






































Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
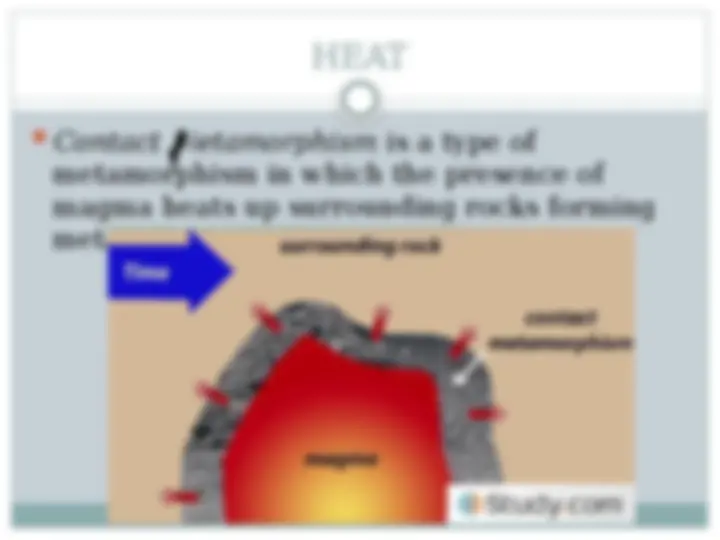
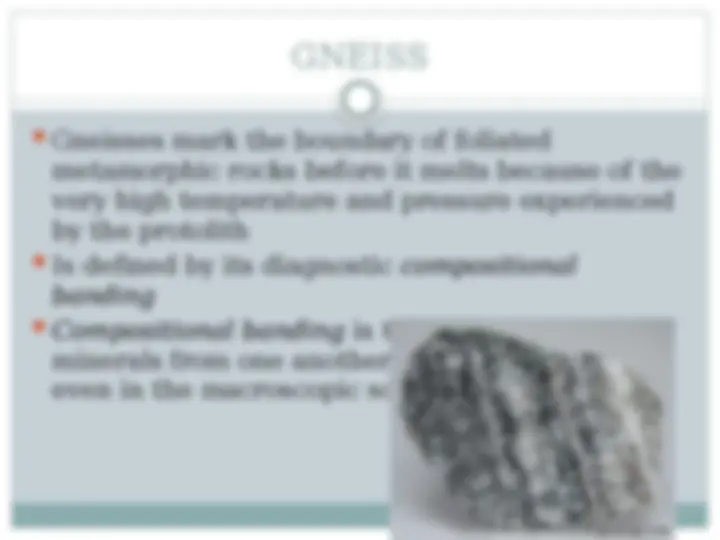
A comprehensive overview of the key processes involved in the formation of sedimentary and metamorphic rocks. It covers the fundamental concepts of weathering, erosion, transport, deposition, and diagenesis that lead to the creation of sedimentary rocks. Additionally, it delves into the various types of sedimentary rocks, including detrital and chemical sedimentary rocks, and their distinguishing characteristics. The document also explores the conditions and mechanisms that drive metamorphism, resulting in the transformation of pre-existing rocks into different metamorphic rock types, such as phyllite, schist, gneiss, marble, and quartzite. By understanding these geological processes, students can gain valuable insights into the dynamic nature of the earth's surface and the formation of the diverse range of rock types that make up our planet.
Typology: Slides
1 / 48

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!









































R O C K S F R O M S E D I M E N T S
How sediments are formed to sedimentary rocks Sedimentary processes have portions that are largely dependent on climatic events (e.g. precipitation and wind) powered by the sun. As rocks are exposed to these surface conditions, their mineral constituents adapt to the change in conditions (temperature, pressure, etc.) which causes significant physical and chemical changes
A R E P R O C E S S E S L E A D I N G T O T H E B R E A K D O W N O F R O C K S
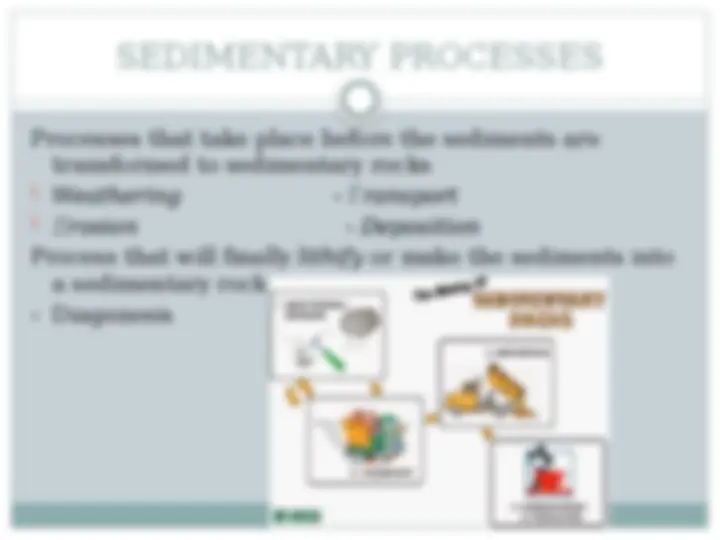
Processes that take place before the sediments are transformed to sedimentary rocks (^) Weathering - Transport (^) Erosion - Deposition Process that will finally lithify or make the sediments into a sedimentary rock
Chemical weathering take mostly on exposed surfaces of rocks If rocks are broken down into smaller pieces, it will be more vulnerable to attacks of chemical weathering Chemical weathering processed result to the ‘decay’ of minerals present in the rock With greater difference in the conditions of mineral formation and surface conditions, minerals are more susceptible to weathering attacks
(^) Erosion Means to ‘eat away’ Is the process of eating away rocks from their source. With physical and chemical weathering already weakening the stability of rocks, erosion takes place with the help of gravity and medium such as water, wind or organisms
Competence is the property of medium (e.g. water, air, etc) to bring bigger sediments Capacity is the property of medium to bring more sediments Sorting is the property that happens smaller sediments are delivered farther away while the larger ones are left behind because of the continuous transport As a summary: with greater distance of transport, sediments tend to become smaller, rounder, spherical in shape, and well-sorted.
Deposition The settling of the sediments in an area before they are finally lithified to form sedimentary rocks It occurs when the energy of the medium/agent is no longer capable of transporting the sediments
Diagenetic processes are important in the formation of sedimentary rocks. Without them, your sediments will remain unconsolidated
T H E E N D P R O D U C T O F P H Y S I C A L W E AT H E R I N G W O U L D B E S M A L L E R U N I T S O F S E D I M E N T S , W H I L E C H E M I C A L W E AT H E R I N G W O U L D B E C H E M I C A L LY- D I S S O LV E D M I N E R A L C O M P O N E N T S A N D R E S I S TA N T M I N E R A L S. B E C A U S E O F T H I S D I S T I N C T I O N O F E N D P R O D U C T S , T H E C L A S S I F I C A T I O N O F S E D I M E N T A R Y R O C K S B E C O M E S E A S I E R
Udden-Wentworth scale (classification is based on size not on composition)
Conglomerates and Breccias Are detrital sedimentary rocks composed of gravel-sized (>2mm in size) elements Conglomerates are composed of rounded (smooth) rock fragments Breccias are composed of angular ones For rounded grains, the sediments came from a source farther away from the area where the sediments are deposited For angular grains, the source of the sediments must be nearby
(^) Sandstones Are detrital sedimentary rocks composed of hand-sized (1/16mm – 2mm in size) sediments Because of their smaller sediment size, the roundness of grains may be difficult to determine Sand is deposited at much lower energies compared to conglomerates and breccias
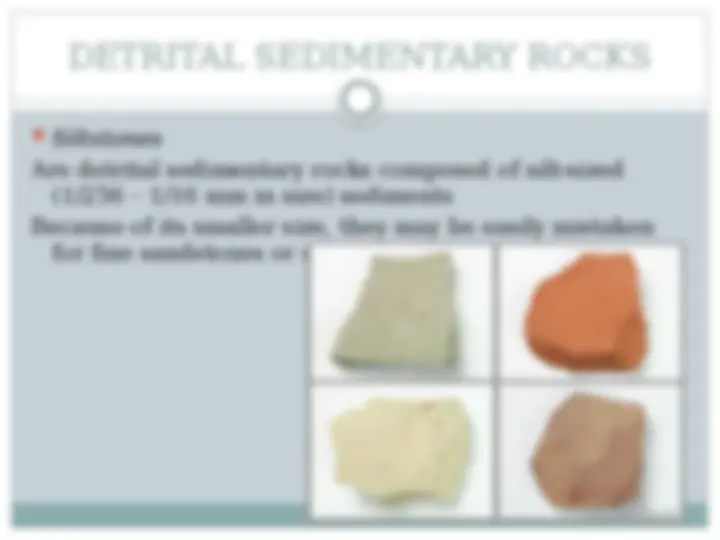
(^) Siltstones Are detrital sedimentary rocks composed of silt-sized (1/256 – 1/16 mm in size) sediments Because of its smaller size, they may be easily mistaken for fine sandstones or claystones