






Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
Syllabus for Teaching PE and Health
Typology: Study Guides, Projects, Research
1 / 9

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!






Tel. Nos.: (043) 778-2170/ (043) 406-0830 loc. 124 Website Address: http://www.batstate-u.edu.ph COLLEGE OF TEACHER EDUCATION Elementary Education Program COURSE SYLLABUS WITH SPECIFICATION UNIVERSITY VISION A premier national university that develops leaders in the global knowledge economy UNIVERSITY MISSION A university committed to producing leaders by providing a 21st century learning environment through innovations in education, multidisciplinary research, and community and industry partnerships in order to nurture the spirit of nationhood, propel the national economy, and engage the world for sustainable development COURSE CODE :^ BEEd 123 COURSE TITLE :^ Teaching PE and Health in the Elementary Grades CREDIT UNIT :^ 3 units COURSE PREREQUISITE :^ None ACADEMIC YEAR :^ Second Semester, 2019 - 2020 REFERENCE CMO :^ CMO No. 20, s. 2013, CMO No. 74, s. 2017 and CMO No. 4, s. 2018 PROGRAM EDUCATIONAL OBJECTIVES The BEEd program aims to produce elementary teachers who have the ability to:
This course deals with the educational foundations of Health and Physical Education as these apply to teaching and learning in the elementary grades. Various teaching strategies and assessment appropriate for each area shall be given emphases in the course. AUDIENCE This 3-unit course is intended for first year undergraduate students of Batangas State University enrolled in Bachelor of Elementary Education program. STUDENT OUTCOMES Graduates of the BEEd program are expected to: a. demonstrate in-depth understanding of the diversity of learners in various learning areas;
b. manifest meaningful and comprehensive pedagogical content knowledge (pck) of the different subject areas;
c. utilize appropriate assessment and evaluation tools to measure learning outcomes;
d. manifest skills in communication, higher order thinking and use of tools and technology to accelerate learning and teaching;
e. demonstrate positive attributes of a model teacher, both as an individual and as a professional; and
f. manifest a desire to continuously pursue personal and professional development.
At the end of the course, students will be able to: ILO 1. Identify the basic knowledge and skills in PE and Health education; ILO 2. Explain the importance of teaching PE and Health in the Elementary Grades; ILO 3. Demonstrate positive attributes of a model PE and Health teacher ILO 4. Apply effective and appropriate teaching strategies in specific grade levels for teaching PE and Health ILO 5. Construct classroom assessment tools in measuring pupils’ skills and knowledge in PE and Health ILO 6. Critique a lesson plan in Elementary PE and Health topics MAPPING OF INTENDED LEARNING OUTCOMES TO STUDENT OUTCOMES Intended Learning Outcome Applicable Student Outcomes a b c d e f ILO 1 ^ ^ ILO 2 ^ ^ ILO 3 ^ ^ ^ ^ ^ ILO 4 ^ ^ ^ ^ ^ ILO 5 ^ ^ ILO 6 ^ ^ ^ ^ ^ MAPPING OF SPECIFIC OBJECTIVES TO INTENDED LEARNING OUTCOMES Upon completing the course, students should be able to exhibit the following objectives congruent with each topic outlined in the course. Topics ILO 1
Introduction to PE and Health Education
A. Active Learning. This is includes question-posing, inquiry, and self-directed learning. B. Cooperative Learning. This allows students to work in groups and be responsible for each other’s learning, and each accountable for their own learning. C. Critical Thinking. This approach to thinking emphasizes stating original claims or opinions and supporting them with reasons. Critical thinking is used expressively when students make interpretations and support them verbally or in writing. Critical thinking is used receptively when students critique other people’s arguments. D. Hands-On. This encourages the students to design activities that they are actively involved. Hands-on participation is as important as verbal participation in the activity. E. Peer teaching. Students receive more time for individualized learning. Direct interaction between students promotes active learning and reinforces their own learning by instructing others. F. Group Dynamics/Activities. Instructor will prepare set of activities for the students. The output of the activity will be presented on class. G. Integrated Teaching Strategy. This put together the parts of a whole in order to arrive at a holistic, complete and more accurate view of reality Assessment Strategies A. Formative and Summative Assessments. Formative assessment covers activities that generate information on how well students are engaged in classroom interactions such as recitations and discussions. On the other hand, summative assessment includes major examinations that describe and measure students’ learning outcomes. B. Performance-Based Assessment. Instructor observes and makes judgements about students’ demonstration of skills and competencies in creating a product, constructing a response and the like in line with the criteria communicated by the instructor through rubrics and other assessment organizers. C. Affective Assessment. Students’ affective traits and dispositions are recorded through instructor’s observation, student self-report, and peer ratings. COURSE REQUIREMENTS A. Class Engagement. Students are expected to actively participate in the various activities prepared by the instructor. To be part of the learning community, students are required to accomplish various tasks required in the course while adhering to the set standards prescribed by the instructors. B. Class Portfolio. This is a compilation of the different outputs in the class ranging from worksheets to rubrics used in the various activities required in the course. The students should comply with these requirements and submit them on time or ahead of time as set by the instructor. Noncompliance to each on the given deadline means a rating of 40%. The class portfolio will be composed of the following: a. Learning Journals b. Lesson Plans in PE and Health c. Sample Exam and TOS in PE and Health C. Examinations. There will be four (4) major written examinations such as Preliminary, Midterm, and Semi-Final to be administered on the date set by the department otherwise specified. These will evaluate students’ knowledge on the topics covered in the class. COURSE POLICIES
Grading System The work of students shall be graded at the end of each term in accordance with the following system: Numerical Grade Percentage Equivalent Description 1.00 98-100 Excellent 1.25 94-97 Superior 1.50 90-93 Very Good 1.75 88-89 Good 2.00 85-87 Meritorious 2.25 83-84 Very Satisfactory 2.50 80-82 Satisfactory 2.75 78-79 Fairly Satisfactory 3.00 75-77 Passing 5.00 Below 75 Failure Inc. *Incomplete Drp Dropped Students who will get a grade of 70-74 must be given a removal examination. A grade of “3.0’ will be given to those who will pass the removal examination and those who will fail will be given a grade of “5.0”. *A grade of “Incomplete” must be complied with by the student within one (1) semester or one hundred fifty (150) days. A student who fails to complete the deficiency/deficiencies at the end of the succeeding semester shall automatically obtain a grade of 5.0 in the course. Major Examinations (Prelims, Midterms, Semi-Finals, Finals) 50% Class Standing 50% Attendance 10% Class Engagement 20% Class Portfolio 20% (TOS, LP Critique, Reflection Paper) _______ TOTAL 100% Attendance Policy Prompt and regular attendance of students is required. Total unexcused absences shall not exceed ten (10) percent of the maximum number of hours required per course per semester (or per summer term). A semester has 18 weeks. For example, a semestral subject with: 3 units (3 hrs lec), 10% x 3 x 18 = 5.4 hrs or 6 hrs. 3 units (2 hrs lec, 3 hrs lab), 10% x 5 x 18 = 9 hrs. 5 units (3 hrs lec, 6 hrs lab), 10% x 9 x 18 = 16.2 hrs or 16 hrs. Please refer to the provisions in the Norms of Conduct for the full text of guidelines for the attendance. Missed Exams Make-up tests will only be given to a student having a valid reason for not taking the examination on the prescribed date. The instructor has the right to disapprove any explanations for absences presented without prior notice and to void opportunity for a make- up test.
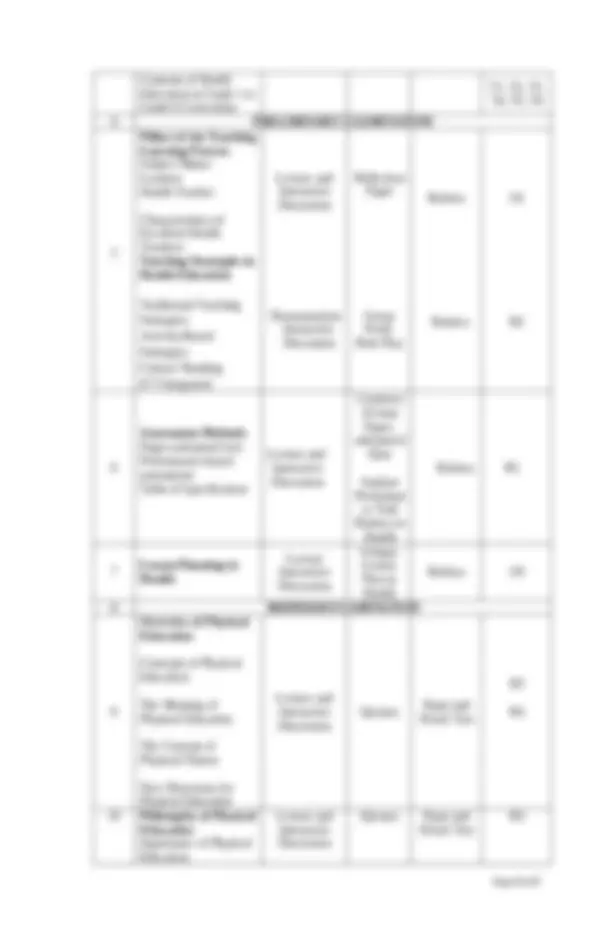
https://www.ijme.net/archive/7/attributes-of-a-good-health-educator.pdf? fbclid=IwAR2ICGUu46XrTv9YbnSpLpeaRoUJ5Q6v0lpdYPsW2gQm- ijOhfZyDKUOTKk O2: Husain Mohd Z. (2014). Determining Teaching Effectiveness for Physical Education Teacher. Retrieved from https://core.ac.uk/download/pdf/82128421.pdf O3: DepEd Order No. 42, s. 2016 Policy Guidelines on Daily Lesson Preparation for the K to 12 Basic Education Program. Retrieved from https://www.teacherph.com/policy-guidelines-daily-lesson-preparation-k-12- basic-education-program/ O4: K to 12 PE Curriculum Guide (2016). Retrieved from https://www.gov.ph/documents/20147/233614/PHYSICAL-EDUCATION- K-12-Curriculum-Guide-Grades-1-and-7.pdf/2a38097c-3d9e-e6a1-ce29- 704b9a3a4ac4?version=1. O5: K to 12 Health Curriculum Guide (2016). Retrieved from https://www.gov.ph/documents/20147/233614/HEALTH-K-12-Curriculum- Guide.pdf/2bddd9f8-91a0-1140-a474-e9000c1c0420?version=1. TENTATIVE COURSE OUTLINE/CALENDAR The following is the list of topics and required readings for the course. However, the instructor has the right to alter the outline any time due to inevitable circumstances or presence of other resources which she deems essential for the class. Week Specific Topic/s Teaching and Learning Activities Assessme nt Tasks Assessment Tools References 1 Orientation and Discussion of Course Syllabus with Specification Introduction Concepts of Health and Wellness Dimensions of Health Health and Wellness as Conceived in Today’s World Lecture and Interactive Discussion Quizzes Paper and Pencil Test
Health Education in the Elementary Grades Objectives, Philosophy and Importance of Health Education Lecture and Interactive Discussion Quizzes Paper and Pencil Test
3 Curriculum Framework of K-12 Health Education Lecture and Interactive Discussion Performan ce Task: Reporting Rubrics
Contents of Health Education in Grade 1 to Grade 6 Curriculum
Pillars of the Teaching Learning Process Subject Matter Learners Health Teacher Characteristics of Excellent Health Teachers Teaching Strategies in Health Education Traditional Teaching Strategies Activity-Based Strategies Critical Thinking ICT Integrated Lecture and Interactive Discussion Demonstration Interactive Discussion Reflection Paper Group Work: Role Play Rubrics Rubrics
Assessment Methods Paper-and-pencil test Performance-based assessment Table of Specification Lecture and Interactive Discussion Construct 10-item Paper- and-pencil Quiz Analyze Performan ce Task Rubrics in Health Rubrics R 7 Lesson Planning in Health Lecture Interactive Discussion Critique Lesson Plan in Health Rubrics O 8 MIDTERM EXAMINATION 9 Overview of Physical Education Concepts of Physical Education The Meaning of Physical Education The Concept of Physical Fitness New Directions for Physical Education Lecture and Interactive Discussion Quizzes Paper and Pencil Test
10 Philosophy of Physical Education Importance of Physical Education Lecture and Interactive Discussion Quizzes Paper and Pencil Test