






































Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
Intermediate Accounting 1 Receivables
Typology: Lecture notes
1 / 47

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!








































A formal claim against another that is evidenced by a written promise, called promissory note, or a written order to pay at a later date, called time draft.
Key takeaways:
Feb. 5 Received a 60-day, 10%, P30,000 promissory note from A Company from merchandise sold. Apr. 4 Collected from A Company in settlement of its note dated January 5. Apr. 10 Received a 30-day, 12%, P25,000 promissory note from B Company in settlement of an overdue account. May 6 Received a 120-day, 12%, P45,000 promissory note from C Company in settlement of an account. May 9 B company dishonored its note on maturity date May 30 Collected the amount due from B Company on account of its overdue note. An additional charge for interest at 12% on maturity value from maturity date is also collected. June 30 Fiscal year-end adjustments are made.
May 9 Accounts Receivable 25, Notes Receivable 25, Interest Revenue 250 (25,000 x 12% x 30/360 = 250) May 30 Cash 25,426. Accounts Receivable 25, Interest Revenue 176. (25,250 x 12% x 21/360 = 176.75) June 30 Interest Receivable 825 Interest Revenue 825 (45,000 x 12% x 55/360)
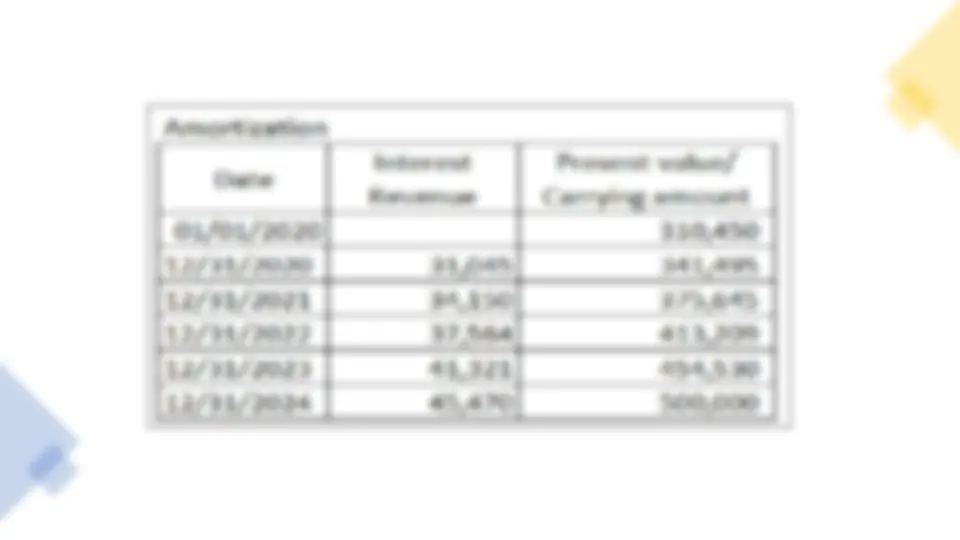
Illustrative Problem: Long-term Interest-Bearing Note with Realistic Interest Rate, one-time payment of Principal On January 1,2020, Toshiba Corp sells a machinery costing P500,000 and with accumulated depreciation of P350,000 as of January 1,2020. The company receives 4-year, P100,000, 10% note. The 10% interest rate is a realistic rate of interest for a note of this type. Journal entries: Jan. 1, 2020 Notes Receivable 100, Accumulated Depreciation 350, Loss on Sale 50, Machinery 500, To record the sale transaction
Statement of Financial Position are presented below as follows at the end of each year: Notes Receivable is treated as current asset if the Notes Receivable becomes collectible within one year from the reporting date. Thus, on December 31, 2022 Notes Receivable is treated as current assets.
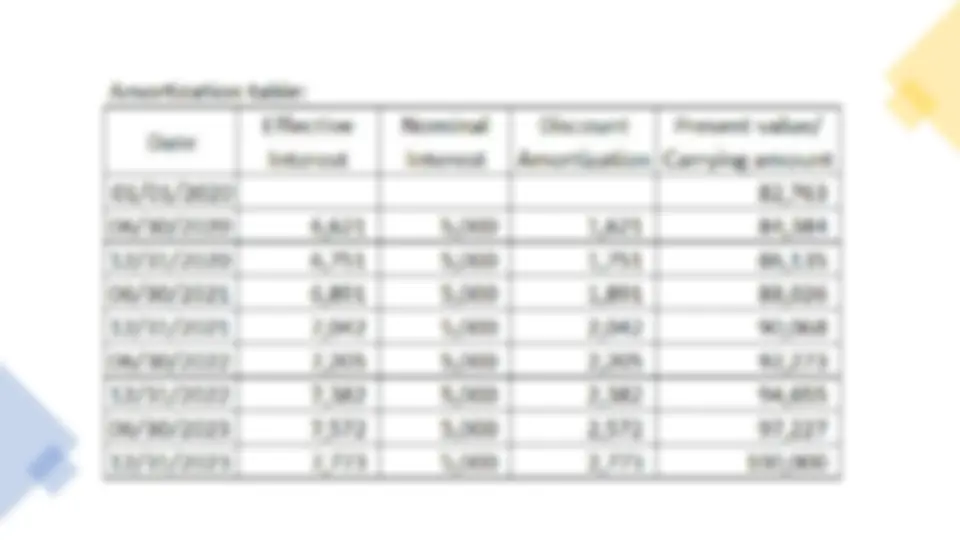
Journal entries: Jan. 1, 2020 Notes Receivable 100, Accumulated Depreciation 350, Loss on Sale 66, Machinery 500, Discount on Notes Receivable 16, To record the sale transaction Dec. 31, 2020 Cash 10, Discount on Notes Receivable 3, Interest Revenue 13, To record the interest due in 2020 and amortization of discount on notes receivable
Statement of Financial Position are presented below as follows at the end of each year: Notes Receivable is treated as current asset if the Notes Receivable becomes collectible within one year from the reporting date. Thus, on December 31, 2022 Notes Receivable is treated as current assets net of Discount on Notes Payable.
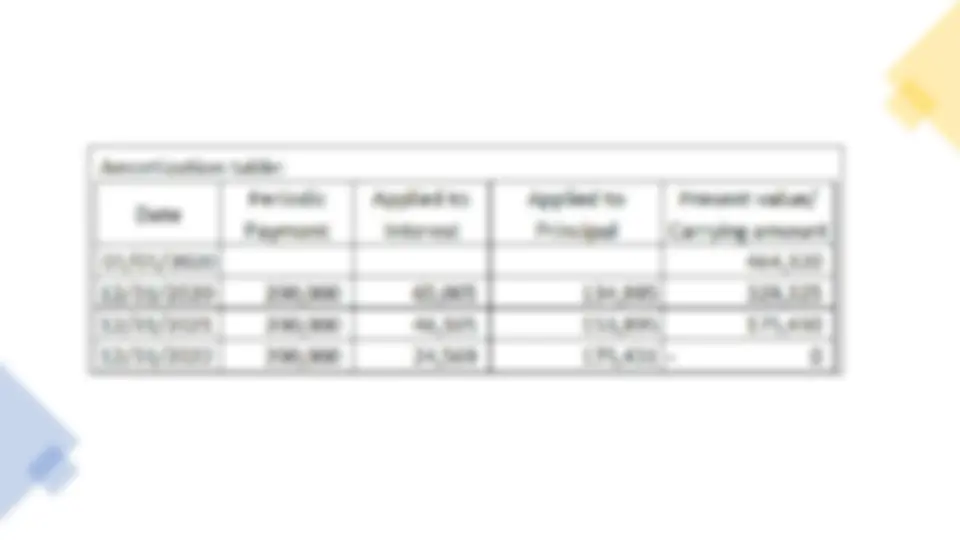
Illustrative example: Long-term Interest-Bearing Note with Unrealistic Interest Rate (Stated rate is higher than Market rate of interest), one-time payment of Principal