



Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
A comprehensive overview of the concept of resistance, including its definition, unit, factors affecting resistance, and related electrical properties. It covers topics such as ohm's law, resistor color codes, and various types of resistors like potentiometers, rheostats, varistors, and thermistors. The document also introduces the concepts of capacitance, inductance, and their associated devices, as well as the principles of electromagnetic induction. It delves into the mathematical relationships and formulas governing these electrical phenomena, making it a valuable resource for students and professionals in the field of electrical engineering and physics.
Typology: Study notes
1 / 4

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!



The property of a material to oppose or limit the flow of
current or charge
Unit : Ohms
Reciprocal : Conductance in Siemens (S) or mho
The higher the number (AWG#), the thinner the wire, the
higher the resistance
Factors Affecting Resistance
✓ Type of material
✓ Length of material
✓ Cross-sectional area of the material
✓ Temperature
2
1
2
1
2
1
2
2
1
2
4
Hard Drawn Copper @ 20 ℃
− 8
Ω − m = 10. 5
Aluminum @ 20 ℃
− 8
Ω − m = 17. 1
Annealed Copper @ 20 ℃
− 8
Ω − m = 10. 37
CM = Circular Mill (area)
1 in = 1000 mils
Temperature Resistance Effects
HDC Al Annealed Copper
Ohm’s Law
Georg Simon Ohm
Henry Cavendish (first to discover)
Resistor Color Chart
st
nd
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
Resistor Variations
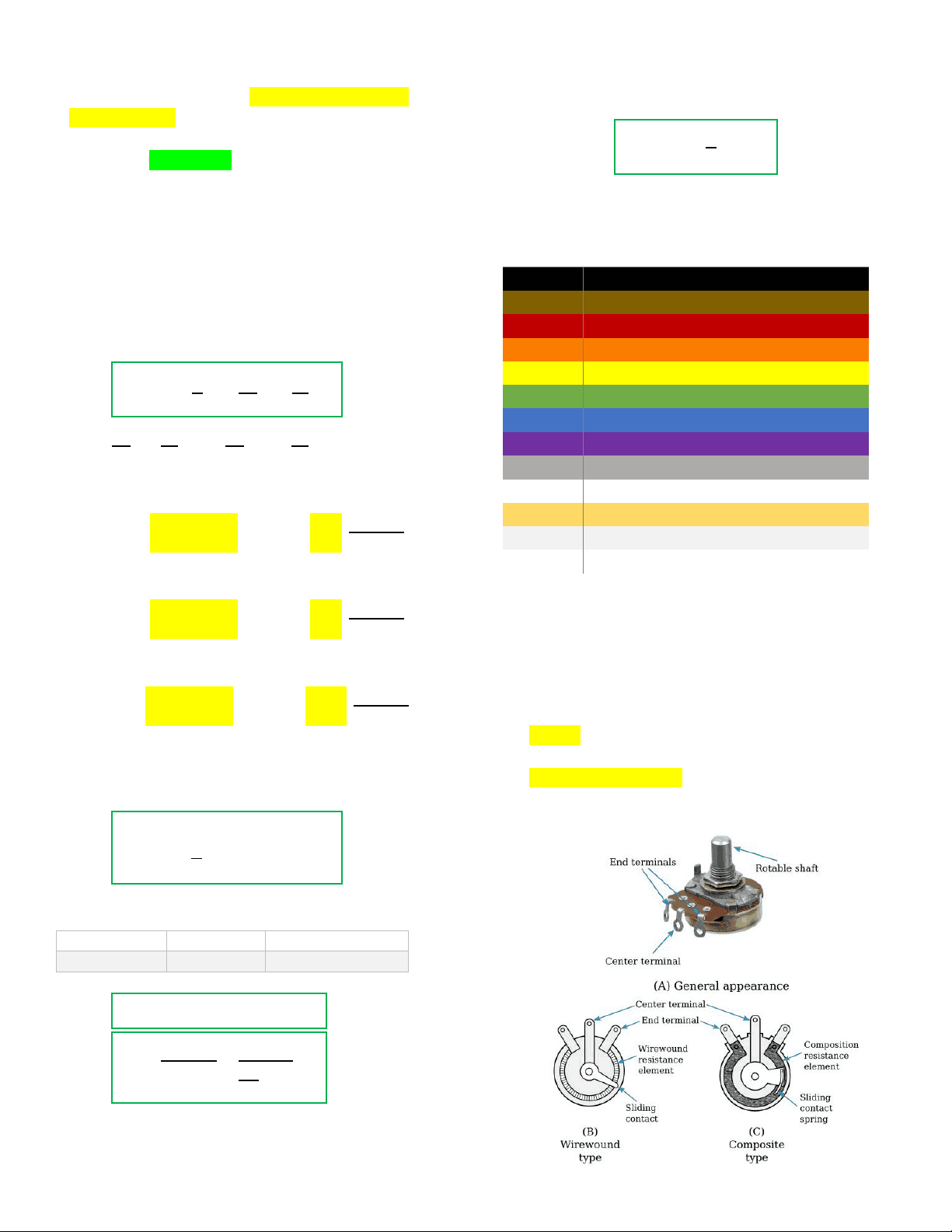
Potentiometer (Variable resistor)
Has three connections, two fixed and one moveable
Tunable; used as knobs to control the volume of a stereo
Constructed like a resistor, but has sliding tap contact
Used as voltage dividers
Has wide range of values, limited current-handling
capability
2
2
2
2
2
1
1
2
1
1
1
0
1
Rheostat
Has two connections, one fixed and other moveable
Variation of potentiometer with a high current rating
Has limited range of values
Varistors
Voltage-sensitive resistor
Thermistor
Temperature-sensitive resistor
Resistance decreases as the temperature rises
Used in fire alarms
Light Dependent Resistor (LDR)
Changes values depending on the amount of light shining on
its surface
Resistance decreases as the amount of light increases
Conductance and Conductivity
Measure of the amount of electric charge stored for a
given electric potential
Stores energy in the form of electrostatic field
Opposes the change in voltage
Unit : Farad (F)
Reciprocal : Elastance – Daraf (F
Capacitor
Device that stores energy in the electric field created
between a pair of conductors
Simple Capacitor :
Two copper plates separated by an air gap or a sheet of mica
Air is low cost – the best reason why air is used as a dielectric
Operation of a Capacitor
Factors Affecting Capacitance
✓ Area of the plates
✓ Distance between the plates
✓ Dielectric material
Parallel-Plate Capacitor
For n plates
Work
Point Charge/Steady Charge – no ½ as capacitor is not
constant
Multiplier
Numerator: source 𝑅
𝑆
: Series Resistance
Denominator: volt meter reading 𝑅
𝐼
: Instrument Resistance
Series: Volt meter; Parallel: Ammeter I I
= load current
Mass Charge
Electron 9.11 x 10
kg - 1.602 x 10
Proton 1.67 x 10
kg - 1.602 x 10
Neutron 1.67 x 10
kg none
Name given to the property of a circuit whereby there is an
emf induced into the circuit by the change of flux linkages
produced by a current change
Opposes the change in current
Classified according to core type: ferromagnetic or air
Unit : Henry
Inductor
Device that stores energy in the form of magnetic field
𝐶 =
𝜀
𝑜
𝜀
𝑟
𝐴
𝑑
𝐶 =
( 𝑛 − 1
)
𝜀
𝑜
𝜀
𝑟
𝐴
𝑑
𝐶 =
𝜀
𝑜
𝐴
𝑑
𝜀
𝑟
1
𝑑
𝜀
𝑟
2
𝑑
𝜀
𝑟
3
𝑊 =
1
2
𝐶𝑉
2
=
1
2
𝑄
2
𝐶
=
1
2
𝑄𝑉
𝑀 =
𝑉
𝑆
𝑉
𝑉
=
𝑅
𝑆
𝑅
𝐼
𝑀 =
𝐼
𝐼
𝐼
=
𝑅
𝐼
𝑅
𝑆𝐻
(nasa ilalim ang hinahanap)
d x
For equilateral triangle with equal charges
Or
Use free body diagram (one reference axis)
√
2
1
√
1
2
𝑅
𝑅
1
1
2
2