

Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
Structure of Ceramics - Electroceramics - Exam, Exams of Analysis and Design of Digital Integrated Circuits
The main points are: Structure of Ceramics, Crystallographic Planes, Packing Factors, Cubic Unit Cell, Locations of Interstices, Diamond Cubic Structure, Filling of Interstices, Projection of Ilmenite, Orthogonal Axes
Typology: Exams
1 / 1

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!

Related documents
Partial preview of the text
Download Structure of Ceramics - Electroceramics - Exam and more Exams Analysis and Design of Digital Integrated Circuits in PDF only on Docsity!
Module 1 Structure of Ceramics
- In an unit-cell, draw the crystallographic planes (101), (1 1 ത2), (214) and directions [1 1 ത2], [013] and [201].
- Estimate the packing factors of simple cubic, body centered cubic and face centered cubic structures.
- How do the packing factors of face centered cubic unit cell and a hexagonal closed packed unit cell compare with each other?
- Determine the type and locations of interstices in the HCP structure and size of largest atom that would fit in them.
- Determine the type and locations of interstices in the BCC structure.
- Calculate the packing factor diamond cubic structure.
- Draw a (110) plan view of Sphalerite ZnO structure satisfy yourself with the site filling.
- Find the difference between the perovskite and ReO 3 structure. Can one be derived from another? Justify.
- What are the differences between Corundum, Ilmenite and LiNbO 3 structures? Explain to yourself in terms of packing and filling of interstices.
- Draw {1 0 -1 0} plane projection of Ilmenite and go through how the interstitials are filled.
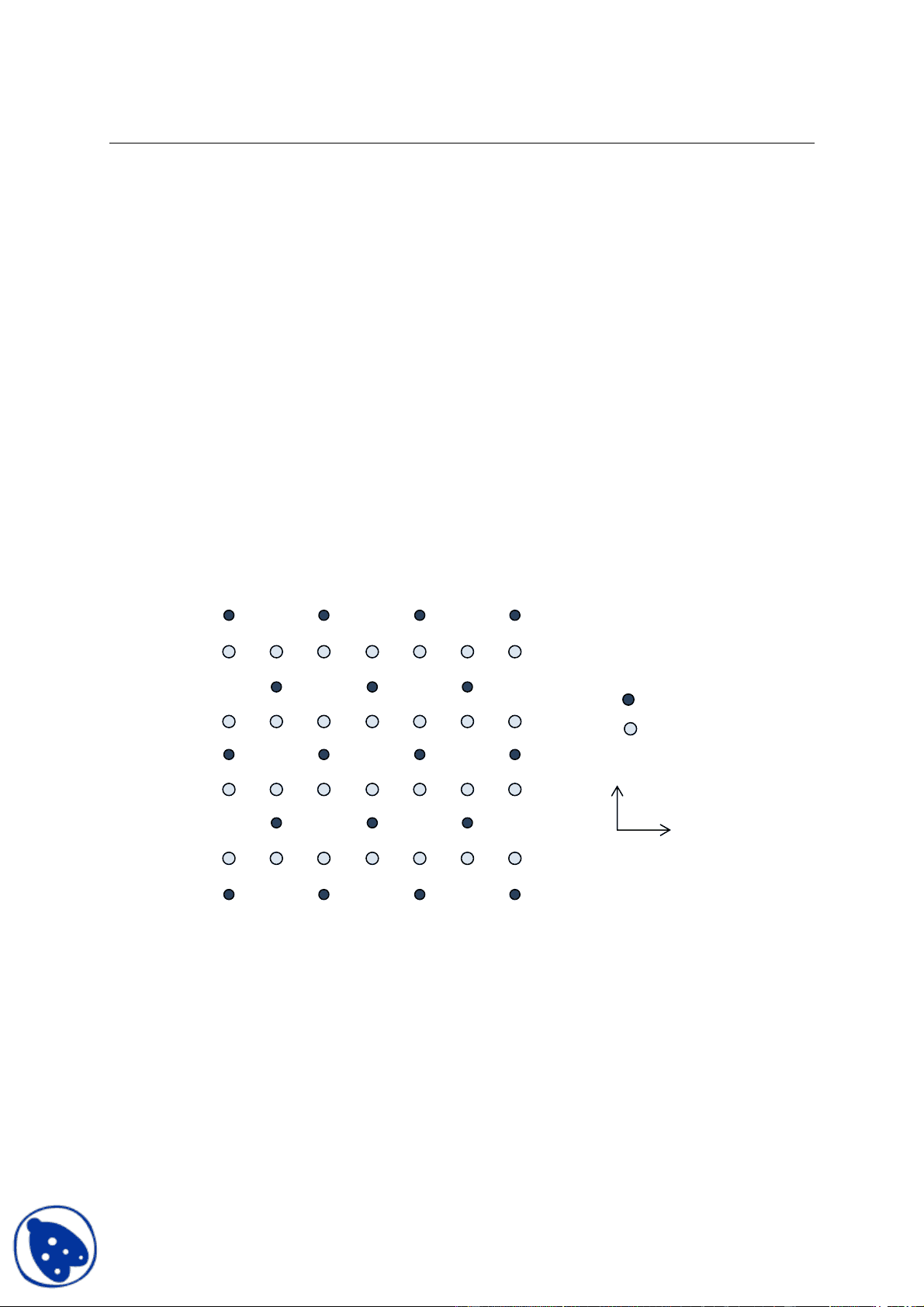
- Following atomic pattern is of a metal oxide compound (Mx Oy) which has a unit cell of dimensions a = b = 4.04 Å, c = 5.80 Å, with orthogonal axes. A plan of the structure projected on the plane normal to the x -axis is shown in figure below.
½ ½^ ½
M
O
a) Outline the conventional unit cell on the pattern itself defining the origin. Determine the type of the lattice. b) Explain the structure in terms of number of unit-cells of the lattice defined in (a). c) What is the formula unit i.e. what are the values of x and y in M (^) x Oy? How many formula units are present in a unit cell? d) Write the fractional coordinates of the atoms in an unit cell. e) What is the co-ordination of the both ions? f) What must be the range of radius of cation to anion for the observed co-ordination? Show the procedure.
z
y

