







































Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
An overview of various types of steel, including their composition, properties, and applications. Topics covered include ferrous alloys, carbon content classification, and the unique characteristics of low carbon (mild) steel, medium carbon steel, high carbon steel, and high speed steel.
What you will learn
Typology: Lecture notes
1 / 49

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!










































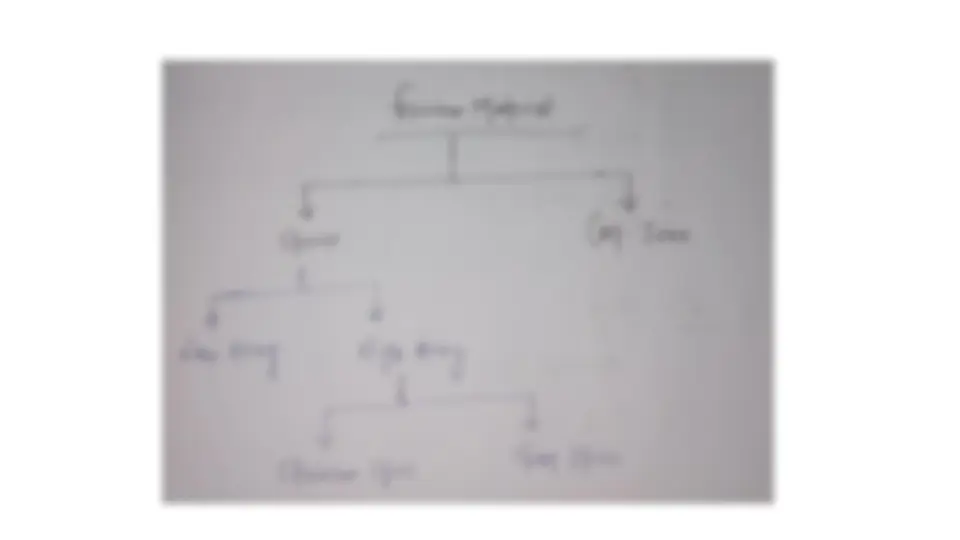
Ferrous Alloy
Steel
is an important constituent because of its ability to increase the hardness and
strength of the steel.
carbon content.
Low carbon steel (mild steel ) less then 0.30 % C
Medium carbon steel 0.30 to 0.70 % C
High carbon steel 0.70 to 2.0 C
When elements like Nickel, chromium, tungsten are present in sufficient quantity,
the steel is called “alloy steel”.
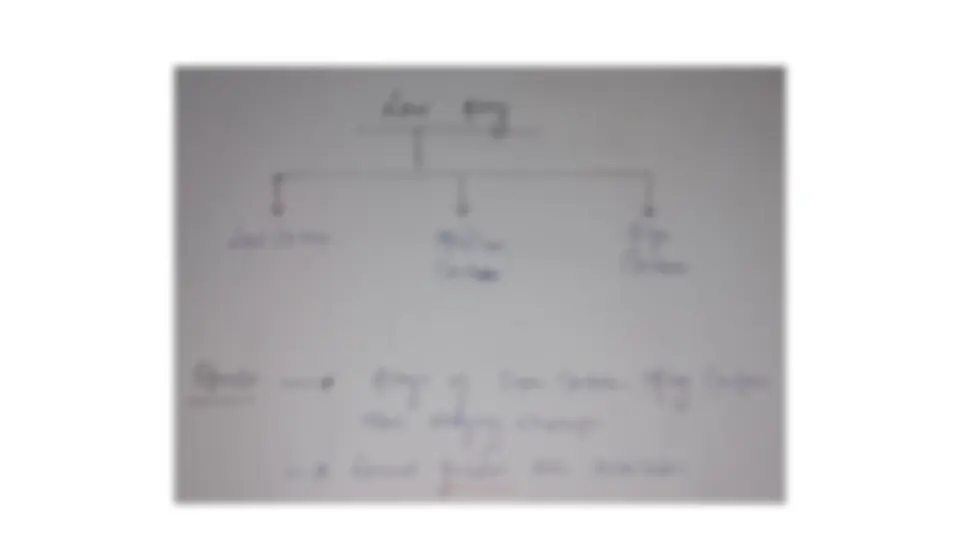
Mild steel
Properties
Application of mild steel
screw machine parts such as screws, nuts and bolts, storage tanks,
automobile frames, sheet.
machined, since the carbon content is low so heat treatment process
is ineffective.
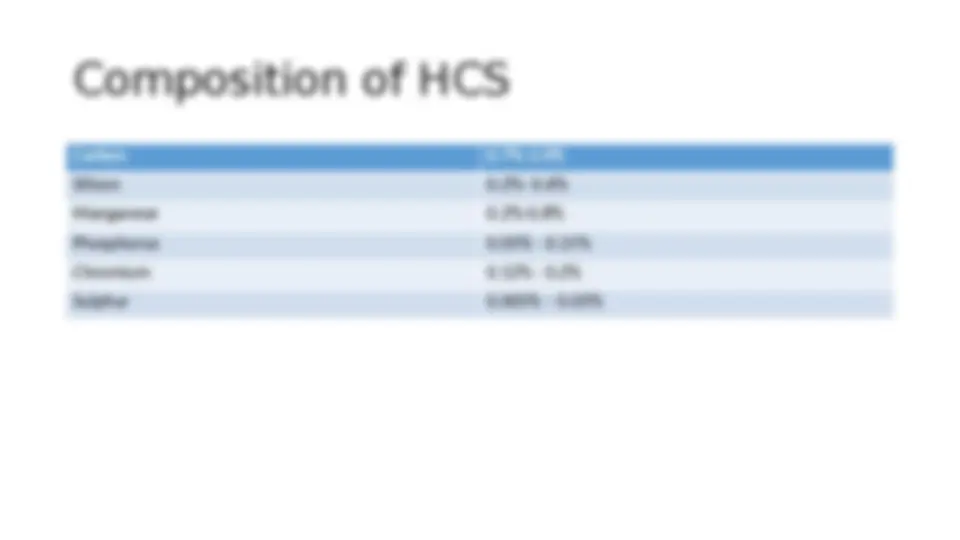
Composition of HCS
Carbon 0.7%-2.0%
Silicon 0.2%- 0.6%
Manganese 0.2%-0.8%
Phosphorus 0.05% - 0.15%
Chromium 0.12% - 0.2%
Sulphur 0.005% – 0.05%
Uses of High carbon steel
drills, taps, hand tools, reamers and for abrasion-resisting properties.
so these are used to make products having high strength and
hardness.
This steel is also used for making product having edges, shear blades
and also for spring wire, wire rope.
High speed steel (HSS)
alloying elements such as tungsten, molybdenum, chromium and
vanadium.
necessary for the tool.
and iron in steel which gives secondary hardening.