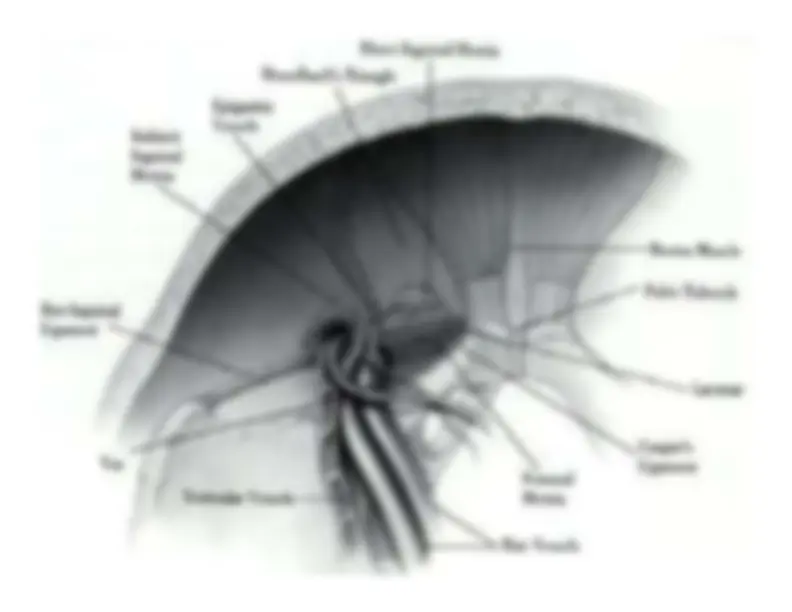
Inguinal Ligament Inguinal Ligament