






Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
Material Type: Notes; Professor: Farris; Class: Astronomy and Lab; Subject: Astronomy; University: Volunteer State Community College; Term: Unknown 1989;
Typology: Study notes
1 / 12

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!







After the Main Sequence...
Eventually a star will run out of H in its core, so it can't carry out H > He fusion.
Rule of thumb: when the energy output changes in the core, the core compresses and its temperature rises. This causes the surface to expand and cool.
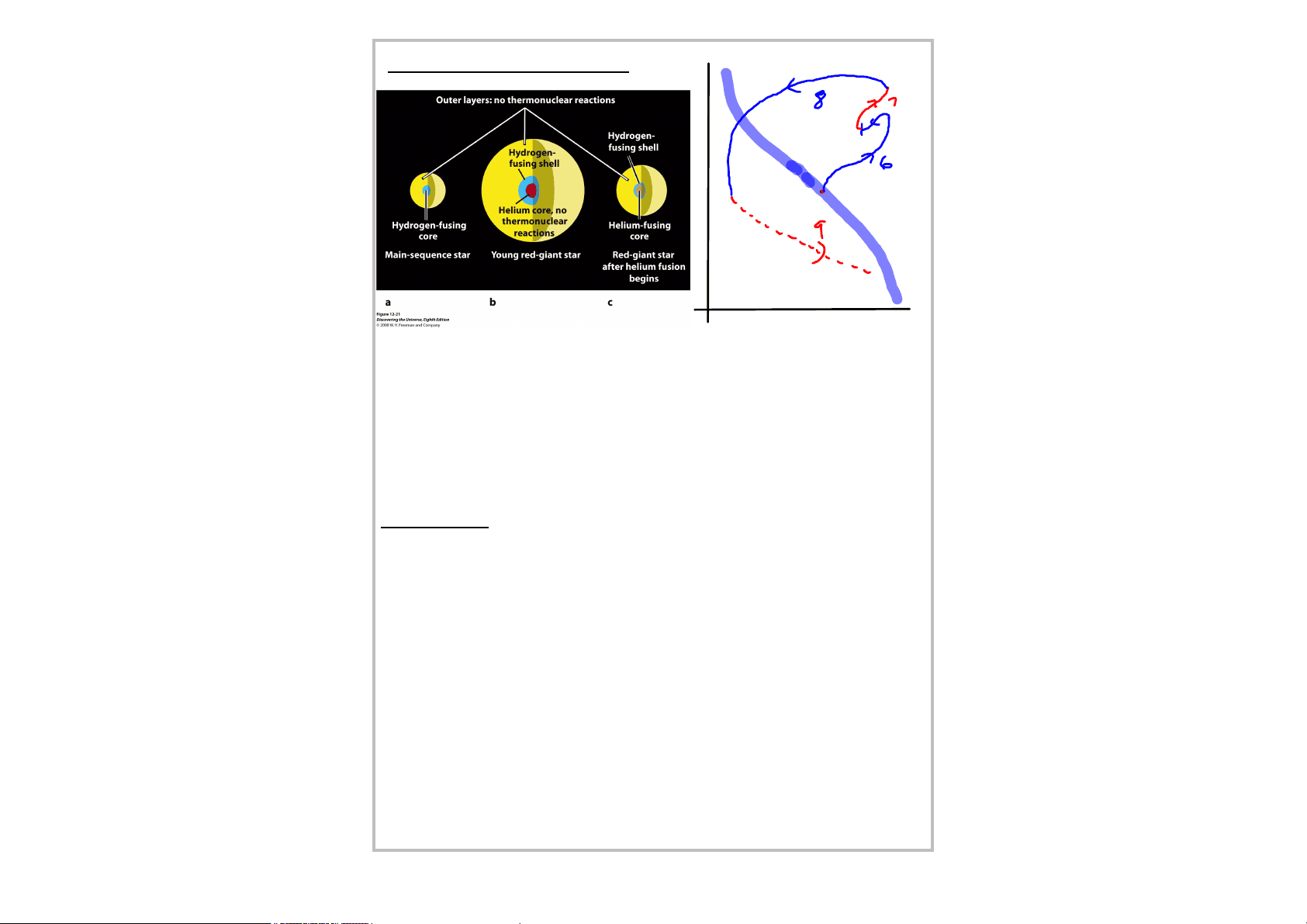
6 Red Giant When the core runs out of H, it collapses and heats up. This increases the rate of H > He fusion in a shell around the core. Eventually the core temperature increases to 100 million K and He begins to fuse into carbon (C) [and C + He fuses into oxygen (O)]. This increase in temp/energy output in the core expands the star's surface, which cools off. The star's surface will be larger, cooler (and redder), and more luminous. surface temp: decreases to ~ 4000 K, then increases to ~ 5000 K size: increases to ~ 100 x Sun, then decreases to ~ 10 x Sun lasts ~ 150 million years
Einstein's 2 postulates (starting points to reconcile EM &
laws of motion):
1) The laws of nature are the same for all observers,
regardless of their motion.
2) The speed of light is the same for all observers,
regardless of their motion.
He first worked this out forspecial relativitydifferent
observers are not accelerating relative to each other (but can
be moving). Let's look at some of the consequences of
these assumptions/postulates in special relativity:
The speed of light is an upper limit on all speeds. Space and time are connected "Spacetime" "Length contraction" the length of an object decreases as
it moves faster.
"Time dilation" time passes more slowly the faster you go. ("Twin paradox") mass increases the faster you move
E = mc² > energy = mass x (speed of light)² There is an equivalence between mass and energy. Either can be converted into the other. (Fusion in a star: H > He. The He produced has slightly less mass than the H you start with. The mass that's "lost" is actually converted to energy, and it's the source of the energy of fusion.)
Einstein next worked the consequences of his 2 postulates for general relativity observers can be accelerating relative to each other. It turned out to be a model of gravity.
Consequences: (all the consequences of special relativity apply) Gravity can "pull" light (It doesn't slow the light, but it stretches the wavelengthwe call it a gravitational redshift.) Gravity (or mass) bends spacetime spacetime is dynamicit's part of the process of nature time slows around mass
Measured effect: bending of starlight by the Sun.
Is relativity a theory of "relativism?"
Title: May 21 12:08 PM (10 of 11)
Title: May 21 12:20 PM (11 of 11)