







Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
An overview of statistical significance, decision errors, effect size, and statistical power. It explains the concepts of type i and type ii errors, the importance of setting the right significance level, and the role of effect size and statistical power in interpreting research results. It also includes illustrations and examples to help understand these concepts.
Typology: Slides
1 / 10

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!







Decision Errors, Effect Size, and Statistical Power Decision Errors, Effect Size, and Statistical Power
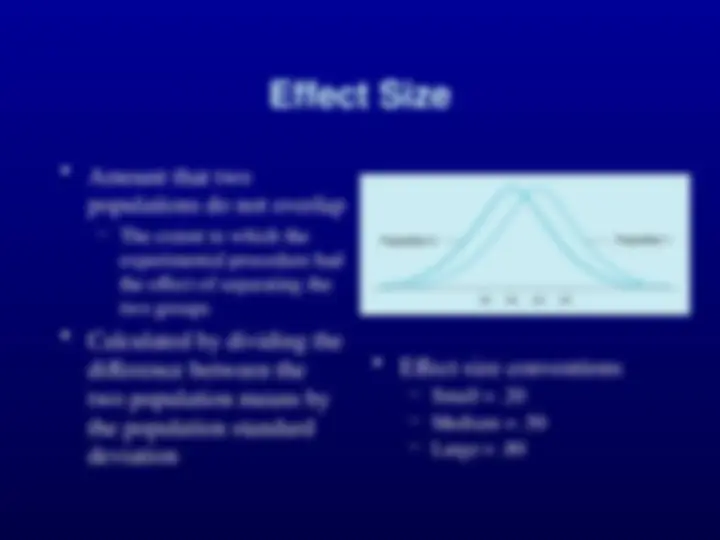
Amount that two populations do not overlap
a. Small effect size b. Medium effect size c. Large effect size
a. The two means are very different b. The variance is very small