



























Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
BIOD 151 Module 5: Problem Set: Essential Human Anatomy & Physiology I w/Lab - Burtt - 2025E Module 5: Problem Set Due No due date Points 5 Questions 75 Time Limit None Instructions Anatomy of the Muscular system: Introduction & Muscles of the Head, Neck and Trunk
Typology: Quizzes
1 / 63

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!
























































Due No due date Points 5 Questions 75 Time Limit None
Anatomy of the Muscular system: Introduction & Muscles of the Head, Neck and Trunk
Attempt Time Score LATEST Attempt 1 440 minutes 2.5 out of 5 Score for this quiz: out of Submitted Jul 3 at 7:59pm This attempt took 440 minutes. Question 1 Name the three types of muscle tissue found in the body. Your Answer: skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, smooth muscle Cardiac, skeletal, and smooth Question 2 What does it mean that skeletal muscles are under conscious control? Your Answer: voluntary muscles attached to bones, control the movement Skeletal muscles are under conscious control, meaning that a person can consciously decide to use these muscles to complete an action. Question 3 What structures are included in the central nervous system? Your Answer: Brain, spinal cord
Brain and spinal cord Question 4 Describe a motor action vs. sensory input in terms of the nervous system. Your Answer: Motor action sends signals from the brain to muscles to cause movement, sensory input brings information from the body to the brain. Messages from the central nervous system to a muscle are called motor actions. Nerves also carry information from the external environment and the muscles to the central nervous system, called sensation or sensory input. Question 5 True or false: The brachial plexus supplies nerves to the lower extremities. True Correct! False Question 6 Describe the difference between tendons and ligaments. Your Answer: Tendons connect muscle to bone and help with movement. Ligaments connect bone to bone and help stabilize joints. Tendons are connective tissues that connect skeletal muscle to bone at each end. Ligaments are connective tissue that connects bone to bone, helping to stabilize joints where bones meet. Question 7 Describe the meaning of muscle origin and insertion. Your Answer: Muscle origin is the fixed attachment point on a bone that doesn’t move during contraction. Muscle insertion is the point where the muscle attaches to the bone that moves during contraction. The origin is the bony site of attachment that is stationary during the movement. The insertion of a muscle is the bony site of attachment that is moved by the muscle contraction.
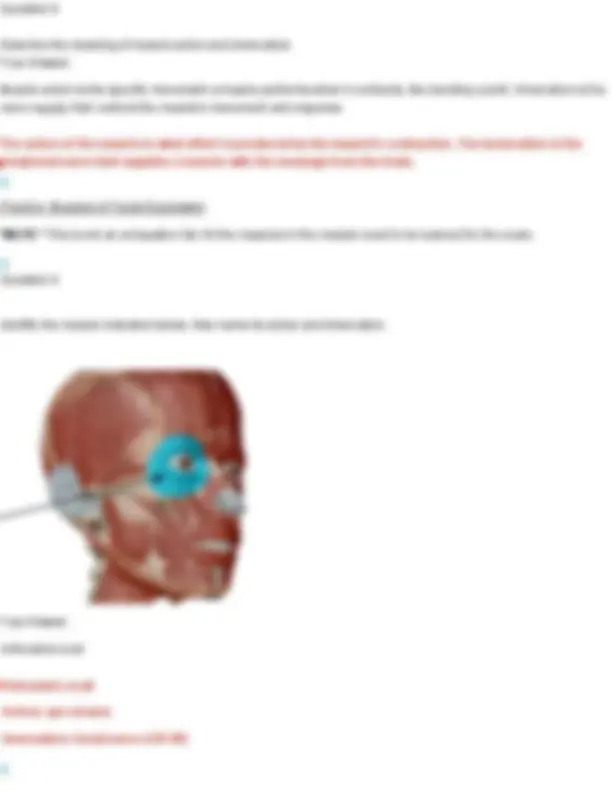
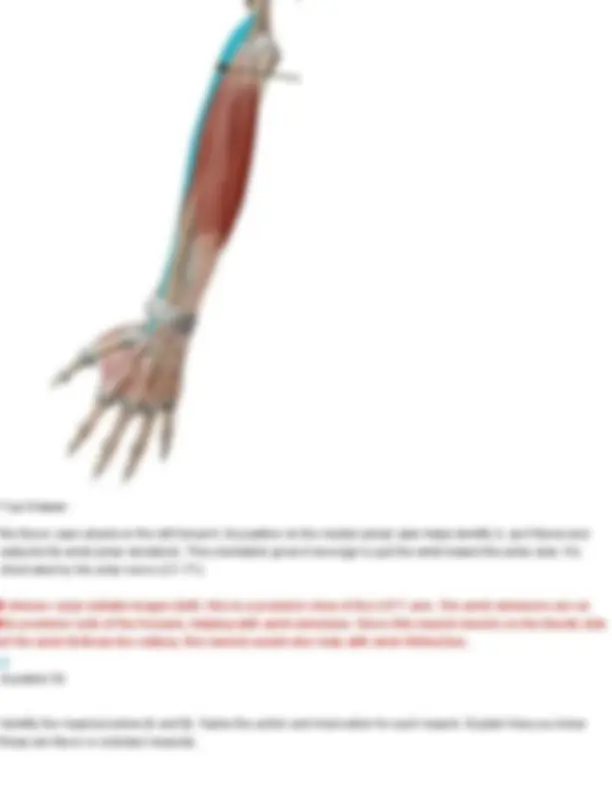
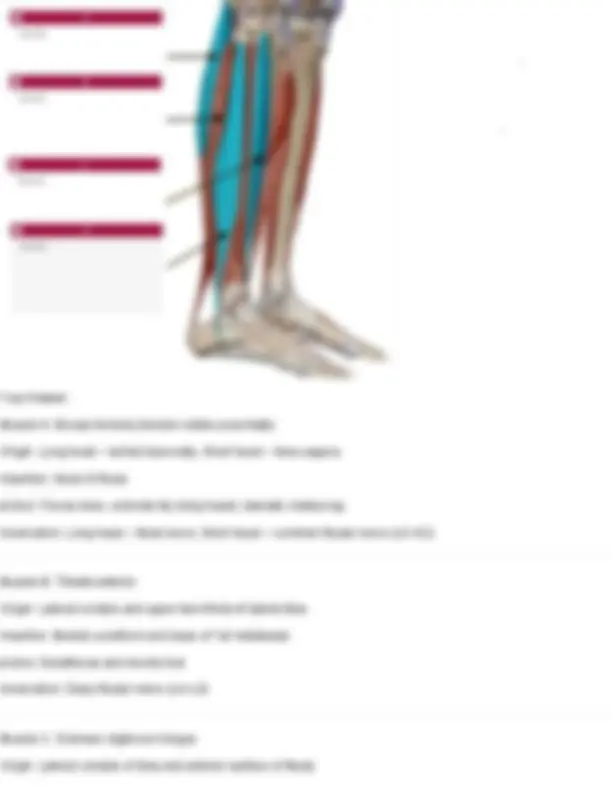
Question 10 Identify the muscle indicated below. Also name its action and innervation. Your Answer: orbicularis oris Orbicularis oris Action: mouth closure: closes lips, protrudes lips forward, presses lips against teeth Innervation: facial nerve (CN VII) Question 11 Identify the muscle indicated below. Also name its action and innervation.
Your Answer: risorius Risorius Action: pulls the corners of the mouth posteriorly (grin or grimace) Innervation: facial nerve (CN VII) Question 12 Identify the muscle indicated below. Also name its action and innervation. Your Answer: occipitofrontalis
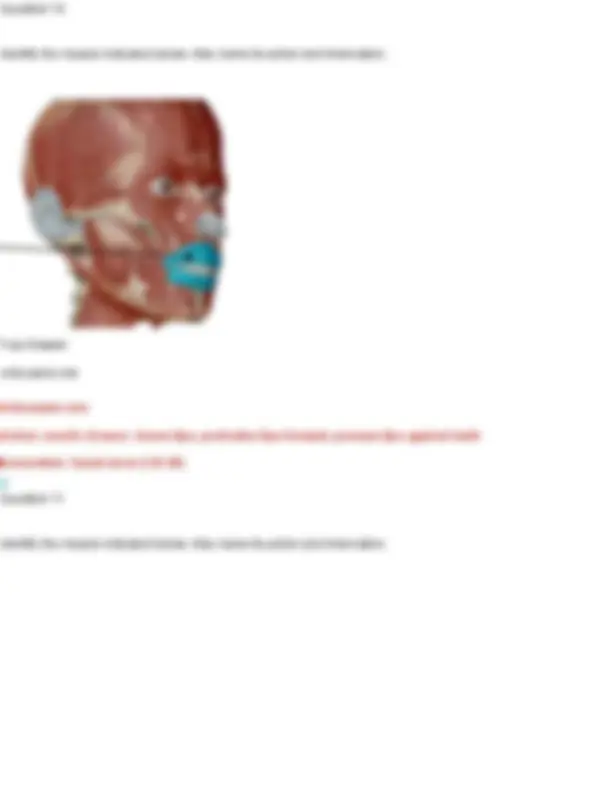
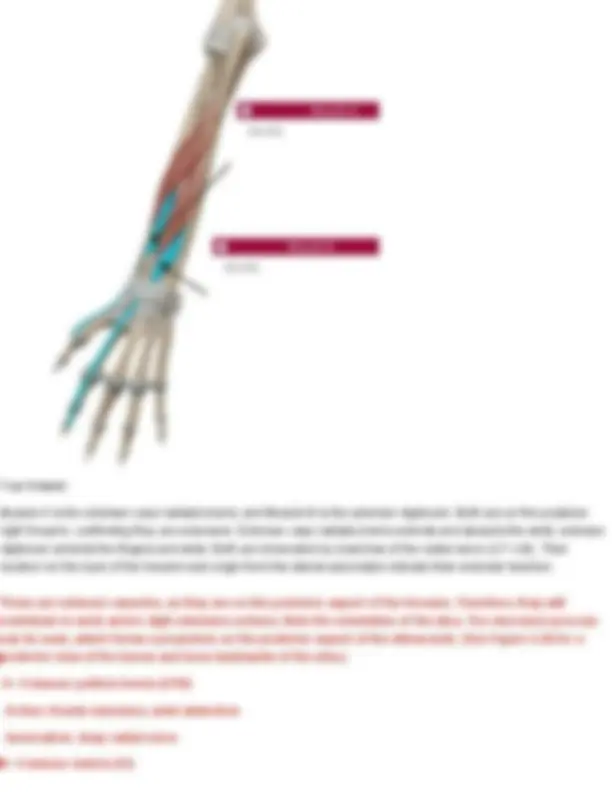
Your Answer: masseter Zygomaticus major Action: pull corners of lips upward Innervation: facial nerve (CN VII) Question 15 Identify the muscle below. Also name its action and innervation. Your Answer: buccinator. Action: Compresses the cheek (as in blowing, sucking, or keeping food between teeth while chewing). Innervation: Facial nerve (cranial nerve VII)
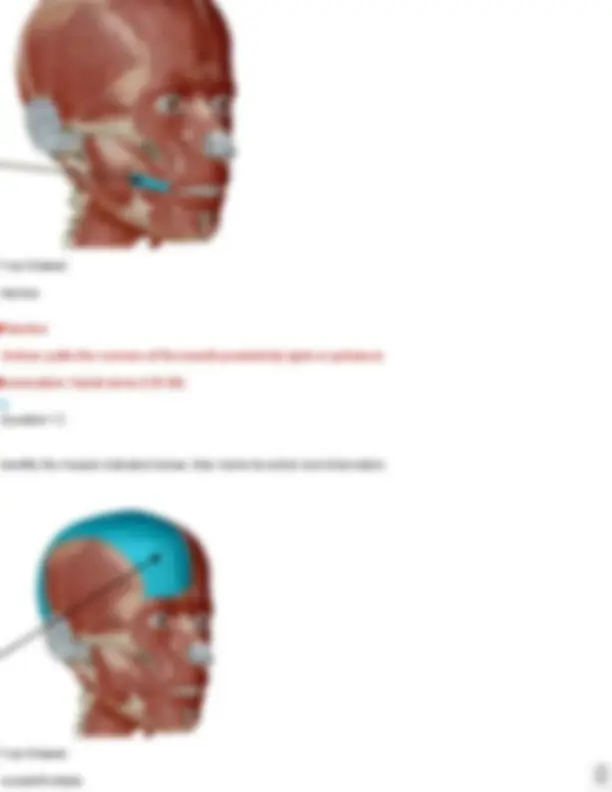
Buccinator Action: compress cheeks Innervation: facial nerve (CN VII) Practice: Muscles of the Head and Neck, Vertebral Column, Abdomen, and Breathing
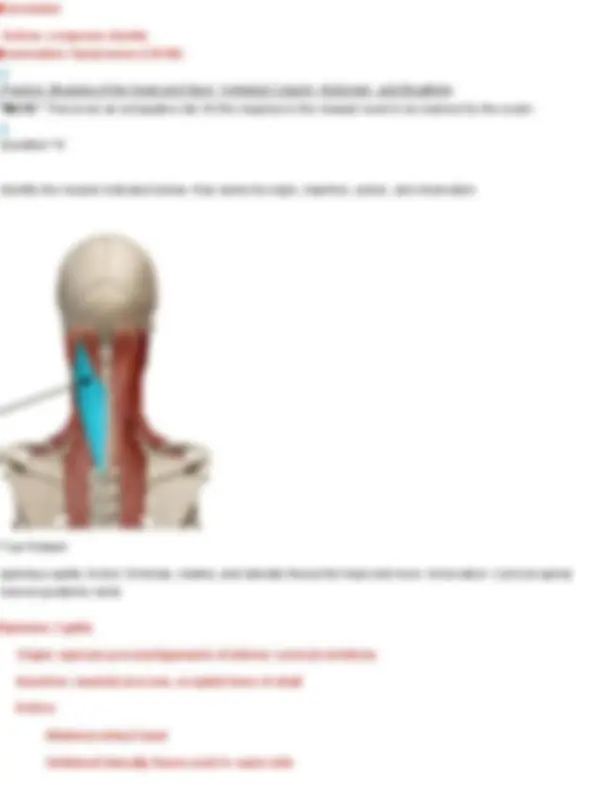
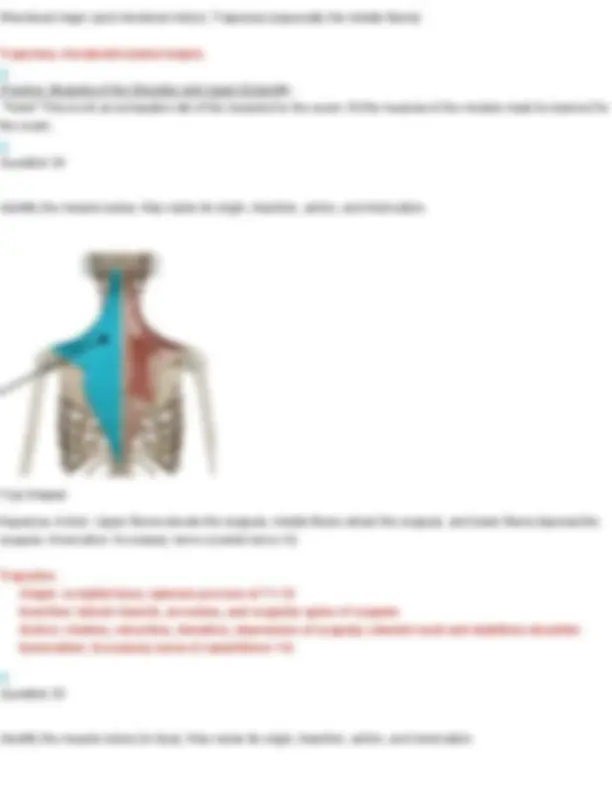
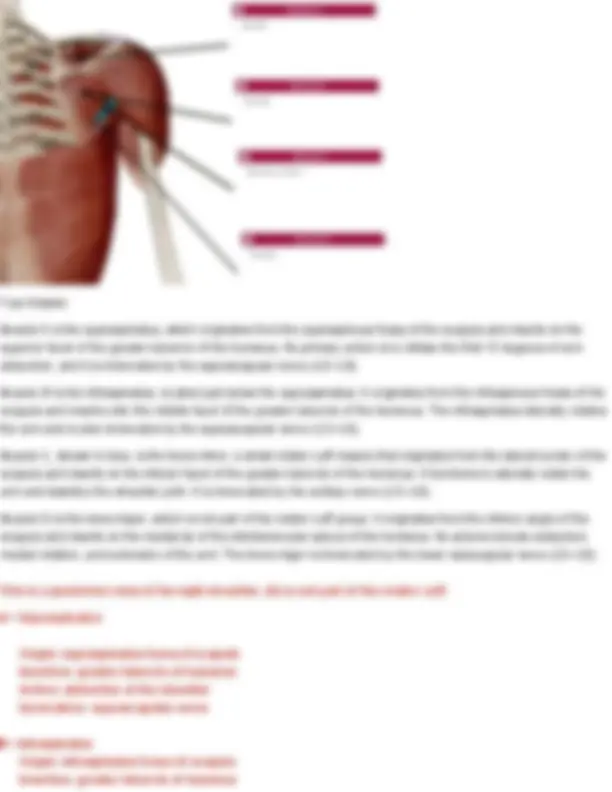
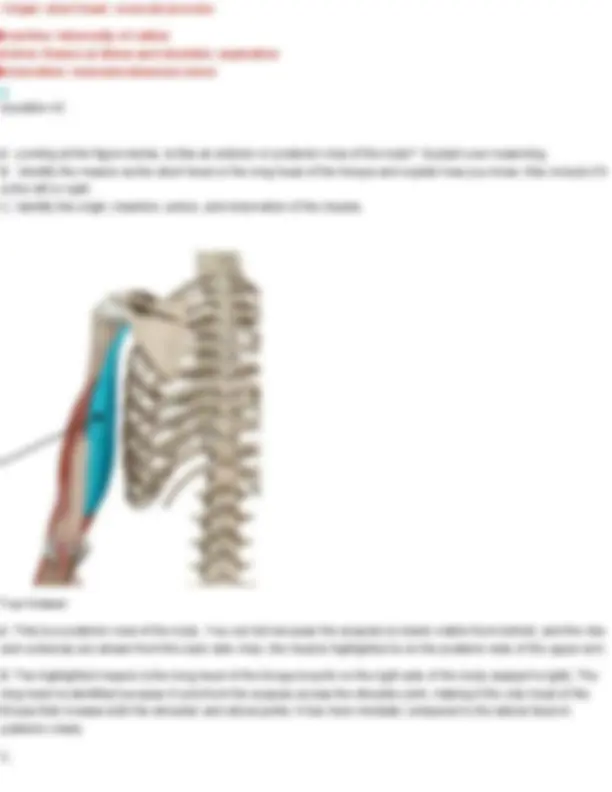
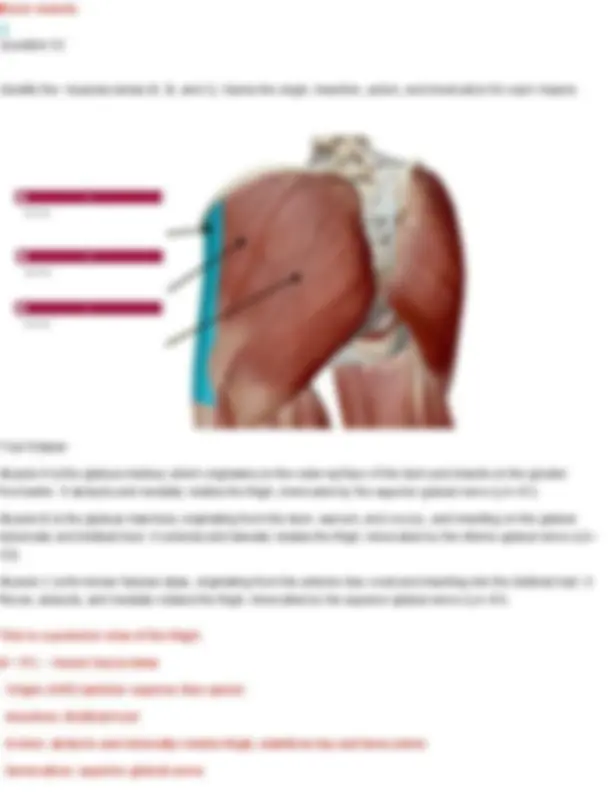
Your Answer: levator scapulae. Action: Elevates the scapula and helps rotate the neck to the same side. Innervation: Dorsal scapular nerve (C5) and cervical nerves (C3–C4) Longissimus cervicis Origin: transverse processes of superior thoracic vertebrae Insertion: transverse process of middle and superior cervical vertebrae Action: Bilateral extend head Unilateral laterally flexes neck to same side Innervation: cervical and thoracic spinal nerves Question 19 Identify the muscle indicated below. Also name its origin, insertion, action, and innervation.
Your Answer: erector spinae. Action: Extends and laterally flexes the vertebral column (helps with posture and standing upright) Innervation: Dorsal rami of spinal nerves Longissimus thoracis Origin: transverse process of all thoracic and lumbar vertebrae Insertion: transverse processes of all thoracic vertebrae Action: Bilateral extension of spine Unilaterally: lateral flexion of spine Innervation: thoracic and lumbar spinal nerves Question 20 Identify the muscle indicated below. Also name its origin, insertion, action, and innervation.
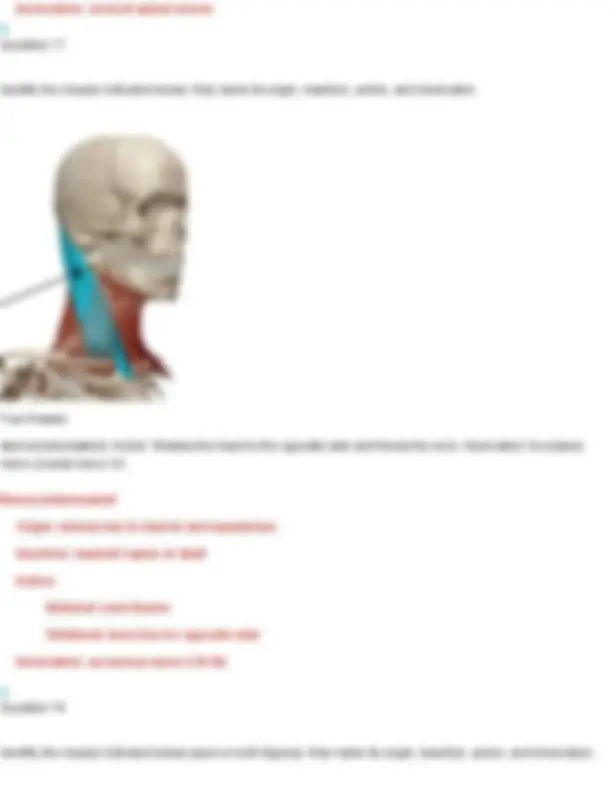
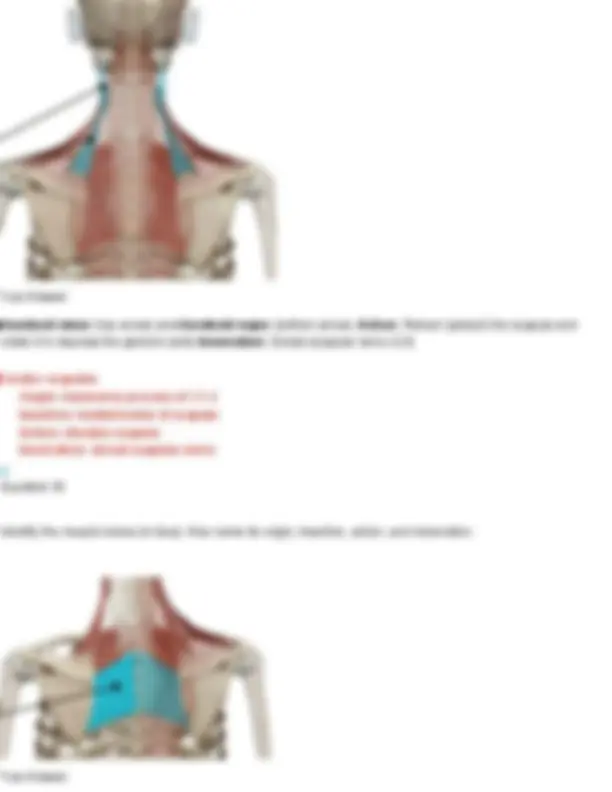
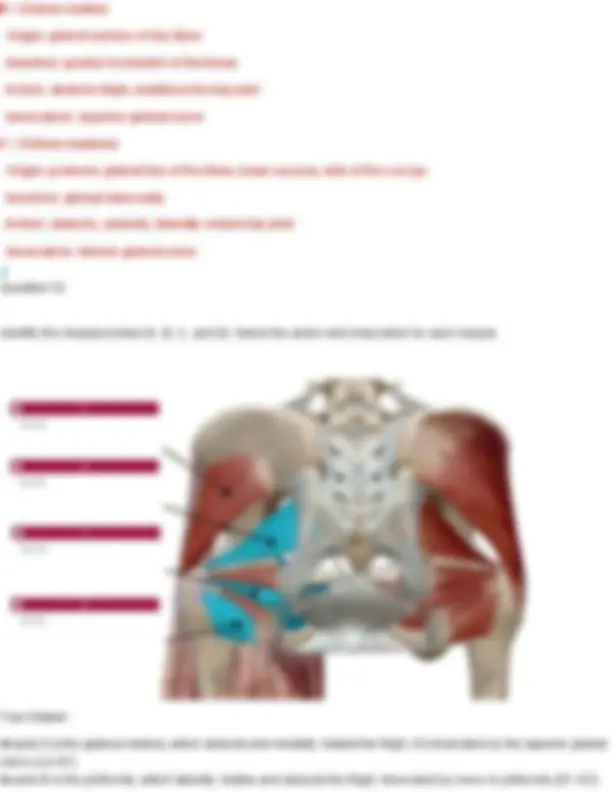
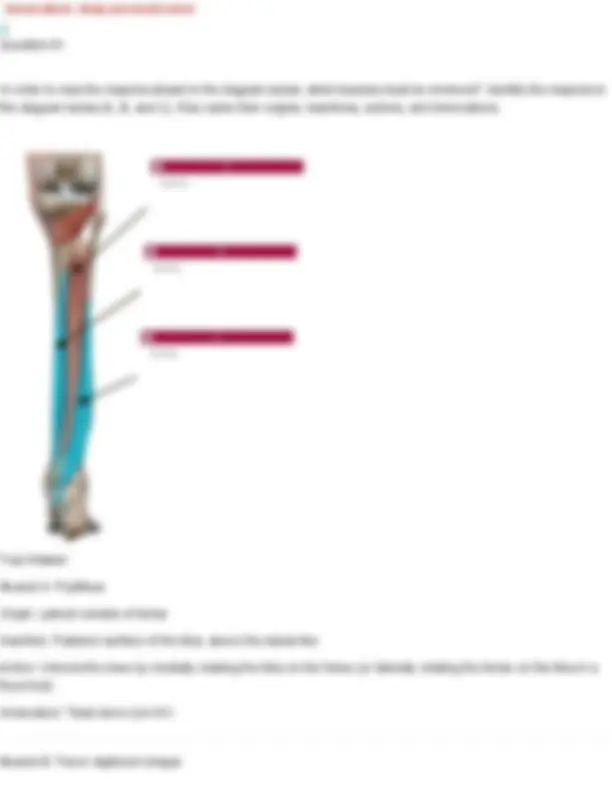
Your Answer: anterior scalene. Action: Elevates the first rib during inhalation and flexes/laterally bends the neck.Innervation: Cervical spinal nerves (C4–C6) Thyrohyoid Origin: thyroid cartilage of larynx Insertion: hyoid bone Action: elevates thyroid, depresses hyoid bone Innervation: hypoglossal nerve Question 22 Identify the muscle indicated below. Also name its origin, insertion, action, and innervation.
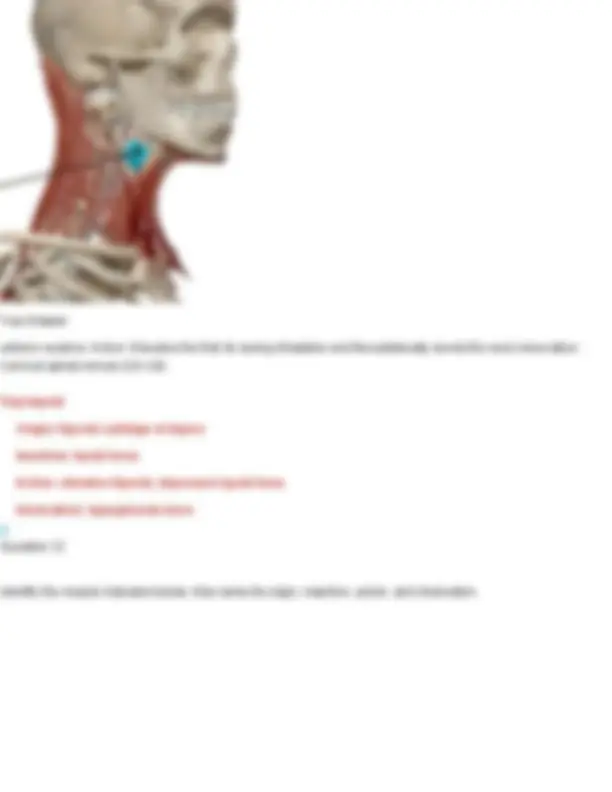
Your Answer: anterior scalene. Action: Elevates the first rib during inhalation and flexes/laterally bends the neck.Innervation: Cervical spinal nerves (C4–C6) Middle Scalenes Origin: transverse processes of C2-C Insertion: first and second ribs Action: elevates ribs 1 & 2 Innervation: cervical spinal nerves Question 23 Identify the muscle shown below of the Erector Spinae group and name its three divisions.
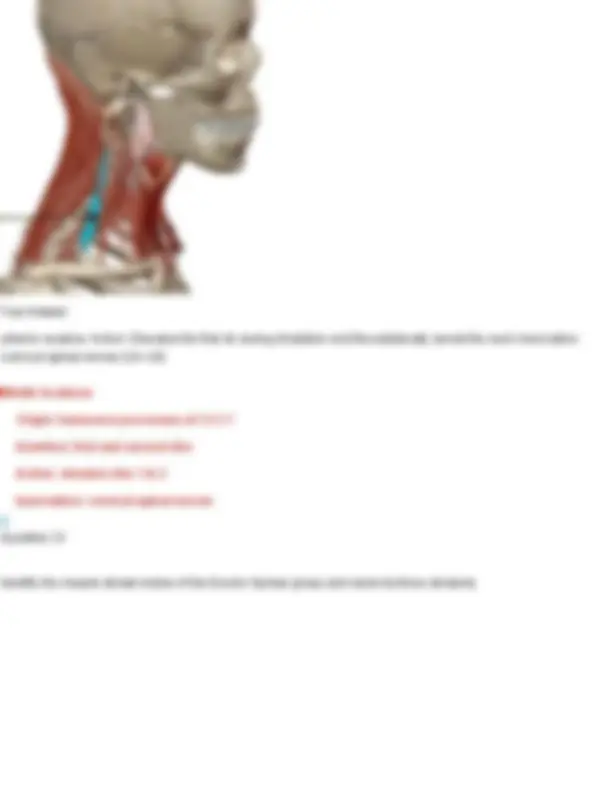
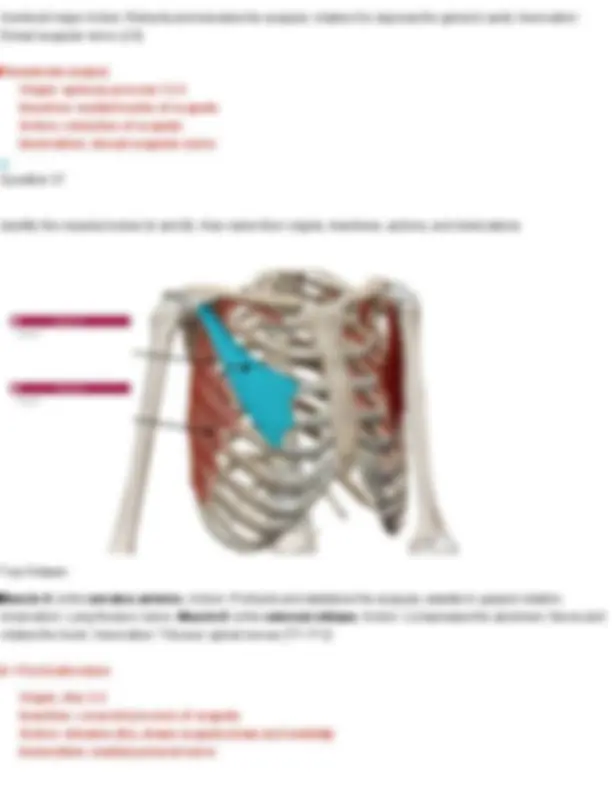
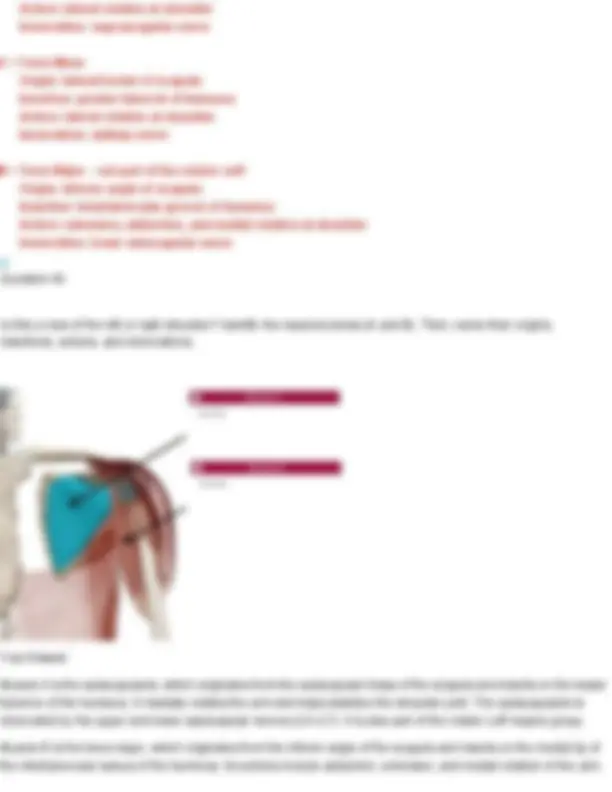
Your Answer: longissimus. Action: Extends and laterally flexes the spine; also helps extend and rotate the head. Innervation: Dorsal rami of spinal nerves Longissimus: Made up of three divisions (longissimus thoracis, longissimus cervicis, longissimus capitis) Question 25 Identify the muscle shown below of the Erector Spinae group and name its three divisions.
Your Answer: iliocostalis. Action: Extends and laterally flexes the vertebral column. Innervation: Dorsal rami of spinal nerves Iliocostalis: Made up of three divisions (iliocostalis lumborum, iliocostalis thoracis, iliocostalis cervicis) Question 26 Identify the muscle indicated below. Also name its origin, insertion, action, and innervation.
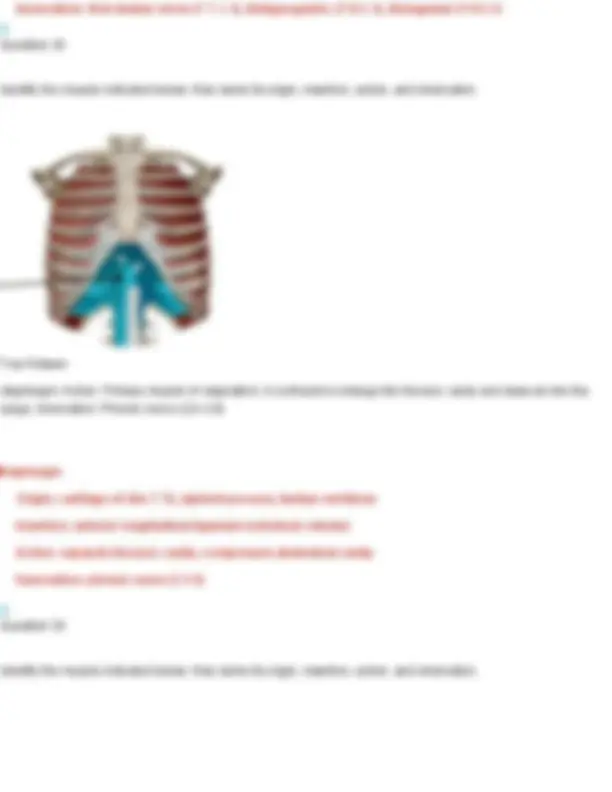
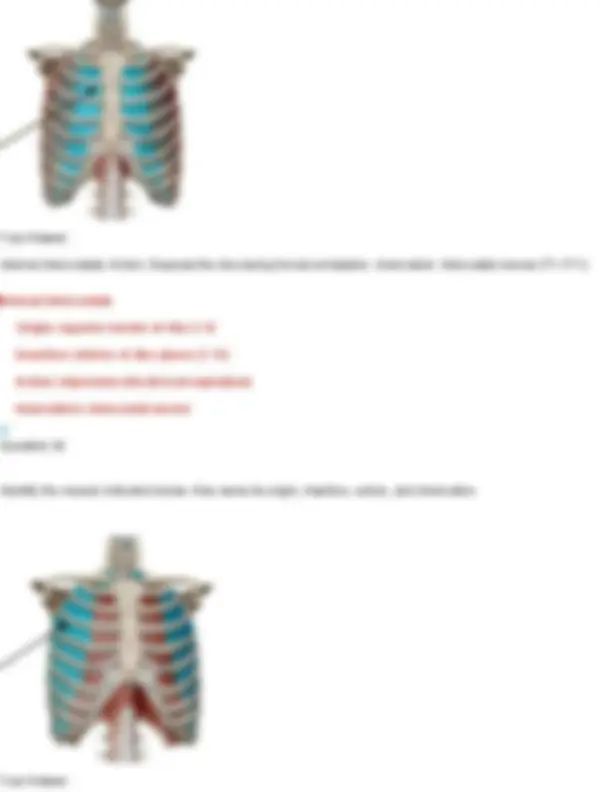
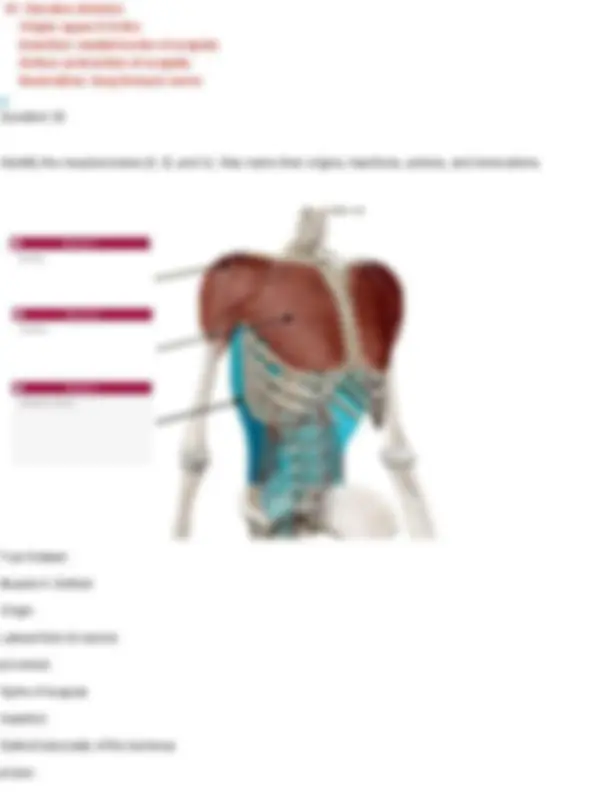
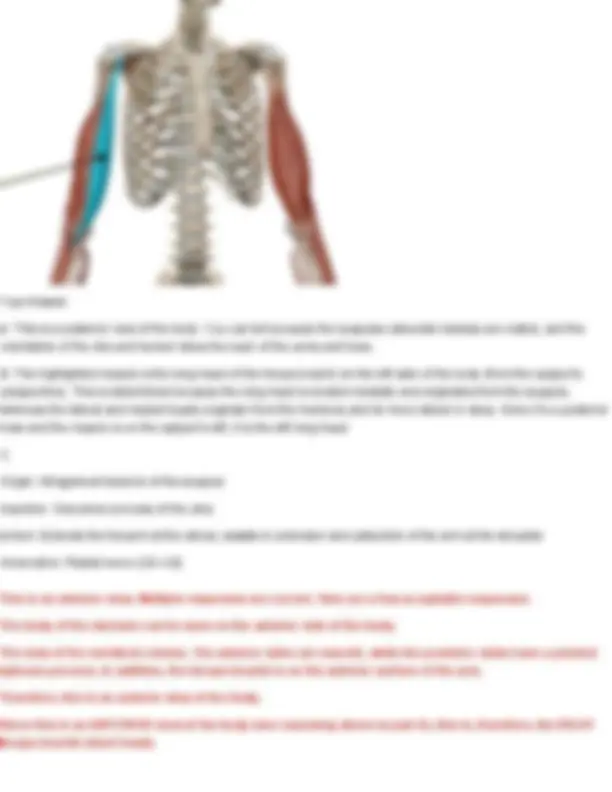
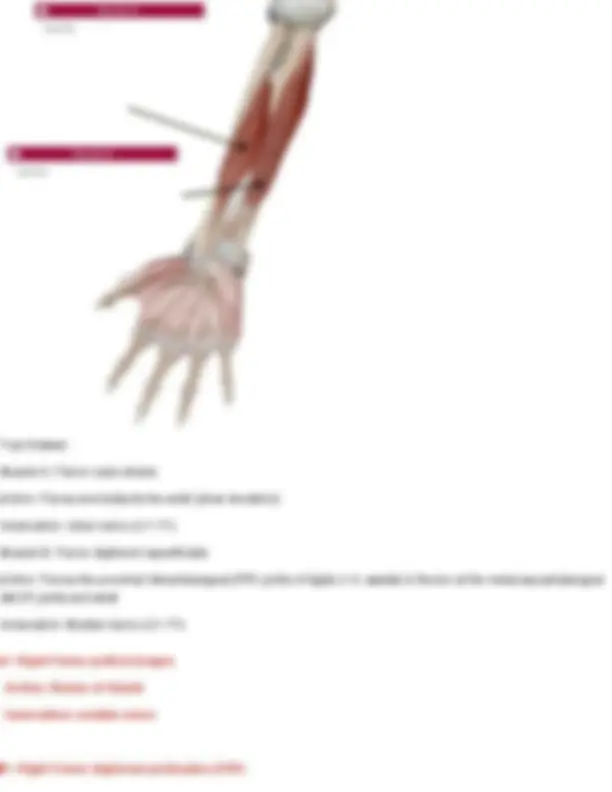
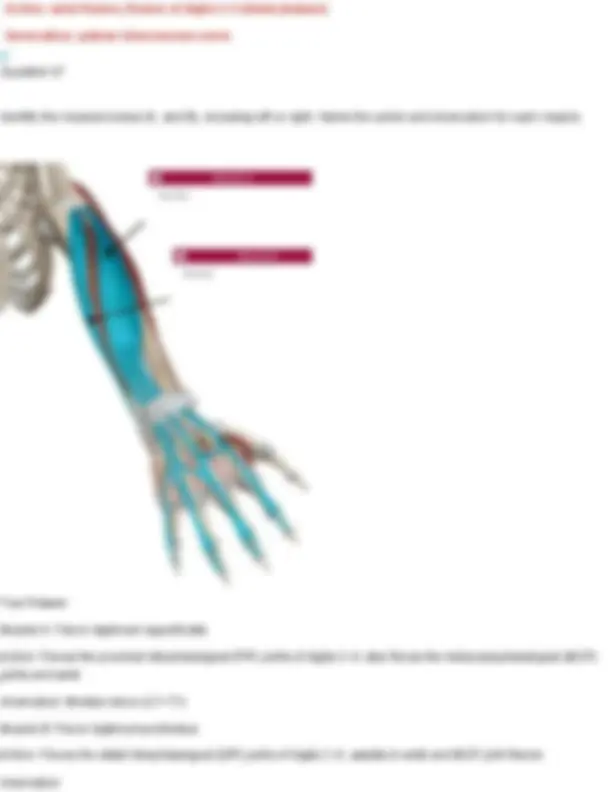
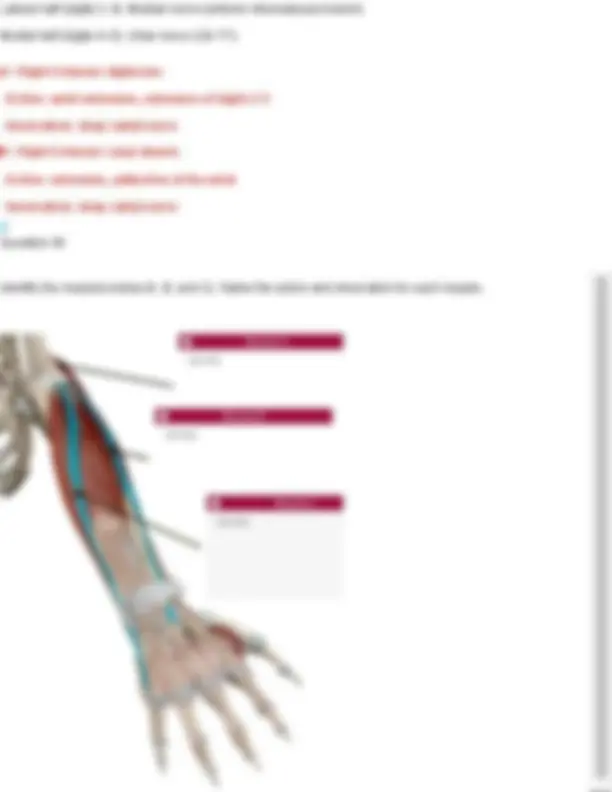
Innervation: first lumbar nerve (T 7- L1), iliohypogastric (T12-L1), ilioinguinal (T12-L1) Question 28 Identify the muscle indicated below. Also name its origin, insertion, action, and innervation. Your Answer: diaphragm. Action: Primary muscle of respiration; it contracts to enlarge the thoracic cavity and draw air into the lungs. Innervation: Phrenic nerve (C3–C5) Diaphragm Origin: cartilage of ribs 7 - 12, xiphoid process, lumbar vertebrae Insertion: anterior longitudinal ligament (vertebral column) Action: expands thoracic cavity, compresses abdominal cavity Innervation: phrenic nerve (C3-5) Question 29 Identify the muscle indicated below. Also name its origin, insertion, action, and innervation.
Your Answer: internal intercostals. Action: Depress the ribs during forced exhalation. Innervation: Intercostal nerves (T1–T11) Internal Intercostals Origin: superior border of ribs 2- 12 Insertion: inferior of ribs above (1-11) Action: depresses ribs (forced expiration) Innervation: intercostal nerves Question 30 Identify the muscle indicated below. Also name its origin, insertion, action, and innervation. Your Answer: