





Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
Main points of this exam paper are: Matrix Multiplication, Bright Lighting, Function Well, Human Eye, Receptor Cells, Wavelengths, Spectral Colors, Primary Colors, Cie Color, Color Space
Typology: Exams
1 / 8

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!





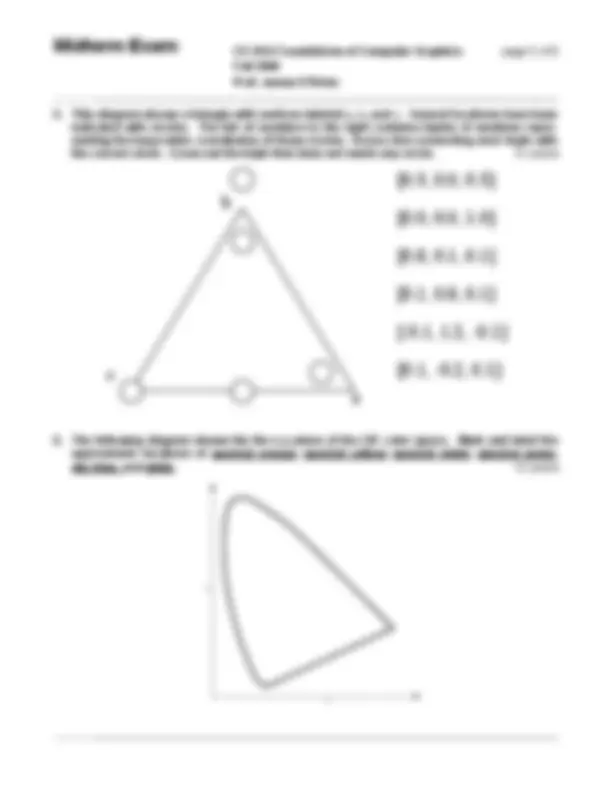
Instructions: Read them carefully! The exam begins at 2:40pm and ends at 4:00pm. You must turn your exam in when time is announced or risk not having it accepted. Make sure you fill in your name and the above information, and that you sign below. Anonymous tests will not be graded. Write legibly. If the person grading the test cannot read something, he/she will simply assume that you meant the illegible portion as a note to yourself and they will ignore it. If you lose points because part of your answer could not be read, you will not be given the opportunity to explain what it says. Be clear and concise. The answers to most questions should be short. If you find yourself writing an excessively long response, you may want to think more carefully about the question. Long rambling answers generally get fewer points that short ones do because there are more opportunities to mark something wrong. You may use one page of notes while taking the exam. You may not ask questions of other students, look at another student’s exam, use a textbook, use a phone or calculator, or seek any other form of assistance. In summary: do not cheat. Persons caught cheating will be subject to disciplinary action. Do not ask questions during the exam. Most questions are unnecessary and they disturb other stu- dents. Figuring out what the exam question is asking is part of the test. If you think you have to make some unusual assumption to answer a problem, note what that assumption is on the test. I have read these instructions, I understand them, and I will follow them. _Your Signature: ____________________________________ Date: ____________________________________ Student ID: ____________________________________ Total Points: XX You Scored: _________ CS 184: Foundations of Computer Graphics page 1 of 8 Fall 2008 Prof. James O’Brien
The mnemonic __________________ reminds people of order of colors in the spectrum. The word __________________ describes two colors that appear the same to the human eye but that have different specular distributions. Bresenham’s line drawing algorithm uses __________________ only arithmetic.
CS 184: Foundations of Computer Graphics page 8 of 8 Fall 2008 Prof. James O’Brien