



















Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
Selcuk University - Neba Wais Alqorni - Introduction International Relations (1,2,3,4,5)
Typology: Assignments
1 / 26

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!



















Realism
A word to strike fear into the hearts of IR teachers and students alike… It’s going to be complicated – I’ll never understand it… It’s complicated – how can I teach it so they’ll grasp it? However, as with everything in life, theory is as complicated as you want to make it. And as with most things, if you understand the basics, it’s much easier to grasp the harder bits… And besides – IR theory is Important Important. If we grasp the theory behind something, everything else is much easier to understand…
Theory is NOT: Correlation Description Interpretation Absence of data Ideology
Why theories? (^) Purpose of theories in international relations: (^) Positivism : Explain and predict by reducing the complexity of reality (examples: Neorealism, Institutionalism). Normativism : Challenge realism with reference to normative standpoints/values and develop strategies of fundamental global change (examples: Feminism and gender equality; Marxism and class struggle; Idealism and human rights).
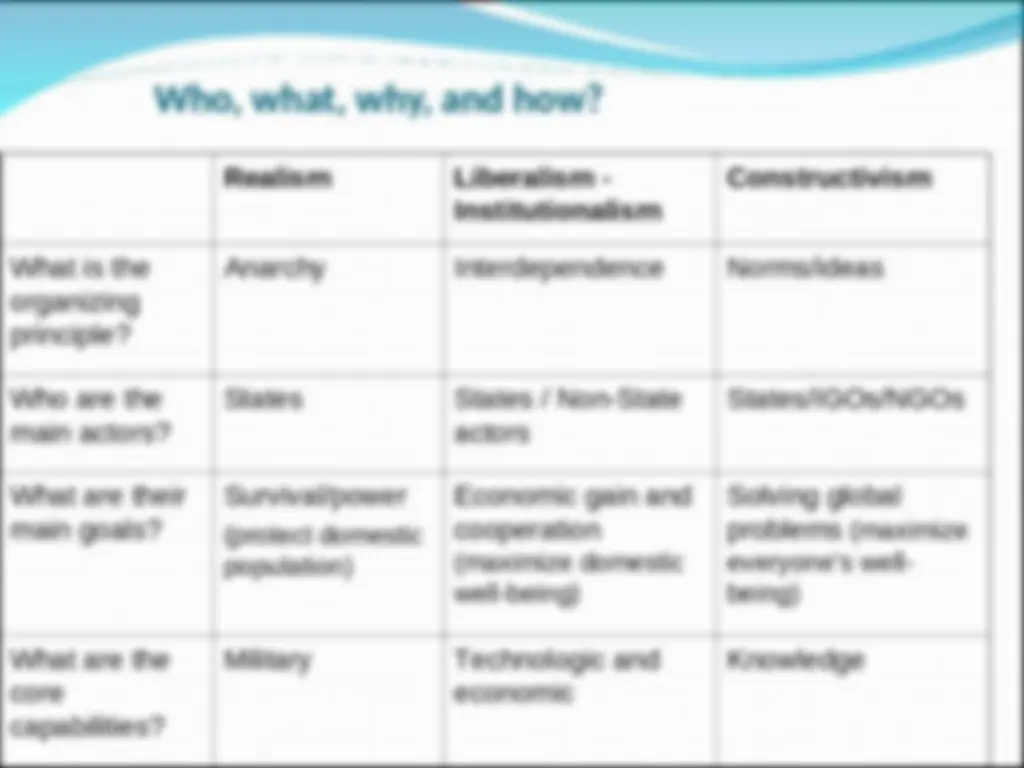
What do perspectives do?
Realism: power struggles among states; solution: balance of power Institutionalism: self-interested cooperation among states; solution: regimes based on shared interests Constructivism (idealism, identity perspective): differences in identities; solution: shared norms
begins with the idealist writers’ claims of inter-war period (1919-1939). According to realists, the inter-war scholars’ approach was flawed, for example they ignored the role of power and overestimated the degree to which human beings were rational. Realism rose from the ashes of idealist approach.
a great debate took place in 1930s & 1940s between the inter-war idealists and realists namely E.H. Carr, Hans Morgenthau, Reinhold Niebuhr, Frederick Schuman, George Kennan etc. who all emphasized the primacy of power and the competitive nature of politics among nations.
Key Propositions of Realism The state as the key actor in international politics States must pursue power to perpetuate the life of the state in a hostile and threatening environment Skeptical of the idea that universal moral principles exist 3 Ss= Statism - Survival - Self-help Distinction between domestic and international politics
International Politics
Classical Realism: key arguments
Structural Realism: key thinkers & texts
Key Points (1)
Key Points (1) Criticism: 1-Statism is flawed both on empirical (challenges to state power) and 2- normative grounds (the inability of sovereign states to respond to collective global problems)