Download pass assignment 1: procedural programming and more Assignments Programming Languages in PDF only on Docsity!
ASSIGNMENT 1 FRONT SHEET
Qualification BTEC Level 5 HND Diploma in Computing Unit number and title Prog 102 : Procedural Programming Submission date Date Received 1st submission Re-submission Date Date Received 2nd submission Student Name Truong Dan Truong Student ID GCH Class GCH0908 Assessor name Nguyen Dinh Tran Long Student declaration I certify that the assignment submission is entirely my own work and I fully understand the consequences of plagiarism. I understand that making a false declaration is a form of malpractice. Student’s signature Truong Grading grid P1 P2 P3 M1 M2 D
Summative Feedback: Resubmission Feedback: Grade: Assessor Signature: Date: Lecturer Signature:
- Table of figure
- Table of diagram
- Table of WBS
- List of tables
- 1 Theory
- 1.1 What is Programming Language?
- 1.2 Type of Programing language and representative programing language......................................................
- 1.3 Procedural programing
- 1.3.1 What is procedural programing?
- 1.3.2 Some Procedural programming languages
- 1.3.3 Features of procedural programming
- 1.3.4 Characteristics of procedural programming
- 1.3.5 Advantages and disadvantages of procedural programming
- 2 Program analysis
- 2.1 Variables, data types are used
- 2.2 Structures are used
- 3 Design program...................................................................................................................................................
- 3.1 WBS
- 3.2 Use-case diagram for student’s management system
- 3.3 Flowcharts...................................................................................................................................................
- 3.3.1 Flowchart for general program.
- 3.3.2 Flowchart for function: printList
- 3.3.3 Flowchart for function: findMax
- 3.3.4 Flowchart for function: findMin
- 3.3.5 Flowchart for function: printMenu
- 3.3.6 Flowchart for function: readList
- 3.4 Evaluate my design:
- References...................................................................................................................................................................
- Figure 1-Programing language Table of figure
- Figure 2-C language
- Figure 3-Pascal language................................................................................................................................
- Figure 4-Fortran language
- Diagram 1-Type of programming language Table of diagram
- Diagram 2-Procedural Programming
- Diagram 3- student’s management system
- WBS 1-breakdown student management problem into small ones Table of WBS
- Table 1- Variables, data types are used List of tables
- Table 2- Structures are used
- Flowchart 1-general program Table of flowchart
- Flowchart 2- function printList
- Flowchart 3-function findMax
- Flowchart 4-function findMin
- Flowchart 5-fuction printMenu
- Flowchart 6-function readList
1 Theory 1.1 What is Programming Language? Computers just recognize information in binary — strings of 1s and 0s. Therefore, programming languages are the tools that is to use to translate the 1s and 0s into instructions that humans can understand and write for computers to follow. (Admin, 2021) Figure 1 - Programing language 1.2 Type of Programing language and representative programing language Diagram 1 - Type of programming language
Figure 2 - C language
- Pascal Like C language, Pascal is basic procedural programing language, however it uses a lot of keywords instead of symbols and braces in C language so it is clearer and mainly to teach beginners rather than writing software. (Admin, 2021) Figure 3 - Pascal language
- Fortran Fortran language is not popular because this is a number crunching language that is suitable for engineers or scientists, who have to calculate values with high precision. Program in Fortran is inflexible and sometimes it makes difficult to read. (Admin, 2021)
Figure 4 - Fortran language 1.3.3 Features of procedural programming
- Pre-defined functions: an available instruction in the library of program. It is to carry out common tasks. For example: in C language, you want to display sentence " Hello World", you can use: printf("Hello World").
- User-defined function: like pre-defined functions, user-defined function is a set of instructions that used to perform a certain task. It can be called and reused many times. However, it is defined according to user needs and not available in the library of program. For example, you can define function that named findMax(a, b) to compare value of variable a and b.
- Local variable: local variables exist only in the function in which the variable is declared, the value of a variable will be lost at the end of the function.
- Global Variables: global variables declared outside all functions, so any function can use global variables to calculate. Their value is only lost at the end of the program
- Programming libraries: The libraries in programming are a place to provide programmers with available functions and methods. The programmers can use these functions whenever they are needed to help shorten reprogramming time.
- Modular: It is the ability to divide software into modules corresponding to functions while allowing management overall
- Parameter passing: pass reference and value to a method function to handle a certain task:
- Call by value: the value of the variable will not be changed.
- Call by reference: the value of the variable will be changed. (Anon., n.d.) 1.3.4 Characteristics of procedural programming
- Process is focused rather than data.
- Each function represents a specific task (example: reading, calculating and printing…)
- Solve a problem in the program in order from top to down.
- Global data can use in all function in a program.
2.2 Structures are used Structures Where to use Purpose of uses Example If Function findMax, findMin
- Find highest/lowest grades Switch…case Function main Select menu item For - Function max, min
- Function printList
- Function readList.
- Access each student’s grades to find highest/lowest grades
- Print list of student IDs/grades. Do..while - Function main
- Print list of menus until user don’t want to use. Table 2 - Structures are used
3 Design program 3.1 WBS WBS 1 - breakdown student management problem into small ones ❖ Explain: After reading the scenario, I have identified the different requests that a teacher needs to manage the grades of a class. In WBS, I have subdivided it into 5 smaller functions of detail to satisfy his requirements When the teacher opens the program, he will meet a menu that includes 5 options:
- The first is to enter the information of students (Number of students, IDs, grades).
- The second is to print all student IDs together with their grades
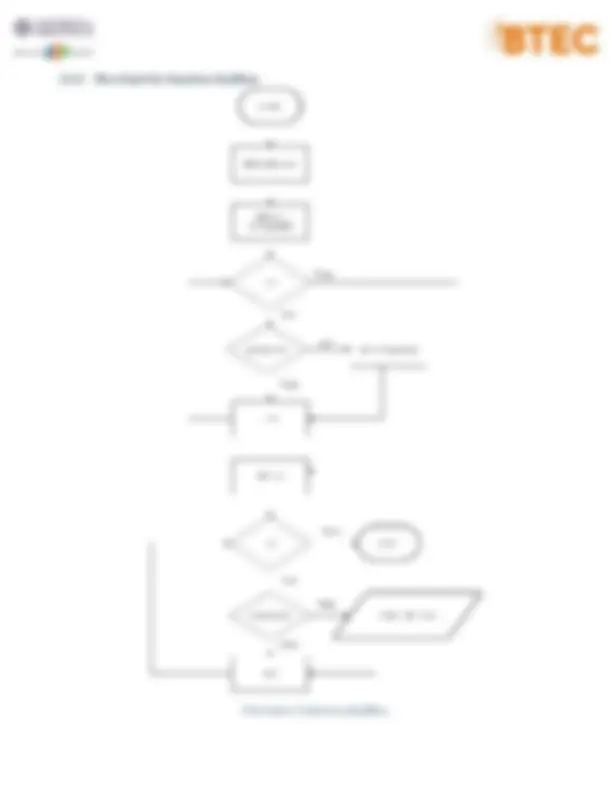
3.3 Flowcharts 3.3.1 Flowchart for general program.
Flowchart 1 - general program
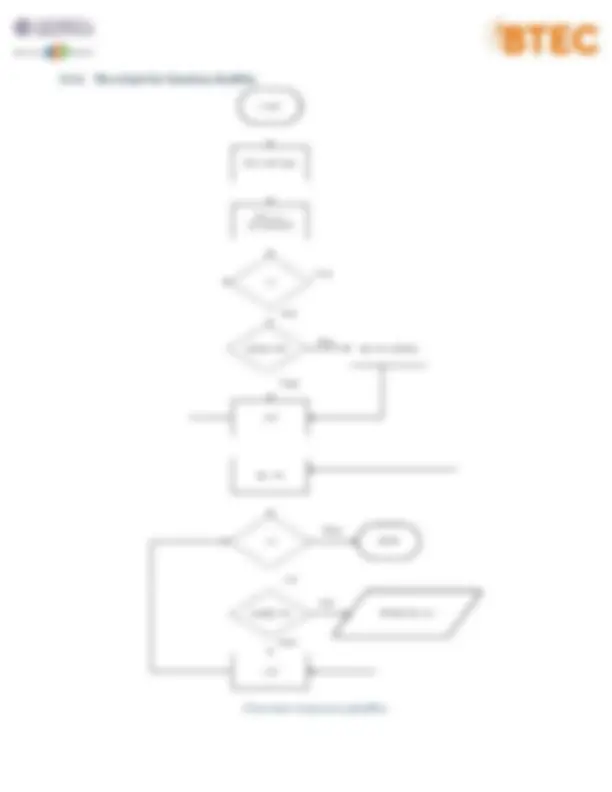
3.3.2 Flowchart for function: printList Flowchart 2 - function printList
❖ Explain by pseudo code: Step 1: START Step 2: DECLARE the variable i Step 3: SET i= Step 4: WHILE i<n is true, repeat Step 5 through Step 6 Step 5: PRINT ID[i], grade[i] Step 6: INCREMENT i by 1 Step 7: STOP
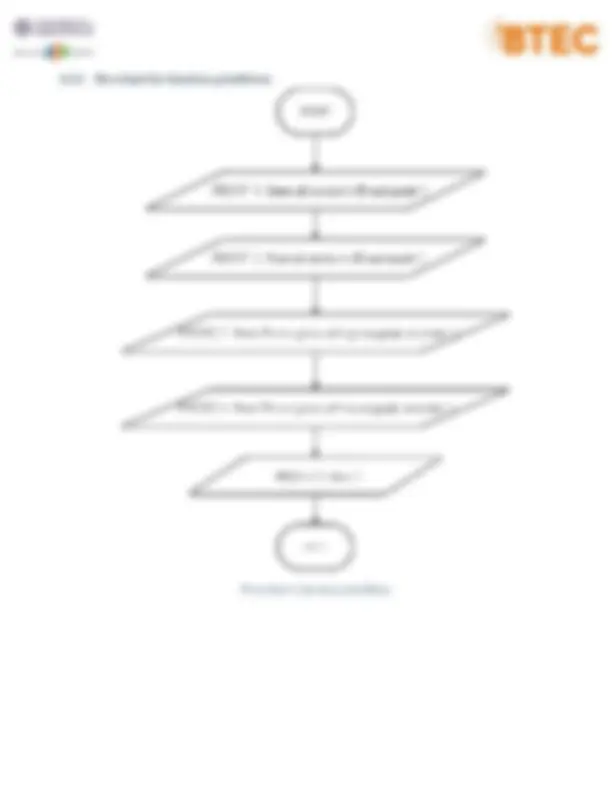
❖ Explain by pseudo code: Step 1: START Step 2: DECLARE the variable i, max Step 3: SET i=1, max=grade[0] Step 4: WHILE i<n is true, repeat Step 5 through Step 6 Step 5: IF grade[i]>max then SET max= grade[i] Step 6: INCREMENT i by 1 Step 7: SET i= Step 8: WHILE i<n is true, repeat Step 9 through Step 10 Step 9: IF grade[i]=max then PRINT ID[i], max Step 10: INCREMENT i by 1 Step 11: STOP
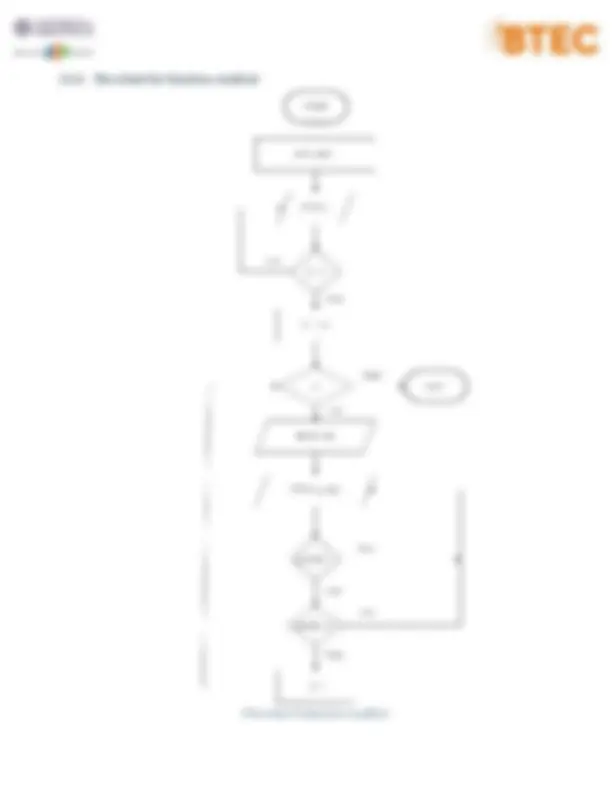
3.3.4 Flowchart for function: findMin Flowchart 4 - function findMin