
























Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
Definitions and examples of various rhetorical devices including Asyndeton, Polysyndeton, Anaphora, Antithesis, and more. Students are encouraged to take notes and review these terms throughout the semester as they will be used frequently in their studies and on standardized tests.
What you will learn
Typology: Study notes
1 / 37

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!






























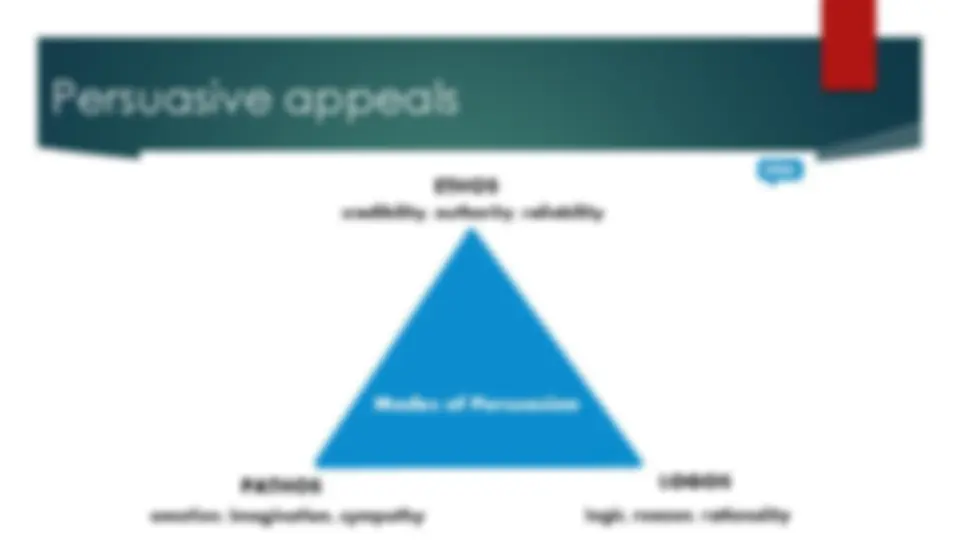
In squads and in your notebooks/binders, refer to the following list of words and see what you remember (definitions and/or examples). Ethos/pathos/logos Allusion, anecdote, hyperbole, metaphor, parallelism, rhetorical questions, restatement, understatement
Asyndeton - definition “Asyndeton is derived from a Greek word asyndeton which means unconnected. It is a stylistic device used in literature and poetry to intentionally eliminate conjunctions between the phrases and in the sentence, yet maintain the grammatical accuracy. This literary tool helps in reducing the indirect meaning of the phrase and presents it in a concise form. Or, when you leave out conjunction junction
Asyndeton - definition A. One type of asyndeton is used between words, phrases and a sentence. “Are all thy conquests, glories, triumphs, spoils, Shrunk to this little measure?” B. Second type is used between sentences or clauses. Without looking, without making a sound, without talking
Asyndeton/Ploysyndeton Polysyndeton and asyndeton are opposite to each other. Polysyndeton includes addition of multiple conjunctions such as in “He eats and sleeps and drinks.” On the other hand, asyndeton is the elimination or leaving out of conjunctions such as in “He eats, sleeps, drinks.” Both create a completely different effect. Polysyndeton slows down the rhythm of speech and makes it moderate whereas asyndeton speeds up the rhythm of the speech.
Asyndeton - function Speed up rhythm Focus/attract readers’ attention “since it suggests that words, phrases and sentences are incomplete and the readers would have to do some work to deduce meanings”. Emphasize a particular idea
Anaphora – function Adds prominence to ideas Add rhythm (more pleasurable to read, and easier to remember) Appeal to the emotions of the audience, in order to persuade, inspire, motivate, and encourage them. Example: “ Every day, every night, in every way, I am getting better and better.”
Antithesis – definition Antithesis, literal meaning opposite, is a rhetorical device in which two opposite ideas are put together in a sentence to achieve a contrasting effect. Antithesis emphasizes the idea of contrast by parallel structures of the contrasted phrases or clauses, i.e. the structures of phrases and clauses are similar in order to draw the attention of the listeners or readers.
What’s the difference between repetition and restatement? Repetition repeats the same words Restatement repeats the same ideas , but using different words
How’s that different from parallelism? Repetition a rhetorical device that involves the repetition of the same word, phrase or sentence. Parallelism is a literary device that juxtaposes two or more similar syntactic constructions, especially those expressing the same idea with slight modifications. Repetition refers to the repetition of words, phrases, or clauses. Parallelism refers to the repetition of the structure. Repetition focuses more on the meaning. Parallelism focuses more on the structure.
Euphemism A nicer way of putting something distasteful, sad, etc. Effect can be to soften the blow, stay tasteful/polite, etc.
Hyperbole/Understatement
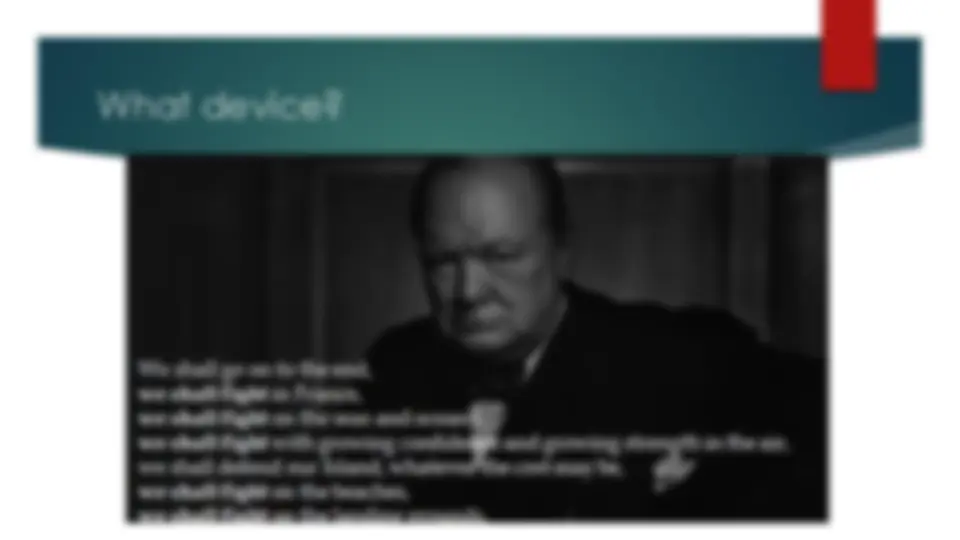
What device? “This is the villain among you who deceived you, who cheated you, who meant to betray you completely…….”
What device? – Asyndeton!