






Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
he content of "Living in the Era" would typically encompass various aspects of contemporary life, including: Societal Changes: Discussions on how society has evolved in terms of values, norms, demographics, and social structures. Technological Advancements: Exploration of the impact of technology on daily life, such as the proliferation of smartphones, social media, artificial intelligence, and automation. Cultural Trends: Examination of current cultural phenomena, including pop culture, fashion, music, art, and entertainment. Global Challenges: Coverage of global issues like climate change, pandemics, geopolitics, and economic developments shaping the present era. Lifestyle and Well-being: Insights into modern lifestyles, health and wellness trends, work-life balance, and personal development.
Typology: Slides
1 / 10

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!







Intellectual Property
https://zhillerlaw.com/small-business-intellectual-property-assets/
Why does Intellectual Property matter?
https://www.copyrighted.com/blog/protect-intellectual-property
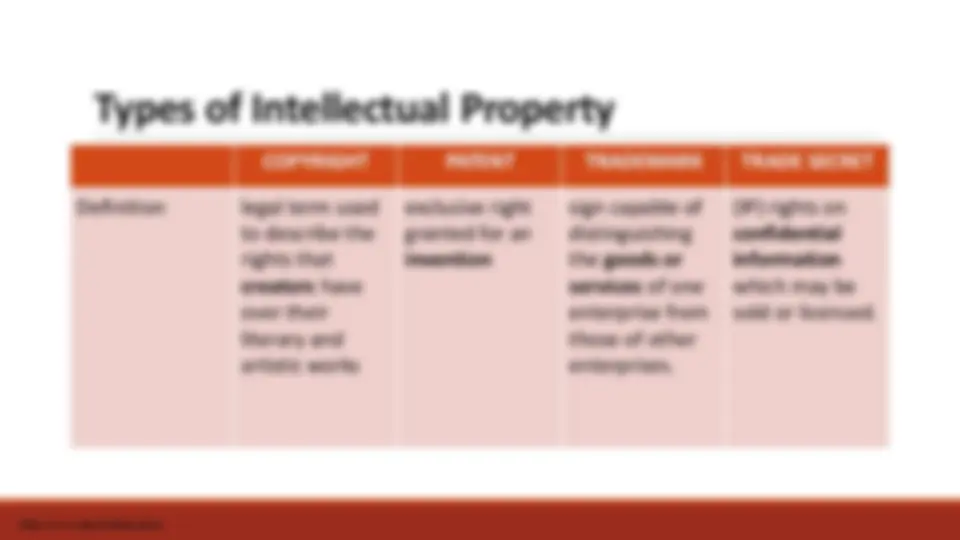
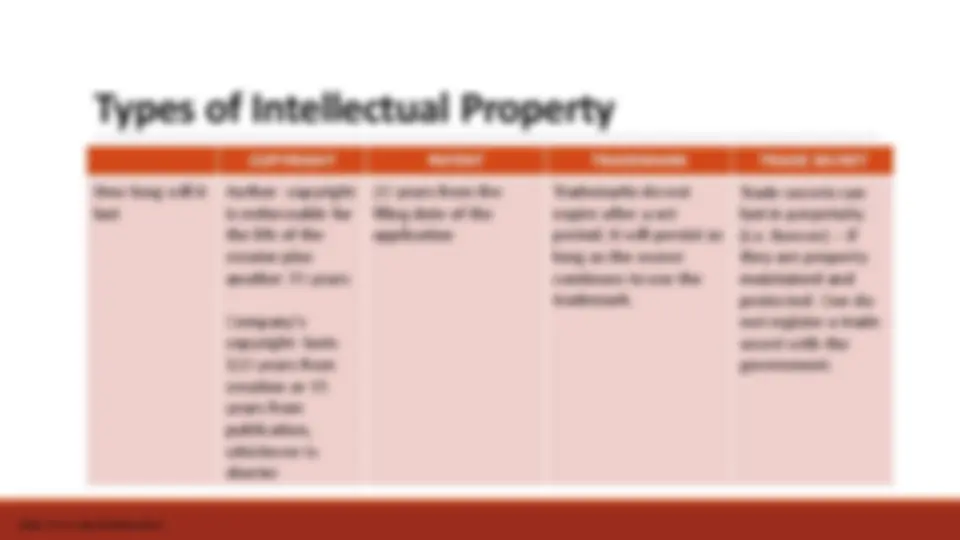
Types of Intellectual Property
https://www.wipo.int/about-ip/en/
Types of Intellectual Property COPYRIGHT PATENT TRADEMARK TRADE SECRET Provided Protection economic rights , which allow the rights owner to derive financial reward from the use of their works by others; and moral rights , allow authors and creators to take certain actions to preserve and protect their link with their work. exclusive right to prevent or stop others from commercially exploiting the patented invention; meaning, the invention cannot be commercially made, used, distributed, imported or sold by others without the patent owner's consent. a trademark registration will confer an exclusive right to the use of the registered trademark ; the trademark can be exclusively used by its owner or licensed to another party for use in return for payment. general concept of protection against unfair competition or is based on specific provisions or case law on the protection of confidential information. https://www.wipo.int/about-ip/en/
Types of Intellectual Property COPYRIGHT PATENT TRADEMARK TRADE SECRET How long will it last Author- copyright is enforceable for the life of the creator plus another 70 years Company's copyright- lasts 120 years from creation or 95 years from publication, whichever is shorter 20 years from the filing date of the application Trademarks do not expire after a set period; it will persist so long as the owner continues to use the trademark. Trade secrets can last in perpetuity (i.e. forever) – if they are property maintained and protected. One do not register a trade secret with the government. https://www.wipo.int/about-ip/en/
“It pays to be original.” https://www.justsaynodeal.com/5-considerations-to-make-before-protecting-your-intellectual-property-for-your-small-business/