


































































Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
Partial molar properties, ideal and non ideal solutions, standard state, Gibbs-Duhem equation are important subtopic in this lecture
Typology: Slides
1 / 81

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!










































































Associate Professor
Department of Chemical Engineering
Sri Sivasubramaniya Nadar College of Engineering
Kalavakkam – 603 110, Kanchipuram (Dist)
Tamil Nadu, India msubbu.in[AT]gmail.com
www.msubbu.in
Contents
Partial molar properties, ideal and non-ideal solutions, standardstates definition and choice, Gibbs-Duhem equation, excessproperties of mixtures.
-^
Criteria for equilibrium between phases in multi component non-reacting systems in terms of chemical potential and fugacity M Subramanian
Introduction
Most of the materials of the real world are not pure substanceswith all atoms or molecules identical but rather are mixtures ofone type or another.
-^
The pure substances from which a solution may be prepared are called
components
, or constituents, of the solution.
called
components
, or constituents, of the solution.
Solutions are not limited to liquids: for example air, a mixture ofpredominantly N
2
and O
, forms a vapor solution. Solid solutions 2
such as the solid phase in the Si-Ge system are also common M Subramanian
Multicomponent Systems – Basic Relations
amount
composition
amount of each component M Subramanian
Mass fraction – preferable where the definition of molecularweight is ambiguous (eg. Polymer molecules)
-^
Molarity – moles per litre of solution
-^
Molality
moles per kilogram of solvent. The molality is usually
Molality
moles per kilogram of solvent. The molality is usually
preferred, since it does not depend on temperature or pressure,whereas any concentration unit is so dependent.
-^
Volume fraction
-^
Mole ratio or volume ratio (for binary systems) M Subramanian
Properties of Solutions
The properties of solutions are, in general, not additiveproperties of the pure components.
-^
The actual contribution to any extensive property is designatedas its partial property. The term partial property is used todesignate the property of a component when it is in admixture with one or more other componentswith one or more other components
-^
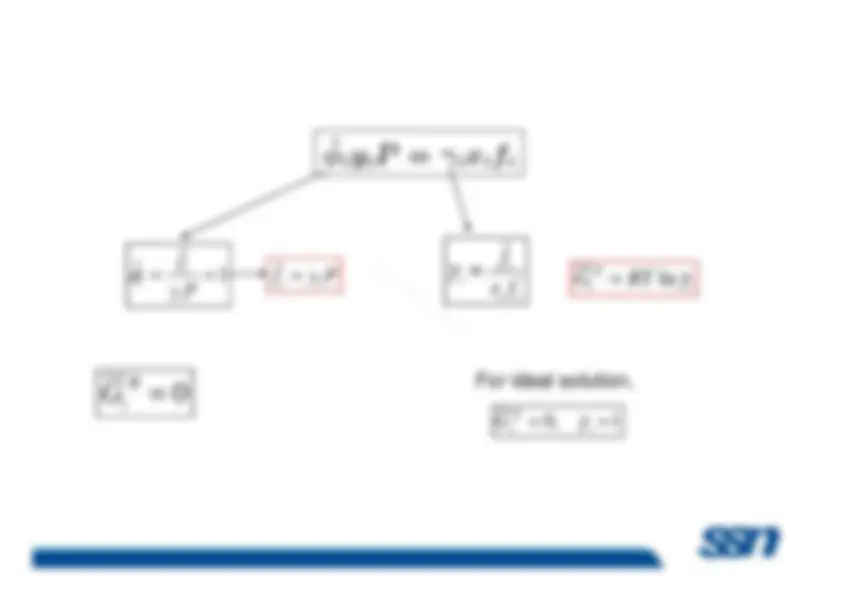
Because most chemical, biological, and geological processesoccur at constant temperature and pressure, it is convenient toprovide a special name for the partial derivatives of allthermodynamic properties with respect to mole number atconstant pressure and temperature. They are called
partial
molar properties M Subramanian
www.msubbu.in
M Subramanian
M Subramanian
Partial Molar Volume
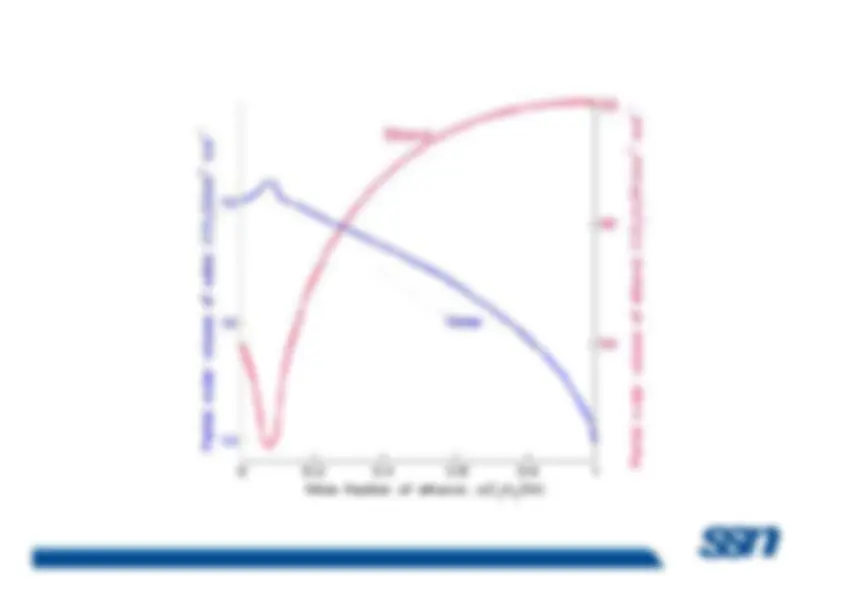
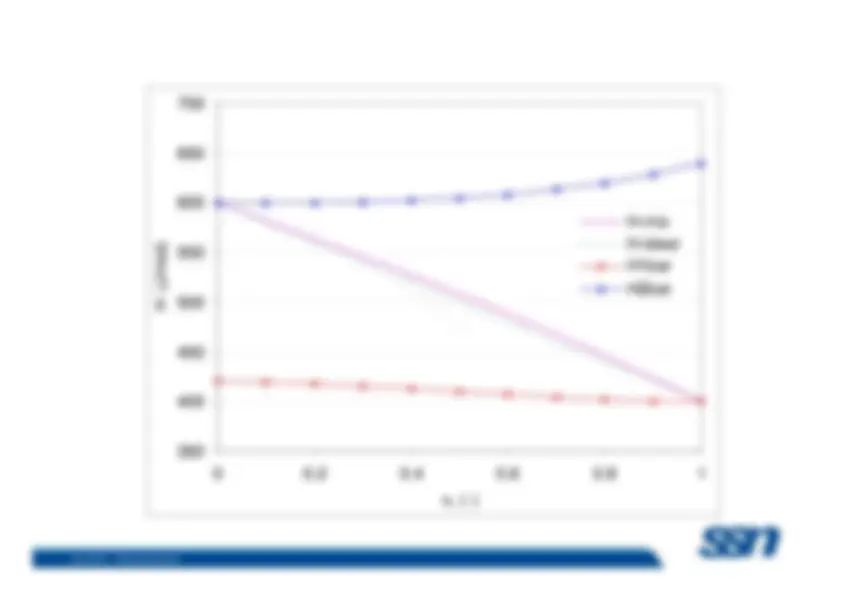
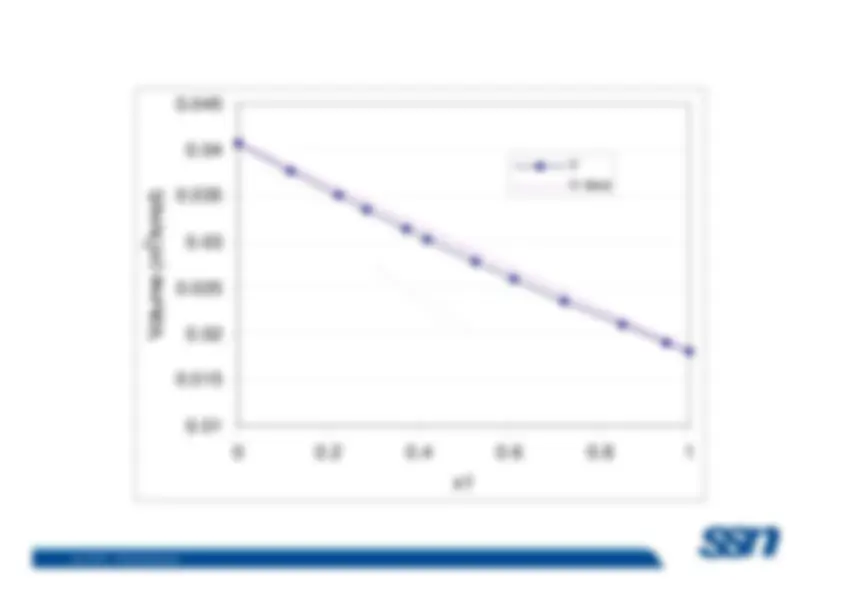
Benzene-Toluene:
Benzene and toluene form an ideal solution.
The volume of 1 mole pure benzene is 88.9 ml; the volume of 1mole pure toluene is 106.4 ml. 88.9 ml benzene mixed with106.4 ml toluene results in 88.9 ml + 106.4 ml, or 195.3 ml ofsolution. (
ideal solution
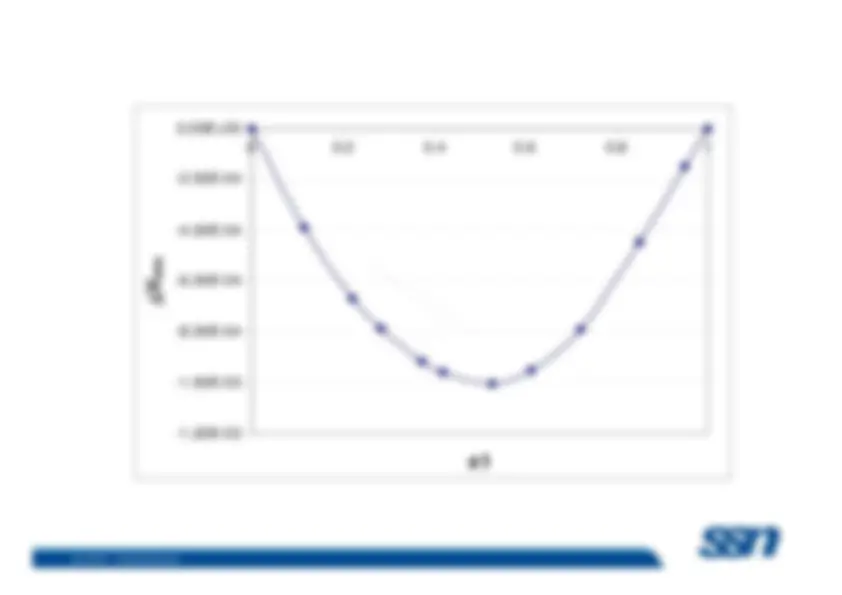
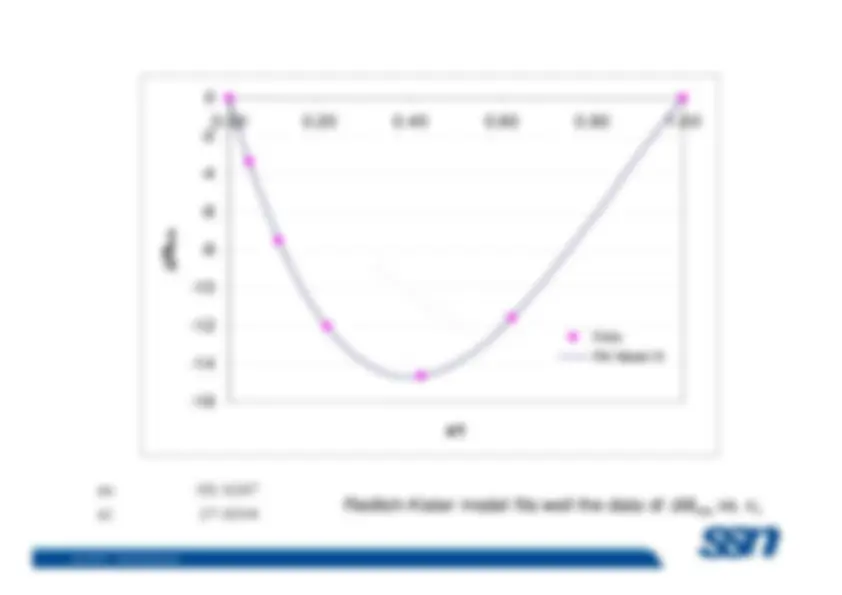
Ethanol-Water:^ –
The volume of 1 mole pure ethanol is 58.0 ml and the volume– The volume of 1 mole pure ethanol is 58.0 ml and the volume^ of 1 mole pure water is 18.0 ml. However, 1 mole watermixed with 1 mole ethanol does not result in 58.0 ml + 18.0ml, or 76.0 ml, but rather 74.
ml.
ethanol is 57.4 ml and the partial molal volume of water is16.9 ml.
(non-ideal solution)
M Subramanian
www.msubbu.in
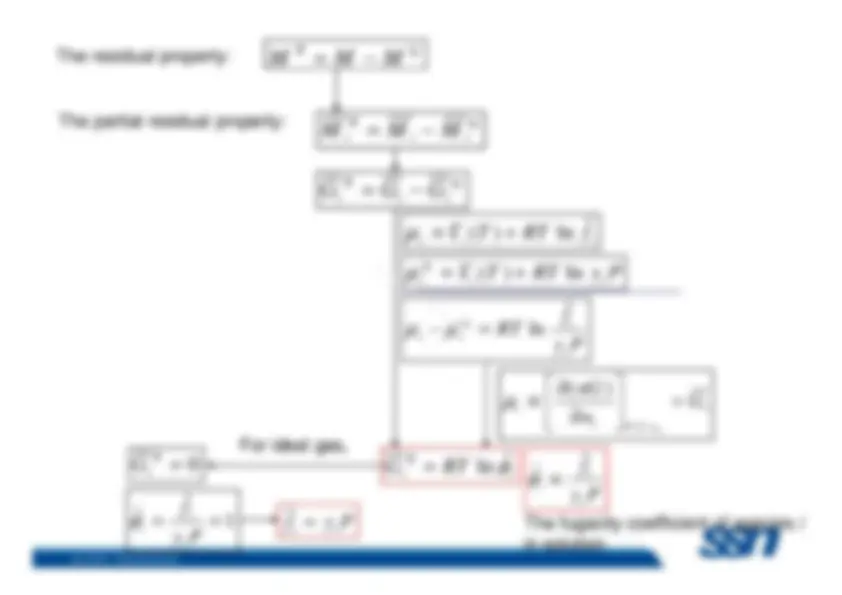
Fundamental Equations of Solution
Thermodynamics
M Subramanian
M Subramanian
M Subramanian