Download Network Types, Protocols, and Devices: Understanding the Fundamentals and more Cheat Sheet Law in PDF only on Docsity!
ASSIGNMENT 1 FRONT SHEET
Qualification BTEC Level 5 HND Diploma in Computing Unit number and title Unit 2: Networking Infrastructure Submission date 25/06/2023 Date Received 1st submission Re-submission Date Date Received 2nd submission Student Name Dinh Viet Trung Student ID GCH Class GCH1110RE Assessor name Nguyen The Lam Tung Student declaration I certify that the assignment submission is entirely my own work and I fully understand the consequences of plagiarism. I understand that making a false declaration is a form of malpractice. Student’s signature Trung Grading grid
P1 P2 P3 P4 M1 M2 D
Summative Feedback: Resubmission
Feedback: Grade: Assessor Signature: Date: Lecturer Signature:
Introduction: Today, the network is an important part of our world. Every social media and technology is connected byinternet and network. So that network is the basic knowledge that we need to know and understand how it works. And in this exercise, we will learn about the positives and negatives of many types of networks. Besides, the impact of network topology and operating principle of network devices will be explained in this exercise. In addition, the interdependence of workstation hardware with related network software willbe analyzed in this exercise. P1. Discuss the benefits and constraints of different network types and standards.
1. Network types:
A. LAN (Local Area Network):
- LANs are a particular kind of network that let computers connect to one another in order to collaborate and share data. LAN is frequently used in homes, offices, and schools since it may be connected through LAN or WIFI cable (wireless).
- Benefits and drawbacks include: Ample bandwidth and quick speed make it suited for seminars and movie screenings... Low price. Simple to set up. Constrained to a narrow region. B. WAN (Wide Area Network):
- Wide Area Networks (WAN) are a class of network that link various geographic
- Benefits and drawbacks include: Average bandwidth level to operate e-commerce apps, services, and programs, making it appropriate for industrial parks, big commercial areas, and high-tech zones... Low price. Difficult to setup. Reasonably low connection limitations.
2. Network standards:
- The rules for data communication that are required for the interoperability of networking technology and processes are defined by networking standards. By allowing diverse vendors to compete on the basis of the quality of their products while remaining compatible with items already on the market, standards aid in the creation and maintenance of open markets.
- At various tiers during data transfer, many standards may be employed concurrently. At each tier, the following common standards are used: Transport layer – TCP, SPX • Network layer – IP, IPX Data link layer – Ethernet IEEE 802.3, X.25, Frame Relay Application layer – HTTP, HTML, POP, H.323, IMAP Physical layer: V.92 (modem), RS-232C (cable) Definition of a network protocol, as well as the protocol's use.
- According to the CompTIA, 2021: A network protocol is an established set of rules that determine how data is transmitted between different devices in same network.
- Purpose of network protocol (CompTIA, 2021):
Essentially, it allows connected devices to communicate with each other, regardless of any differences in their internal processes, structure or design. Network protocols are the reason you can easily communicate with people all over the world, and thus play a critical role in modern digital communications.
- Some common types of protocols. (CompTIA, 2021): Hypertext Transfer Protocols (HTTP): This Internet Protocol defines how data is transmitted over the internet and determines how web servers and browsers should respond to commands. Secure Socket Shell (SSH): This protocol provides secure access to a computer, even if it’s on an unsecured network. SSH is particularly useful for network administrators who need to manage different systems remotely. Short Service Message (SMS): This communications protocol was created to send and receive text messages over cellular networks. SMS refers exclusively to text- based messages. Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP): ICMP protocol is made to send error messages in a network. It works with the IP protocol. It helps to diagnose network communication issues. ICMP is mainly used to determine whether or not data is reaching its specified destination in the best ways. Transmission Control Protocol (TCP): TCP is a connection-oriented reliable protocol. Two devices need to establish a connection before start using TCP and sending the data. It also provides an acknowledgment to the sender device regarding the status of the data being sent. So in case, the sender receives a negative acknowledgment, it resends the data Internet Protocol (IP): Standardized by IEEE in 1974, this protocol is responsible for addressing and fragmenting data packets in digital networks. Its goal is to ensure the successful delivery of packets from source to destination. For this purpose, the IP specifies a format that defines the type of description of data packets called IP datagrams. Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP): This protocol works on IP networks, assigning IP addresses to devices and hosts connected to the network. It also allows them to communicate with each other efficiently. In addition to the IP address, DHCP also assigns the subnet mask, default gateway address, the domain name server (DNS) address, and other pertinent configuration parameters. Domain Name System (DNS): The Domain Name System (DNS) is the phonebook of the Internet. Humans access information online through domain names, like nytimes.com or espn.com. Web browsers interact through Internet Protocol (IP) addresses. DNS translates domain names to IP addresses so browsers can load Internet resources. Some International Standards Organizations and some name of the standards used in Networking:
- Some International Standards Organizations: (jagroopofficial, 2022) American National Standards Institute (ANSI) International Standards Organizations (ISO) Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineering (IEEE)
1. Network Topology:
- Network topology is a method of setting up the network's components and showing how to connect them so that they form a spatial geometric structure.
- Additionally, there are topology kinds including mesh, dual ring, tree, and hybrid. Here are some typical types along with their benefits and drawbacks. A. Star Topology:
- A network architecture known as a star topology consists of all the information nodes connected to a central hub, computer, or switch that serves as the coordination center for the whole system.
- Advantage: Centralized network User-friendly Very reliable Highly efficient Easily manageable No point-to-point connection
Safe to use
- Disadvantage: High cost Everything depends on the central device Highly dependent on the central device High maintenance Prone to damage Wireless systems have low data transfer rates Immobile network system B. Bus Topology:
- Bus Topology is a network topology in which every device is connected to every other device through a bus connection. The device that wishes to communicate with another device must first pass via the Bus before transferring data to the final component in the communication chain.
- Advantage: It is the easiest network topology for connecting peripherals or computers in a linear fashion It works very efficient well when there is a small network Length or cable required in less than a star topology It is east to connect or remove devices in this network without affecting any other device It is easy to understand topology
- Dual ring topology: Only one direction of data flow is possible with a single ring topology since it is half-duplex. By adding a second link between network nodes, ring topologies may be converted to full-duplex.
- Advantage: Equal access to the resources It is cheap to install and expand Minimum collision Easy to manage Speed to transfer the data is very high in this type of topology
- Disadvantage: They were not scalable Total dependence Difficult to troubleshoot the ring Addition and removal of any node during a network is difficult and may cause issue in network activity D. Mesh Topology:
- Mesh topology is a complex and extensive system of linked point-to-point connections between nodes. Full or partial mesh networks are also possible. While full-mesh topologies are unexpected, partial mesh topologies are primarily linked, with a few nodes having just two or three connections. completely linked.
- Full mesh topology: All nodes and devices are directly linked in a complete mesh structure. A topology with a complete mesh increases the type of redundancy. The backbone network employs these kinds of network topologies. Other routes are selected for traffic balancing if there is heavy traffic between any nodes.
High cost Time-consuming to build and maintain High risk of redundant connection Each node has an increased workload E. Tree Topology:
- A network of nodes that is organized hierarchically. causes root nodes and common nodes to become parent-child dependent. If a root node has an issue, this layout may be susceptible to failure. This design employs a lot of cable and is complex and difficult to handle.
- Advantage: Detection of error Sturdiness Easy expansion Device support Low cable requirement
- Disadvantage: Installing tree topology Security Reliability Cost Maintenance
F. Hybrid Topology:
- The tree topology, which combines the bus and star layouts, is an excellent example of a hybrid topology since it combines two or more distinct topological structures.
- Advantage: It is very reliable It is extremely flexible Can be modified as per requirement Handles large volume of traffic
- Disadvantage: It is a type of network expensive Design of a hybrid network is very complex Hubs which are used to connect two distinct networks, are very costly Installation is a difficult process
2. Communication:
- Sending information or a message from a source to a certain destination is referred to as communication. A protocol will control the flow of communication. Every protocol type will be unique to a certain communication type.
- As an illustration, two persons can communicate with one another, but they must all consent to using the same protocol. They must agree on the language they will use if they wish to speak verbally. If you decide to send a message, you must pick a format that the
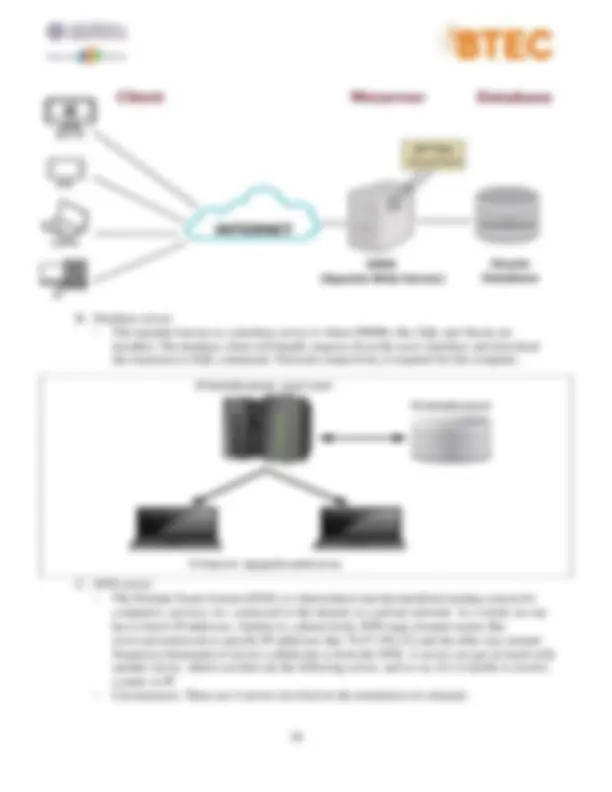
significant for determining how fast a web page loads on a browser use as fast internet connection allows you to download web pages and videos flawlessly, higher bandwidth will effectively improvise the user experience and let your users avail the very best from your website. P3. Discuss the operating principles of networking devices and server types.
1. Networking Device:
A. Repeater:
- Definition: In the first layer of the OSI model, a repeater is a device that amplifies and transmits signals over long distances in a steady manner to assist speed up internet access even in remote areas. The wifi transmission will get stronger and be able to go to devices linked to the modem with the assistance of the repeater, which will aid in amplifying the physical signals in the input.
- Circumstance: They duplicate, amplify, and recover the information-carrying signal on the transmission line with the restriction that the protocol and transmission between the two portions of the network must match.
B. Hub:
- Because it contains between 4 and 24 connection ports and may send signals to many connected devices, the HUB is a device that is referred to as a multi-port repeater. When a transmission is sent to a HUB port, the other hub ports immediately receive it and relay it to previously connected devices.
- Two varieties of HUB exist: Active HUB: Used more frequently and requires electricity to function. All ports save the one at which the signal is received by the active hub relay the data signal. These are independent hubs that may enhance, clean, and transmit data signals across a network. This sort of HUB is utilized to assure signal speed when consumers use it and to magnify the signal to the other hub ports. Smart HUB (Intelligent Hub): transmits data signals from all ports aside from the one at which they are received. It is identical to Active HUB and has no impact on the data stream, but it differs in that there is an additional chip for error detection. C. Bridge:
- The OSI model's second layer has a device called a bridge that combines two smaller networks into one big network. When two computers utilize two distinct networks, a bridge will copy the packet and deliver the data to the machine it needs to receive. Bridge is also capable of managing several information streams concurrently.