



Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
RC coupled amplifier I'm make it more essay in my notes u understand it. Very essaly and make your study more essay way.
Typology: Thesis
1 / 4

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!



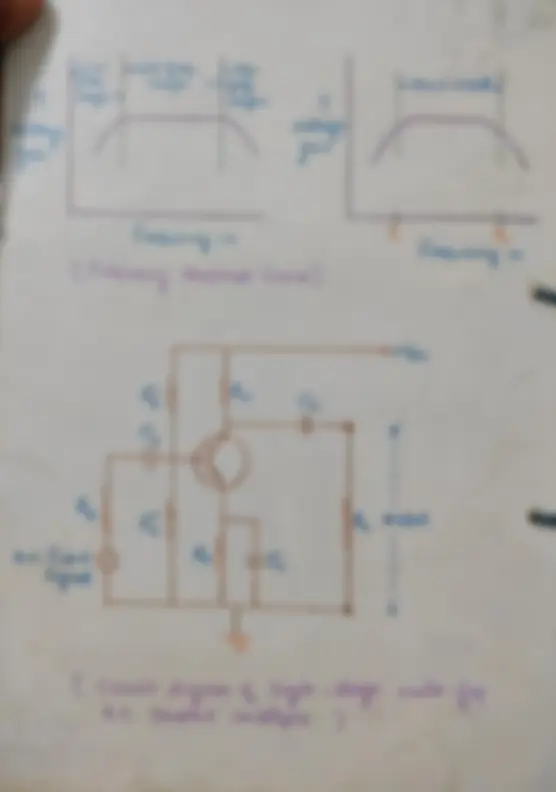
amplifier.
coupled amplifier (single^
multimeter, signal
amplifier
is a device^
or increases magnitude
of the^
current or (^) power.
voltage
or
between base and^ emitter of^ a^ transistor, it
amplified.
of the
amplifier
are described^ below-
signal
is connected to^
between base^ and^
emitter.
Resistance Rs is
the internal^
is in series with capacitor
Cp.
It blocks^ the direct^
current of^ the collector circuit from (^) reaching
of the
an arrangement^
which is^
used for^
of the^
transistor (^) by voltage
divider method.
is a^
resistance
connected in^ the emitter circuit for
stabilization. CE is the
bypass
capacitor
which blocks
undesired alternating^
component
of the^ amplified
current.
is the^
resistance across which output
amplified
current flows in^ the^
collector
circuit.
Cc is called the^ coupling
capacitor
which
blocks direct^
current of^ the amplifier^
in
reaching
across the^
load
resistance Ri single^
stage
amplifier
and hence to^ the second unit
of similar amplifier^
in case^ of cascade^
amplifier.
Required
reverse bias to^ the
collector emitter
circuit is^ provided^
means of^ 6 volt
battery
to the^
NPN
transistor.
Frequency
Response
Voltage
of the^ amplifier
is defined as:
Output voltage
of the^ amplifier
Voltage gain= Vin
Input
voltage
of the^ amplifier
Voltage
of the^ single^
stage stage
common emitter amplifier^
in terms^
ofh-parameters
Av (^) Zin(hoet 1RL)
Negative
indicates that^ output
and input
voltage
where Ay
voltage gain ofthe^
amplifier
hpeforward
current (^) gain of
amplifier
in common emitter
configuration
hoe
output
admittance
which
includes various
condensers formed
between
different
elements of transistor.
R load resistance
Hence voltage
on the
reactance
d output capacitance
C, which are formed^
between different elements^ of^ the^ transistor
condenser
voltage and due^ to this
reason
of the amplifier
as
represented
in the
The
with variation in (^) frequency
is called
response curve.
Band
at which gain of the
falls (^) to 70.7% or 1W
Nature of the frequency response curve can be understood as below-
At mid frequency ranger- In this range, effect of coupling condenser Cc and output
condenser C, can be neglected. Reactance of C[X= 1/ 27t fCe ] is very small, since Ce
in equivalent circuit (high reactance in parallel may be neglected).Hence the equivalent
circuit of RC coupled amplifier does not contain condensers in the mid frequency range
hence the voltage gain remains constant.
(1) Reactance of coupling condenser Ce becomes very high and its effect can not be
passing to RL decreases and as a result output voltage and consequently voltage gain of
(2) Reactance of condenser CE connected in the emitter circuit becomes very high and
The
resistance makes^ the^ emitter^ less (^) forward
output
voltage reduces hence the voltage gain also reduces.
At high frequeney range- In this range effect of couplinig condenser Ce is neglected
while effect^ of (^) condenser
can (^) not be
Xo= 1/2n^
becomes very small and small reactance in parallel can not be neglected. Due to this
the
Yege-