Partial preview of the text
Download HNF - HEAD NECK FACE and more Study Guides, Projects, Research Medical Sciences in PDF only on Docsity!
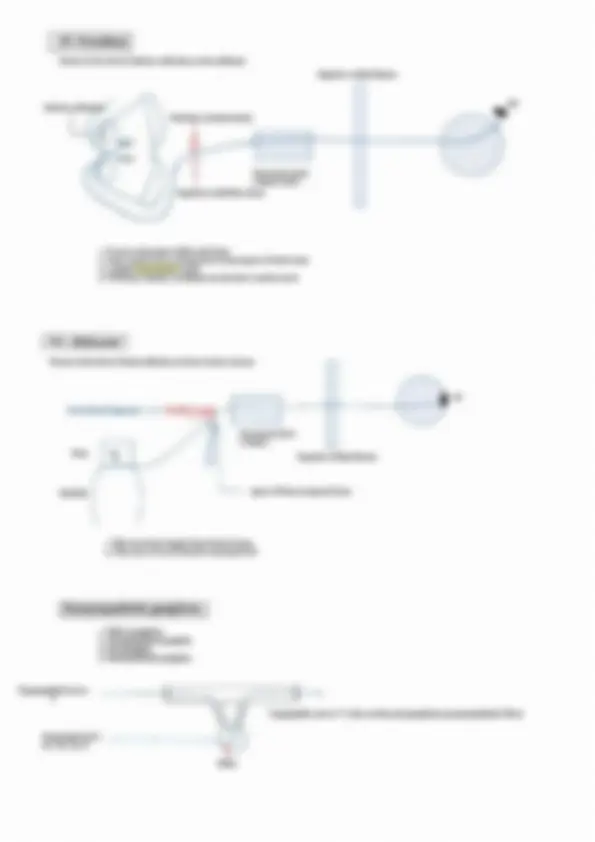
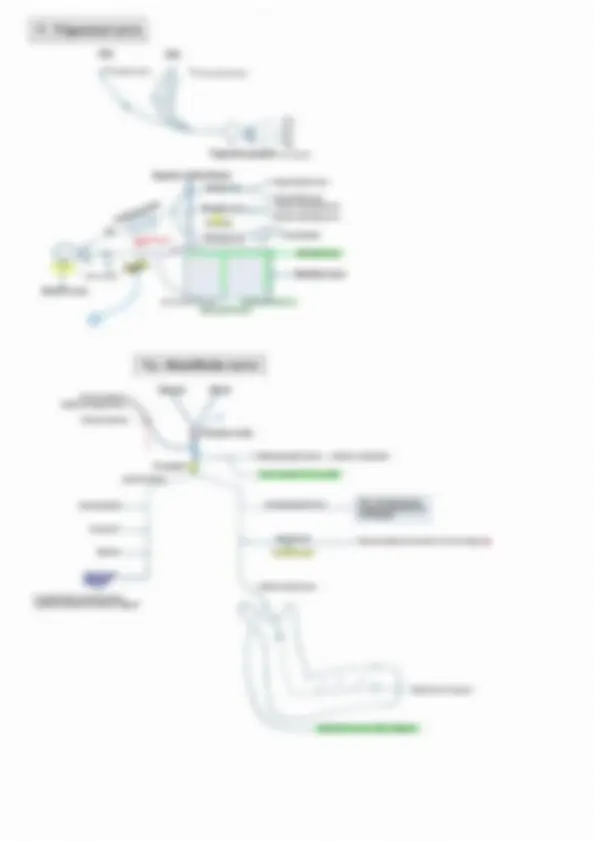
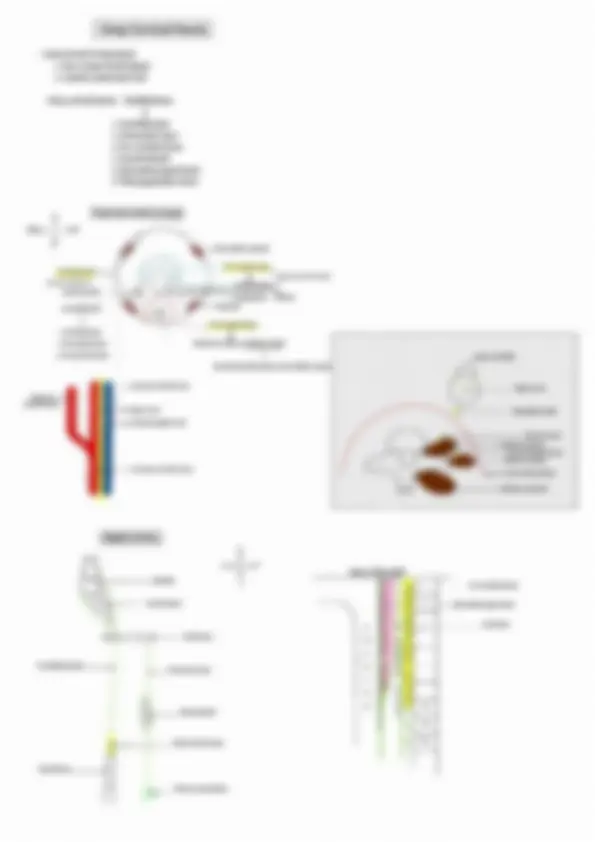
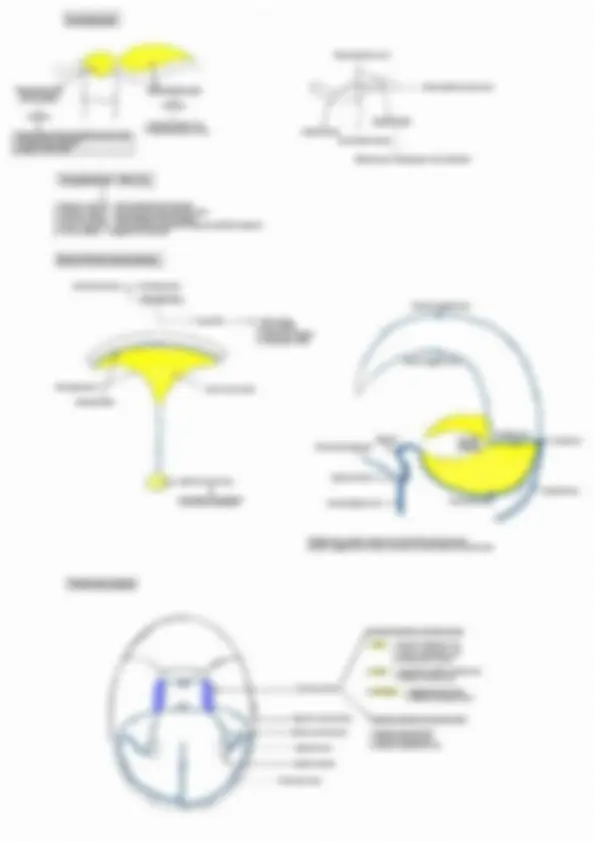
Head, Neck & Face Cranial nerve nuclei & columns Pharyngeal arches 1- V3 - muscles of mastication II - VII - muscles of face Il -1X IV mes - muscles of palate, pharynx, larynx Ve Tongue & EOM are somatic muscles of Head & Neck Neural tube Alar plate - Sensory Sulcus limitans Basal plate - Motor Alar plate GSE - General Somatic Efferent - EOM & tongue muscles ‘SVE - Special Visceral Efferent - Muscles of pharyngeal arches GVE - General visceral efferent - Smooth muscles & Glands GVA- General visceral afferent - General sensation from viscera SVA- Special Visceral Afferent - Taste GSA - General somatic afferent - General sensation from body wall SSA - Special Somatic Afferent ——> Olfaction -I nerve — Nonnuclei E Vision - II nerve — No nuclei Hearing & balance - VIII nerve — vestibular & Cochlear nuclei cse_| sve [ove | ovasva | osa | sma cha ah, ‘Nucleus for jaw reflex: . 7 * i @ V3 Mid brain | 1 |e EWN ‘Mesencephalic nucleus Proprioception , ow iE Pons evI |¢ V3 |eSSN }€— Principle/ chief sensory nucleus - Touch & Pressure evi |oisw A ve V Medula K ms J Spinal nace - Pain & Tempratue a Pan + x |" ‘Trigeminal nerve = 4 nuclei = 3 sensory +1 motor kh eek Node Sete - -L1--- c2 spinal level ‘Muscles of palate & pharynx — Cranial Accessory via Vagus OR Vago-accessory complex Injury to Nucleus Ambiguous — Ipsilateral bulbar paralysis, — Ipsilateral loss of gag reflex EWN ————IIl nee sphincter pupillae & Ciliaris ssn ————Vilnerve _ submandibular & Sunlingual gland, Lacrimal gland sees ttes ISN ———___HXnerve __. parotid gland DNX ———_Xnerve__- smooth muscles & glands of thoracic & abdominal viscera | Parasympathetic cranial nerves Parasympathetic outflow - IIL, VIL, IX, X, $2, $3, $4 Sympathetic outflow -T1 to L2 pseudo IV: Trochlear Presnt at the level of inferior colliculus in the midbrain Superior orbital fissure so Posterior cerebral artery Cavernous sinus (lateral wall ) Superior cerebellar artery 1. IV nerve decussate within mid brain 2. Only cranial nerve coming from dorsal aspect of brain stem 3. Longest intracranial course 4. Thinnest/ slender/ smallest( not shortest ) cranial nerve VI : Abducent Presnt at the level of facial colliculus at lower border of pons Petroclinoid ligament —> Dorello’s canal — Cavernous sinus Cinside ) Pons | VI Superior orbital fissure Medulla Apex of Petrus temporal bone 1. This nerve has longest Intra dural course 2. This nerve is mc involved in increased ICP | Parasympathetic ganglions | 1. Ciliary ganglions 2, Pterygopalatine ganglion 3, Otic ganglion 4. Submandibular ganglion Topographical nerve v Functional nerve IIL, VIL, IX, X V : Trigeminal nerve Superior opbital fissure Frontal nerve 'V sensory tegeminal nocens) 7 ‘Trigeminal ganglion (nar esate) Supratrochlear nerve Nasociliary nerve, Supraorbital nerve ‘Anterior ethmoidal nerve Posterior ethmoidal nerve V3 : Mandibular nerve ‘Nervous spinosus ‘Middle meningeal artery Foramen spinosus Anterior division, Lateral pterigoid >——_| ‘Temporalis ~—_| ‘Masseter >—__} ar It supplies skin & mucosa of cheek, itpierees buecinator but doesn't supply it Sensory tie ganglion ‘Medial pterygoid muscle —, Muscle of mastication / ‘Skin of auricle & temple femporomandibular joint | Parotid gland General sensation from anterior 2/3 rd of tongue I Inferior alveolar nerve ‘Mental nerve ( sensory ) IX: Glossopharyngeal Nerve Medulla oblangata “Tympanic plexus Lesser petrosal nerve ‘Jugular foramen <1} | al ao Nerve of Herrings —>y Foramen ovale Middle ear Otic ganglion —” Stylopharyngeus Carotid body & carotid sim Posterior 1/3 rd of tongue ‘& cireumvalet papillae (General & taste sensation) 4 4 cla i of Summary of parasympathetic ganglion ‘Seeretomotor pathway for parotid gland Inferior salivatory nucleus IXnerve Jacobson's nerve ‘Tympanie plexus Lesser petrosal nerve Otic ganglion ‘V3 Nerve Auriculotemporal nerve Parotid gland Ganglion Topographic nerve Functional nerve Ciliary ganglion Nasociliary nerve (V1) II Nerve Pterygopalatine ganglion Maxillary nerve (V2) Greater petrosal nerve (VII) Submandibular ganglion Lingual nerve (V3) Chorda tympani (VIL) Otic ganglion Mandibular nerve (V3 ) Lesser petrosal nerve ( IX ) X: Vagus Nerve longest Cranial nerve ‘Medulla oblangata t Jugular foramen. Carotid body & carotid sinus '<— Thyrohyoid membrane Cricothyroid muscle ‘Supply mucosa of larynx below voeal cord ‘Muscles of larynx except cricothyroid ‘Muscle of pharynx - Cricopharyngeus partotinfarsonstcor Internal laryngeal nerve - Supply mucosa of larynx above vocal cord '. Galen's anastomoses "XI: Spinal XI — supply Trapezius & Sternocleido mastoid Cranial XI + supply Muscles of palate & pharynx ‘Muscles of palate except TVP ‘Muscles of pharynx except Stylopharynges & ericopharyngeus Middle constrictor Sternocleido mastoid & Traperius XII : Hypoglossal Nerve 4 All muscles of tongue except Palatoglossus Hypoglossal canal ent Only strap muscle not supplied by Anca cervicalis & Geniohyoid ‘Anca cervicalis Sternohyoid Omohyoid Sternothyroid Exceptions 1. All muscles of mastication are supplied by Anterior division of Mandibular nerve (V3) except Medial pterygoid which is supplied by trunk of V3 2. All muscles of palate supplied by Vagoaccessory complex Except TVP which is supplied by Mandibular nerve (V3 ) 3. All muscles of pharynx are supplied by Vagoaccessory complex except Stylopharyngeus ( supplied by IX ) & Cricopharyngeus ( supplied by Recurrent laryngeal nerve ) 4. All muscles of larynx are supplied by Recurrent laryngeal nerve except Cricothyroid which is supplied by External Laryangeal Nerve 5-All tongue muscle are supplied by Hypoglossal nerve except palatogloassus which is supplied by Vagoaccessory complex Investing layer Supraclavicular nerve Suprasternal space Supruclavicular space ‘Bone ossified around nerve (Burn’s Space ) Contents Contents 4 1. External jugular vein Lateral branch 2. Supraclavicular nerves Medial branch Intermediate branch 1, Sternal head of Sternocleidomastoid muscle 2, Interclavicular ligament 3. Jugular venous arch Investing layer - Rule of 2 1. Encloses 2 muscles — Sternocleidomastoid trapezius 2. Encloses 2 Spaces — Suprasternal & supraclavicular space 4, Encloses 2 Glands — Sunmandibular & Parotid gland 4. Forms 2 ligaments ~ Stylomandibular ligament & Sphenomandibular ligament ‘5: Forms 2 pulleys — Diagastrie & Omohyoid Dura & Dural venous sinuses Cranial duramater- Endosteal layer ‘Meningeal layer (> pnral folds ———> 1. Falxcerebra 2. Falk eerebelli 3. Tentorium cerebelli 4, Diaphragma sellae Dural venous sinus ‘venous sinus Inferior saga sus tralght is ‘represent ony meningeal nye Transverse section ‘Superior petrosal sinus Inferior petrosal sinus Sigmoid sinus v Referred pain of diaphragm at tip of shoulder ‘Superior saggital sinus Tnferior saggital sinus Sigmoid Intemal petrosal sinus Jugular foramen —> > Occipital sinus Intemal jugular vein. ‘Straight sinus mainly continuous towards left transverse sinus ‘Superior saggital sinus mainly continuous towards right transverse sinus Incoming channels to cavernous sinus 1. Orbit — 1. Superior Opthlamic vein 2. Inferior ophthalmic vein 3. Central vein of retina 2. Brain — 1, Superficial middle cerebral vein 2. Inferior cerebral vein 3. Meninges — 1. Sphenoparietal sinus 2. Middle meningeal sinus ‘Outgoing channels of cavernous sinus 1. Superior petrosal sinus 2. Inferior petrosal sinus ‘3, Superior ophthalmic vein Jugular foramen ‘Transverse sinus Inferior petrosal vein —— Basilar venous plexus Foramen magnum Spinal cord, ‘Vertebral venous plexus (Batson’s plexus ) Relations of cavernous sinus Optic chiasms Roof Internal carotid artery LISS Uneus | Pituitary gland Lateral relation. Medial relation O Sphenoidal air sinus Foramen lacerumé—— (Floor) Internal carotid artery (ICA) Anterior relation — Superior orbital fissure ( Rupture of ICA aneurysm inside cavernous sinus lead to pulsatile proptosis Posterior relation — apex of petros temporal bone Blood suppl . : Anterior ethmoidal artery Anterior cranial fossa supplied by all 3 branches of V nerve <— Ophthalmic artery <— Internal carotid artery Posterior ethmoidal artery Internal carotid artery “Accessory meningeal artery’ »Maxillary artery <— External carotid artery Middle meningeal artery ‘Meningeal branches of ascending pharyngeal artery VII, IX, X, XID C1, Ca, C; p “__.ertebral artery < ‘Subclavian artery Venous drainage of face Supratroclea &eupraotital veins —, ‘Superior ophthalmic vein Angular vein Posterior Auricular vein Facial vein Posterior division —— External jugular vein Internal jugular vein <— Subelavian vein Subelavian Artery 1 1 om Scalenus anterior Supplies toate and nena pace focervical artery Vertebral artery. Dorsal scapular artery Presont nf Deep yh frases cae arey abet Internal thoracic artery Inferior Thyroid artery , Deep brancit Thyrocerveal trunk Tranwverse mit atom cplar len Superficial branch. ‘Triangles of neck Trapezius Posterior Triangle ea 1. Occipital triangle Posterior belly of digastric 2, Supraclavicular triangle ( Subclavian triangle ) Anterior belly of digastric Hyoid bone Anterior belly of omohyoid s) Sternocleidomastoid Posterior belly of omohyoid Posterior Triangle Great Auricular nerve K<______ Lesser occipital nerve 1. Skin 2. Superficial fascia External jugular vein—> 3; Platisma Great Auricular nerve (GAN ) Anterior/ Transverse 1. Runs with External jugular vein cutaneous nerve of neck 2. Supplies lobule of the ear 3, Supplies to skin at angle of mandible 4. In Frey's syndrome ——> Regenerating Auriculotemporal nerve me fuse with GAN >Buccal Nerve point Supraclavicular nerve |» Semispinalis capitis 2 —} + Spenius capitis |_. Covered by prevertebral fascia |} —> Levator scapulae oe 8. Posterior S. Anterior S. Medius Contents of triangle cfetplarafem & ‘Spinal accessory nerve ‘Superficial to prevertebral fascia Situated between prevertebral fascia & investing layer Injury in posterior triangle ‘Sternocleidomastoid is spared but Trapezius is involved shrugging of shoulder Difficulty in retraction of scapula Difficulty in overhead abduetion Subelavian vessels Winging of scapula ‘Trunk of brachial plexus tn 1.Skin 2 Superficial fascia 3; Platisma 4. Transverse cutaneous nerve of neck 5, Cervical branch of VII Nerve (spy plasms) ‘Middle constrictor Thyrohyoid ‘Membrane & muscle Inferior constrictor 1. Internal jugular vein 2. Common carotid artery {3 Internal carotid artery 4, External carotid artery (5 branches) a. Superior Thyroid artery b. Lingual artery c. Facial artery’ d. Ascending pharyngeal artery e. Occipital artery 5. Nerves — X — superior laryangeal Extémnal Internal laryngeal x x 6. Carotid sheath 7. Ansa cervicalis 8, Sympathetic chain Spinal accessory nerve Pharyngeal wall Masel cont Longitudinal muscles() Circular muscles(3) (nner) (Outer) Pharyngeal raphae «co Stylopharyngeus ‘Superior constrictor (VAC) ‘hyde ‘orn (vsc)Palatopharyngeus. Middle constrictor (VAC) ve) Salpingopharyngen Inferior constrictor “Thyropharyngeds(VAC) Inseion: Poe borer of td age hela Cricopharyngeus(RLN) Killian’s fae — Zenker's diverticulum Senin poser wal of payee Structures passing between constrictors 1 Auditory tube WP “Ascending palatine artery Pharyngobasilar fascia Palatine branch of ascending pharyngeal artery (Sinus of Morgagni ) ‘Stylopharyngeus IXnerve Pharyngeal raphae <— Inferior laryngeal nerve — ‘Superior laryngeal vessles ‘Thyrohyoid membrane. ‘Skeletal framework | ‘Unpaired cartilage (3) Paired cartilage (3~4) Thyroid === Aretenoid Apex ees “Hyaline cartilage Coxntenlaty Epiglottis Cuneiform aul Interior of larynx / Quadrangular membrane Saccule of laryax. ———>', (Upwards & anterior ‘extension of sinus ) ime yak ‘Vestibular ligament <—— Sinus of the larynx Pe dl ‘Vocal ligament Cricovocal cartilage ( conus elasticus ) <— Cricoid cartilage 1. Lining epithetium of larynx — Pseudostratified ciliated columnar epitheli aug. Voul cord Upper border & anterior surface of eit where stratifed squamous epithelium s present) 2. Vocal cords are devoid of mucous gland 3. Vocal cords receive from saccule of larynx ( Hence called Oil can of larynx ) Muscles of larynx v Controls inlet of larynx Controls Rima glottidis Controls tension in vocal cord §4.¢<-—_ ‘Thyroepiglotticus Rima glottidis —_- Intermembranous part ( Opening of inlet Inter Cartilaginous part _— “Thyroarytenoid rasan fend \—Epiglottis << Thyroid cartilage sciiation —Vocalis > Relaxation of posterior 2/334 Sina Treen ‘in anterior 1/3rd_ Closing of inlet be Vocal cord. Arytenoid << Anttenoid \_______, Oblique arytenoid 1 ‘Transverse arytenoid muscle a muscle t Cricothivroid Posterior cricoarytenoid muscle ‘Bends thyroid Sartilage forwards Only abduetdr of vocal cord Maintains aisWay patent hence Tension in vocal cord. called safety muscle of larynx. aa Law Lateral cricoarytenoid muscle Abduetion Bf vocal cord ( Closes intermembranous part of vocal cord ) (Go helps in whispering) 3 complete closure of Rima glotidis 7 Inter aryteMoid muscle