



















































































Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
Nurs 472 Exam 3 - Nurse 472 Nurs 472 Exam 3 - Nurse 472
Typology: Exams
1 / 92

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!





















































































-Approx 3 weeks long -Zygote implants i n the uterine wall with three cell layers: Endoderm (inner layer ) R espiratory system, D igestive system, L iver, and P ancreas Mesoderm ( middle layer ) S keleton, C onnective tissue, C artilage, M uscles, C irculatory, L ymphoid, R eproductive, and U rinary systems Ectoderm ( outer layer ) B rain, S pinal cord, N ervous system, and O uter body parts (skin, hair, nails)
Week 4- -Rapid growth and cell layer differentiation -By the end, ALL basic organs are established, bone begin to ossify, some human features are recognizable
9 week – birth -Body organs and systems continue to develop End of first trimester ( 12 weeks’ gestation) : EXAM
- _Some reflexes present_*
Time span of conception:
hCG (referred to as the “pregnancy hormone”) ➔ Used to test for pregnancy through urinalysis. ➔ Blood hCG test can be Qualitative (yes or no result) or Quantitative (number result which can be used to determine how far along the pregnancy is based on the level of hCG hormone present in the blood) ➔ hCG produces progesterone to help maintain endometrial lining of the uterus. Human placental lactogen (hPL) or somatomammotropin (hCS) human chorionic ➔ Responsible for regulating fetal and maternal metabolism, helps to develop maternal breasts for lactation. ➔ Decreases insulin sensitivity in the mother which will in turn increase the available nutrients for the fetus. Estrogen - ➔ Causes breasts to enlarge, uterus to enlarge, and the external genitalia to enlarge. ➔ Also responsible for stimulating myometrial (middle layer of the uterus) contraction. ➔ It is important for inducing uterine contractions Progesterone - ➔ Responsible for M aintaining the endometrium lining, D ecreasing contractility of the uterus, S timulating maternal metabolism and B reast development. Provides N ourishment early on in the conception phase up to the embryo and then to the developing fetus. Relaxin - ➔ Together with progesterone, relaxin is responsible for M aintaining the pregnancy, R elaxation of the pelvic ligaments, and S oftens the cervix in preparation for birth.
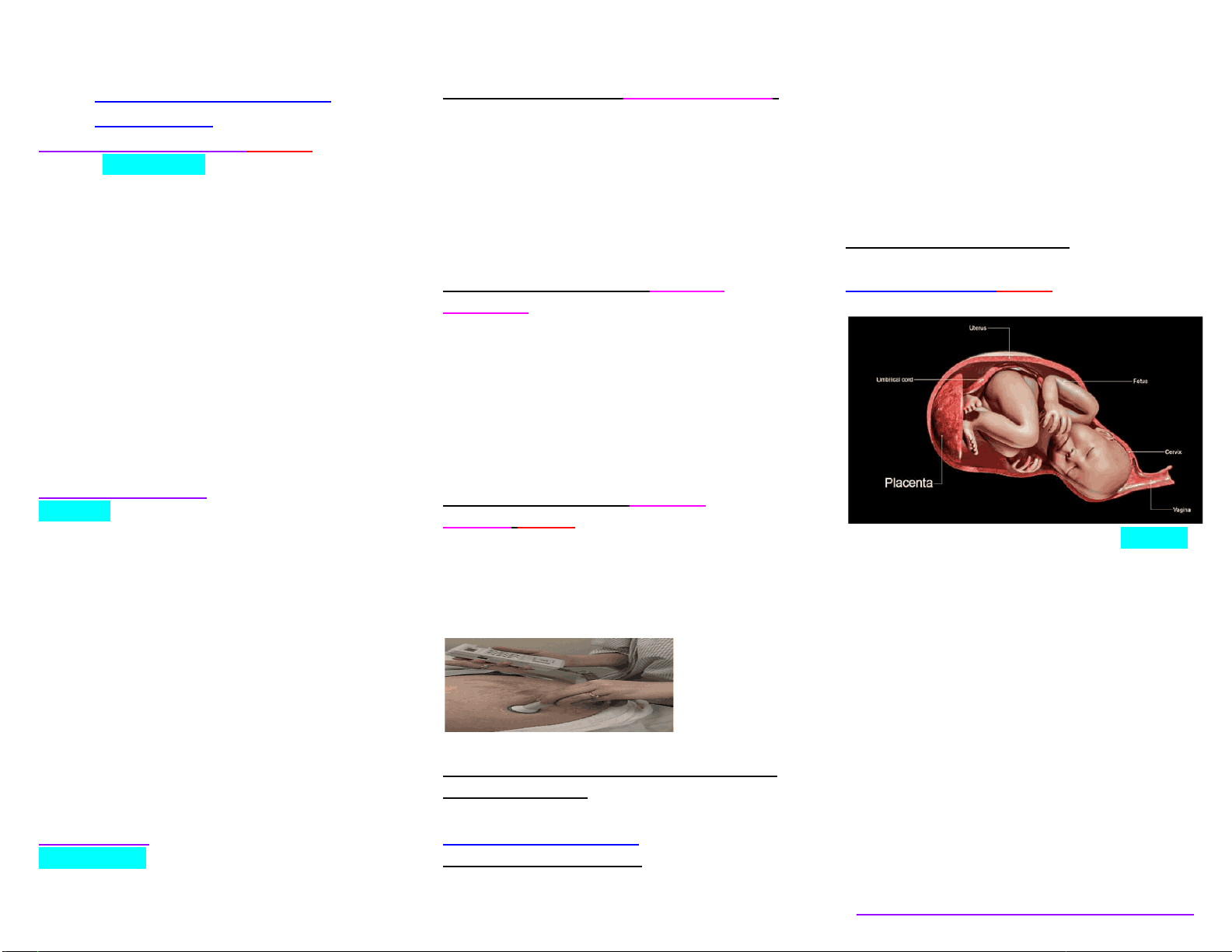
As the placenta is developing the umbilical cord is also developing from amnion (innermost membrane that encloses the embryo). -Formed from the amnion
As the pregnancy progresses the amount of amniotic fluid increases (1 liter at full term) -It is made up of maternal blood and fetal urine. Role of AMNIOTIC FLUID ● Helps maintain a constant body temperature for the fetus ● Permits symmetric growth and development ● Cushions the fetus from trauma ● Allows the umbilical cord to be relatively free of compression ● Promotes fetal movement to enhance musculoskeletal development
● • Transportation of Blood from the placenta to and through the fetus and then back to placenta. ● *Fetal circulation is different from adult circulation due to the presence of certain vessels and shunts. ● • Three shunts during fetal life (they close after birth) ○ Ductus venosus : connects the umbilical vein to the inferior vena cava ● Ductus arteriosus: connects the main pulmonary artery to the aorta ● Foramen ovale: anatomic opening between the right and left atrium
● M ultifactorial disorders ● N ontraditional inheritance
more alternatives of a gene that are on a specific position on a specific chromosome that can produce the same characteristic of that gene (ie, a gene that produces eye color can have an allele that produce blue eyes or an allele that produces brown eyes)
what we see in a person *A human inherits two genes ; one from each parent one allele comes from the mother and one from the father. When these alleles are the same, they are homozygous and when they are different they are heterozygous ****In this picture mom has homozygous and dad has heterozygous If the two alleles differ the dominant one will be expressed in the phenotype of the actual person
A single gene in the heterozygous state is capable of producing a phenotype ➔ The offspring of the affected parent will have a 50% chance of inheriting two normal genes thus being free from the genetic disorderAND a 50% chance of inheriting 1 normal and one abnormal gene and thus inheriting the disorder
-Two copies of an abnormal gene in a homozygous state are needed to produce a phenotype ➔ The individual must inherit 2 copies of the abnormal gene to show signs and symptoms of the disorder Both parents must be heterozygous carriers ➔ The offspring has a 25% chance of inheriting 2 normal genes AND a 50% chance of inheriting 1 normal and 1 abnormal gene (these will be carriers of the disorder), AND a 25% chance of inheriting 2 abnormal genes thus inheriting the disorder
➔ They are associated with an abnormal gene that is present on the X chromosome.
Males have XY and females have two XX. If a male inherits an X-linked abnormal gene, he will express the condition because he has one X chromosome. ➔ Because females inherit 2 X chromosomes they can either be heterozygous or homozygous for any allele. ***** X-linked disorders in females are expressed similarly to autosomal disorders ➔ _Males are most likely to be affected_* because all the genes on the male’s X chromosome will be expressed since the male has only one X chromosome. Women will most likely be carriers if they have 1 normal and one 1 affected chromosome and t hey will need to have 2 abnormal X chromosomes to exhibit the disease itself. ➔ Males do not transmit their X chromosome to their male offspring. Their X chromosome always comes from their mother. If a mother is a carrier, there is a 25% chance she will have an affected son, a 25% chance that her daughter will be a carrie r, and a 25% chance that she will have an affected son, and a 25%chance that her daughter will not be a carrier.
-It is very rare and when it occurs men are severely affected.
*****Best time to talk about genetic evaluation and counseling is before conception
Autosomal Dominant Inheritance: ● N eurofibromatosis, H unington’s disease, A chondroplasia, P olycystic kidney disease **** Autosomal recessive inheritance: Most common conditions associated with this genetic pattern: C ystic fibrosis, P henylketonuria, T ay-sachs, S ickle cell disease (most common in those of African decent) •X-linked recessive: ● H emophilia, C olor blindness, D uchenne muscular dystrophy X-linked dominant:
provide education about attaining a healthy pregnancy ●
Preconception Care ● o Folic Acid (1) ● ▪ Insufficient folic acid intake can lead to neural tube defects and taking folic acid reduces the incidence of neural tube defects by 2/3. Depending on risk profile, it is recommended that people take ● 400-800mcg folic acid/day. CDC guidelines CDC Guidelines for preconception care
● Immunization status ● Underlying medical conditions ● Reproductive health care practices ● Sexuality and sexual practices ● Nutrition ● Lifestyle practices ● Psychosocial issues ● Medication and drug use ● Support system Alcohol misuse - No time during pregnancy is safe to drink alcohol, and harm can occur early, before a woman has realized that she is or might be pregnant. Fetal Alcohol Syndrome and other alcohol-related birth defects can be prevented if women cease intake of alcohol before conception. Folic acid deficiency - Daily use of vitamin supplements containing folic acid (400 mcg) has been demonstrated to reduce the occurrence of neural tube defects by two thirds.
● Establishment of trusting relationship ● Focus on education for overall wellness ● Detection and prevention of potential problems ● Comprehensive health history, physical examination, and laboratory tests
● Reason for seeking care ● Suspicion of pregnancy ● Date of last menstrual period ● Signs and symptoms of pregnancy ● Urine or blood test for hCG ● Past medical and surgical history ● Personal history (includes) ● Occupation ● Possible exposure to teratogens ● Exercise ● Recreational patterns (alcohol, tobacco, and drugs) ● Alternative and complementary therapies ● Sleep patterns ● Nutritional habits ● General lifestyle ● Woman’s reproductive history: ● Menstrual ● Obstetric ● Gynecologic history Example: LMP 5/15/2020. NEE_GIL
Calculating estimated due date (edD)
Gravida : a pregnant woman (If someone has been pregnant twice she’s a G2) Gravida I ( primigravida ): first pregnancy Gravida II ( secundigravida ): second pregnancy, etc. Para: a woman who has produced one or more viable offspring carrying a pregnancy 20 weeks or more. Ex: If someone has a 4 year old child and they are now pregnant and just had a miscarriage at 8 weeks we will call her Gravida 2 and a Para 1. Primipara: one birth after a pregnancy of at least 20 weeks (“primip”) Multipara : two or more pregnancies resulting in viable offspring (“multip”) Nullipara: no viable offspring; para 0 ●
● G (gravida): # of pregnancies, including the current ● T (term births): the number of pregnancies ending > weeks’ gestation, at term ● P (preterm births): the number of preterm pregnancies ending
20 weeks or viability but before completion of 37 weeks ● A (abortions): the number of pregnancies ending before 20 weeks or viability ● L (living children): number of children currently living
● Shannon just gave birth to a baby boy. She has a two-year-old son at home and another son who is deceased. She has also experienced two miscarriages. ● LET’S DETERMINE SHANNONS OBSTETRIC HISTORY: ● G: 5 ● T: 3 ● P: 0 ● A: 2 ● L: 2 ● G5, P ● Vitals signs (BP, RR, temp, HR) + height and weight (compare at each prenatal visit). Get a urine sample when the patient is changing into a gown.
Have them change into a hospital gown and empty their bladder to get a clean catch urine specimen. Will get a urine specimen at every prenatal visit. ● Urinalysis can be used to R/O: UTI (we look for W hite Blood cells, N itrates, B lood, which can all be indicative of infection .) ➔ We can also look at glucose and protein. ➔ Glucose in the urine could indicate gestational diabetes. ● Protein = kidney disease or hypertension
Lymph nodes (any swelling is NOT normal) Nasal mucosa/gingival tissue , mild edema normal (due to increased levels of estrogen) Thyroid, slight enlargement normal (due to hormonal fluctuations) ○ Chest ■ Heart/Lung sounds - Heart sounds=normal. Lung sounds=clear.
pregnancy could result in a very soft systolic murmur. Another possibility is an increase in HR by 10-15 BPM which is NORMAL ➔ Slight increase in HR/RR are normal findings. Estrogen causes muscle relaxation leading to Chest diameter/Tidal Volume increase
Increase in estrogen and progesterone. And increase in blood volume will make breasts fuller , more nodular, increased sensitivity , blood vessels prominent ➔ Striae gravidarum (stretch marks) This is normal, common in women with larger breasts. ➔ Dark pigmentation of of nipple and areola ➔ Enlargement of Montgomery glands ➔ In the third trimester. Colostrum (yellowish secretion that precedes mature breast milk) excreted in 3rd trimester
Linea nigra - runs from the symphysis pubis to the umbilicus
within 72 hours after childbirth, if she is Rh sensitive Follow up visits Visit schedule: After the first prenatal visit the expectant mother will follow up Every 4 weeks up to 28 weeks pregnant. ➔ From 29 - 36 weeks she will go every 2 weeks. ➔ After 37 weeks up to delivery she will go every week. During these appointments we will Assess:
st
S potting or bleeding = M iscarriage P ainful urination = I nfection S evere persistent vomiting =H yperemesis gravidarum F ever >100F, and lower abd pain with dizziness and accompanied by shoulder pain = R uptured ectopic pregnancy
R egular uterine contractions= P reterm labor P ain in calf, often increased with foot flexion= D VT S udden gush or leakage of fluid from vagina= P remature rupture of membranes A bsence of fetal movement for >12 hours = F etal distress or demise
S udden weight gain, periorbital or facial edema, severe upper abd pain, or headache with visual changes =G estational hypertension and/or preeclampsia D ecrease in fetal movement >24 hours= P ossible demise
Ultrasonography- performed in the initial stages of pregnancy to determine gestational age. ➔ At 18-20 weeks ➔ An anatomy scan is used to look for any congenital malformations and verify dates and growth. ➔ 3rd scan done around 34-37 weeks gestation. To evaluate the size of the fetus, assess fetal growth, and identify the position of the placenta for upcoming delivery. Nurse : -Let the Patient know the US is a low risk procedure. Will not experience sensation from sound waves.
required. Such as US, amniocentesis, and genetic counseling. ➔ These screening tests are performed between 15-22 weeks of gestation. ➔ Increased levels may indicate neural tube defect, Turner ➔ syndrome, tetralogy of Fallot, multiple gestation, hydrocephalus, omphalocele, gastroschisis. ➔ • Decreased levels may indicate Downs or trisomy 18 ➔ • A test for this protein is usually performed b/w 15 and 18 ➔ weeks' gestation Nuchal translucency screening Noninvasive (US) Assessing for fluid accumulation in the subcutaneous space between the skin and the cervical spine of the fetus. ➔ Any abnormalities in this fluid could be indicative of congenital abnormalities such as trisomy 13, 18, 21; turner syndrome, heart deformities, or physical deformities. ➔ The FNT test is considered abnormal when it is 2.5 mm > in the fluid space. ➔ Test performed between 10-14 weeks gestation. Amniocentesis More invasive - transabdominal puncture of the amniotic sac to obtain the amniotic fluid for analysis. ➔ Performed to detect chromosomal abnormalities, and several hereditary metabolic abnormalities in the fetus before birth. Nurse: It is a risky procedure so inform the mother. Could be bleeding, infection, pregnancy loss, fetal needle injuries. Performed in the second trimester 15- weeks gestation). -Not a routine test, done as a follow up from genetic screening abnormalities. ● H ave a patient empty the bladder to reduce the risk of bladder puncture. ● L et her know we will be performing a 20 minute electric fetal monitoring strip before and after. ● A dminister RhoGAM after the procedure ● A ssess maternal vital signs and fetal HR every 15 minutes after procedure for 1 hour. ● O bserve puncture sites for bleeding or drainage. ● A dvise clients to monitor the site for b leeding, f ever, l eaking amniotic fluid, v aginal bleeding, u terine contractions, or any changes, Increase or decrease in fetal activity. Chorionic villus sampling (CVS)-EXAM Invasive procedure done by using an 18 gauge needle. Goes through the placenta or cervix to aspirate some of the chorionic fluid ➔ Invasive test to assess for chromosomal abnormalities. Such as down syndrome, cystic fibrosis, hemophilia, taysac disease, sickle cell anemia ➔ Performed at weeks 10-13. ➔ Will be done transabdominally or transcervically. For 15 minutes. Nurse: Instruct patients to watch for signs of c ramping, f ever, and v aginal bleeding. No strenuous activity for 48 hours. -Assess fetal activity -Administer RhoGAM. Nonstress test Used to assess fetal wellbeing. Done if mother complains of decreased fetal movement or if mother has high risk with: diabetes****. Intrauterine growth restrictions, preeclampsia, postterm pregnancies, kidney disease, multiple fetuses. It is performed routinely about twice weekly for about 28 weeks ➔ Uses external monitors to assess fetal heart rate in relation to fetal movement. ➔ Test is Reactive or nonreactive Reactive at least 2 fetal HR accelerations from the baseline of at least 15 bpm in 15 seconds within a 20 minute recording period. Non reactive test = absence of at least 2 fetal HR accelerations within 20 minute period. ○ Reactive = good fetal well being. ○ Nonreactive = additional testing needs to be performed such as a Biophysical profile. Nurse:
● R eturn of first-trimester discomforts ● S hortness of breath and dyspnea ● H eartburn and indigestion ● D ependent edema (encourage them to elevate and elastic stockings) ● B raxton Hicks contractions- Painless irregular contractions that occur without dilation. NOT true labor. Tell mom these are normal and teach difference between true labor and braxton ➔ True labor: They are longer, stronger, and become more closer together at regular intervals- Walking will strengthen true labor contractions ➔ Braxton- They tend to decrease in intensity and taper off- Tell mom to drink lots of water because dehydration can trigger braxton contraction- Lie on the left side when resting to relieve discomfort- Breathing techniques ex, Lamar's technique to help ease some of the discomfort NURSING MANAGEMENT TO PROMOTE SELF-CARE ● Personal hygiene - They sweat a lot, and should shower daily. Baths in a tab are okay for early pregnancy, but as pregnancy progresses showers are safer. ● Avoidance of saunas and hot tubs -they can increase mom’s temp and cause tachycardia. ● Perineal care- Increased discharge is normal- encourage loose underwear Dental care -Let dentist know so no xray ● Breast care- cotton bras, hygiene, loose clothing ● Clothing- Loose fit cotton, avoid high heels ● Exercise- caution for women with preterm labor, poor weight gain, anemia, edema, dizziness , SOB multiple gestation, decreased fetal activity, cardiac disease ● Sleep and rest- enough sleep to promote performance during the day. Feed on a regular schedule, go to bed and wake up at the same time ● Sexual activity and sexuality- Flactuations are normal and sex is okay unless there is a risk for vaginal bleeding, placenta previa, risk of preterm labor, premature rapture of membranes or presence of infx ● Employment - continue to work- watch out for environmental hazards like heavy lifting, ● Travel -It is okay. Second trimester is the best time to travel. Bring pregnancy record in case of an emergency, risk for dvt so be sure to walk a little, calf exercises for circulations, drink water ● Immunizations and medications- It is best to not take any medications during pregnancy. However, if they are being treated for seizures, high BP, asthma or depression. The benefits of continuing meds outweigh the risk for the fetus. Immunizations and medications -*********Avoid live vaccines
for preparing for labor and birth) -Uses your mind as a way to relax your body during labor so that you feel less pain and focus on the baby than the pain Nurse: Remain quiet so you don't break the woman’s concentration
● P aced breathing ● S low-paced breathing ● M odified-paced breathing ● P atterned-paced breathing ● F ocal points ● G uided imagery ● M assage ● Nursing Considerations: ● Remain quiet , so not to break the women’s concentration
Birth Setting: ● Hospital- Anyone with high risk pregnancy should go to the hospital Cons: It is loud, strict on who can be with mom, visit and medical model of care. ● Freestanding birthing center - If you don't want to give birth at the hospital and are worried about complications at home. Cons: Need to transfer mom quickly to the hospital in case of an emergency ● Home birth - Natural and requires minimal medical intervention Pros: privacy, comfort, convenience, surrounded by fam Cons: Need to transport mom in case of emergency, limited pain management
● Obstetrician - Doctor who finished a 4 yr residency in obstetrics and gynecology in addition to medical school -Handle high risk pregnancies ● Midwife- Registered nurses who have graduated from a nurse midwifery education prog -They typically care for low risk moms in a variety of settings -Provide prescriptions, childbirth care, prenatal care, postpartum care and well baby ● Doula - Can be hired in addition to midwife or obstetrician -Not responsible for delivering the baby -Provide encouragement, emotional and physical support
● Substantial evidence presented by the AAP shows improved outcomes for breast-fed infants ● AAP recommends exclusive breastfeeding until 6 months of age and continues until 1 year ● Cost-effective, natural, effective in reducing childhood/adult obesity
C heaper, B ondings, S uppress ovulation, L owers risk of breast and ovarian cancer in premenopausal women, weight loss, increase absorption of lactose in the infant, passing on immunologic properties to prevent infx in baby, baby less likely to develop food allergies and constipation, risk for ear infections and respiratory infx is reduced, less likely to be overfed hence reduced risk of adult obesity
outcomes -Support mom as she switches to bottle feeding
OM , d iabetes, a sthma, a topic d ermatitis, r eflux, diarrhea, etc.
types of formulas available, preparation and storage, equipment needed, and positions for feeding -Hold infant closely, support head, communicate during feeding for bonding
● Provide the advantages and disadvantages of both and allow the parents to make an informed decision ● Health promotion/EBP encouraging and educating all women on breast-feeding. Placenta Previa T his is when the placenta either covers or partially covers the cervical os. Cervical os is the opening of the cervix ● Nursing Management of Pregnancy at Risk: Pregnancy-Related Complications: Placenta Previa; p. 698-700 (Maternity & Peds) ●
➔ Maternal VS and uterine contractility (pain scale) ➔ Fetal HR via doppler or external monitor. NEVER introduce anything vaginally can cause increased bleeding ➔ Cardiopulmonary status ➔ Support and education, most woman will require c-section
● For active/excessive bleeding- IV in place for fluids and/or blood transfusion ● Obtain labs (CBC, coagulation studies blood type/Rh) ● Give Rhogam at 28 weeks PRN ● Administer/monitor tocolytic medications, as indicated ● Oxygen at bedside AVOID INTERNAL VAGINAL EXAMS, MAY DISRUPT THE PLACENTA AND CAUSE HEMORRHAGE Don’t forget to review: ● Picmonics: ● Ectopic Pregnancy: ● Signs and symptoms ● Prolapsed Umbilical Cord: ● Conditions to monitor in the fetus ● Indicated for c-section ● Decelerations (and Accelerations) ● Fetal HR accelerations ● True vs. False Labor ● Oxytocin (Pitocin) ● Indications for use postpartum ● Abruptio Placentae ● Signs and Symptoms Lippincott Advisor for Education: ● Group B streptococcal disease of the newborn ● Leading cause of neonatal sepsis ● Shoulder Dystocia: ● McRoberts maneuver ● Most common cause in fetus- macrosomia/increased birth weight ● ● Preterm Labor ● Definition
-Routine S creenings for STIs even if they are asymptomatic -Teach signs and symptoms of STI -D iscourage anal intercourse or use male condom
Women’s Health Care: ● As a woman transitions through life, her reproductive goals will change, and her healthcare needs will change as well. *******It is important to have community-centered care available
● Must have knowledge about common women’s health issues ● Understanding of the scope of women’s health care and be prepared to intervene to prevent problems and promote health
(Maternity & Peds) Types of Contraceptive Methods ● B ehavioral ● B arrier ● H ormonal ● P ermanent *** Key to contraceptive care is that it should be initiated before engaging in sexual activity -People should abstain until they've decided what they want to use ● Considerations : ● E ase of use ● S afety ● E ffectiveness ● M inimal side effects ● “ N aturalness” ● N on Hormonal method ● I mmediate reversibility ● P revention of an unwanted pregnancy must be a conscious decision, made prior to engaging in sexual activity. *******Contraception should be initiated before engaging in sexual activity.
Abstinence- The only guarantee/ most effective way to prevent pregnancy and STIs Fertility awareness- (uncommon/unreliable)- It is a natural method. ➔ The woman is aware when she is ovulating so she either avoids sex or uses protection *****Ovulation occurs at day 1 of the menstrual cycle and the days preceding ovulation are when pregnancy is most likely. Fertility awareness methods: ● Cervical mucus ovulation method - Assess the characteristics of her cervical mucus to determine when she is ovulating - Towards or
Emergency contraception- This is the plan B pill. Should be taken within 72 hrs of unprotected sex. The sooner they are taken the more effective
These can contain: Estrogen, progesterone , or combinations of both They are Monophasic (Fixed dose of estrogen and progesterone) or multiphasic (Alters the amount of estrogen and progesterone in each cycle ★ Must be taken at the same time each day to maintain adequate hormone levels for contraception ★ Progesterone only pills (POPs)- Appropriate for woman who cannot take estrogen ➔ Increased risk of breakthrough bleeding and pregnancy with POPS
These are also hormonal. May be estrogen/progestin combo or progestin-only Depo-Provera MOA: Injected every 12 weeks (Q weeks/3mo) ➔ Works by : Suppressing ovulation and the production of FSH and LH by the pituitary gland ➔ Increases viscosity of cervical mucus which can act as a barrier and causes endometrial atrophy Primary side effect of injectable contraceptives is : menstrual cycle disturbance /Breakthrough bleeding
● Implanted in the arm, subdermal (Nexplanon) and left in place for 3 years. ● They release a slow dose of a highly effective contraceptive method ● Time released method deliver synthetic progestin that inhibits ovulation ● Effective for 3 years , highly effective Side effects: irregular bleeding, headaches, weight gain, breast tenderness, and depression ● Fertility is restored quickly after removal
Hormonal or nonhormonal Copper/paragard( non hormonal )- Inserted through the cervix and sits in the uterus- Acts as a barrier preventing the sperm from entering into the fallopian tube Hormonal - Contains progesterone ● T-shaped device placed inside the uterus ● Inhibition of sperm motility and viability, and change in speed of transport of the ovum in the fallopian tube ● W ill make periods lighter, s horter, and less painful ● Ideal choice for women with heavy, painful periods -ParaGard (nonhormonal, good for 10 years) -Mirena (hormonal), good for approx 5 years -Skyla (hormonal), good for approx 3 years ● M aintenance free RISKS:
Permanent birth control methods -Should only be used by people who don't want any children at all Tubal ligation Sterilization for women ● A laparoscope is inserted; fallopian tubes are grasped and sealed using rings, or ties Vasectomy Sterilization for men ● Usually performed under local anesthesia ● Involves cutting the vas deferens, which carries the sperm
Nursing assessment ● M edical history ● Fa mily history ● O B/GYN history ● P ersonal history (eg smoking) ● D iagnostic testing (Pap smear, STI) ● P hysical exam Considerations: ● M otivation ● C ost ● C ultural and religious beliefs ● C onvenience ● E ffectiveness ● S ide effects ● D esire for children in the future ● S afety of the method ● C omfort level with sexuality ● P rotection from STIs..(only condoms ) ● In terference with spontaneity RELIGIOUS CONSIDERATIONS
Nursing intervention: C lient/couple participation in decision making, C lient education, M isconceptions, M echanism of action; Advantages and disadvantages, danger signs to report