
















































































Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
The use of graphic organizers as a tool to enhance students' thinking skills in economics. It discusses various types of graphic organizers, their uses, and examples. These tools help students to depict knowledge, understand relationships, and analyze concepts in economics.
What you will learn
Typology: Slides
1 / 107

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!





























































































The Use of Graphic Organizers to Enhance Thinking Skills in the Learning of Economics
L
earning how to think is not as complicated as some people have believed. Once learned, thinking skills can be readily applied to lessons in all curriculum areas and further to enhance students’ life-long learning. While our knowledge about subjects can change, fade, or become obsolete, our ability to think effectively remains constant. Effective thinking strategies allow students to acquire the necessary knowledge and apply it appropriately.
Graphic organizers, as illustrated by Drapeau (1998), can be used to enhance students’ thinking skills by encouraging brainstorming, generating new ideas, connecting parts to the whole, drawing sequence, analyzing causes and effects...etc. These are exactly important traits of economics students to make sense out of economic phenomena and to make effective decisions about economic issues (CDC, 1989).
Prawat (1991) reminds us that thinking skills are most effectively taught within a subject matter context. This allows students to use the skills in a meaningful context and to achieve deeper learning of the subject matter.
The graphic organizers introduced in this book include description of the thinking strategies, step-by-step suggestions on how to introduce it to students, and exemplars within each content area. In many cases, the ideas will apply directly to the text teachers wish to use. At other times, teachers will need to modify the ideas to meet their needs. While we have provided a number of ideas and strategies, we hope that this book will be a useful guide and resource to stimulate teachers’ own ideas and variations, and will encourage and support the use of graphic organizers to enhance students' thinking skills in the learning of Economics.
Chapter 1 • 1
The Use of Graphic Organizers to Enhance Thinking Skills in the Learning of Economics
Graphic organizers provide an optional way of depicting knowledge and understanding (Sorenson, 1991), so it is particularly beneficial for students who have difficulty with expressing relationship among parts of economic concepts in written word.
Students who use graphic organizers in the classroom develop their ability to use them independently as study tools for note taking, planning, presentation, and review (Dunston, 1992). In other words, graphic organizers are beneficial to students’ learning inside and beyond classrooms.
4 • What are Graphic Organizers?
The Use of Graphic Organizers to Enhance Thinking Skills in the Learning of Economics
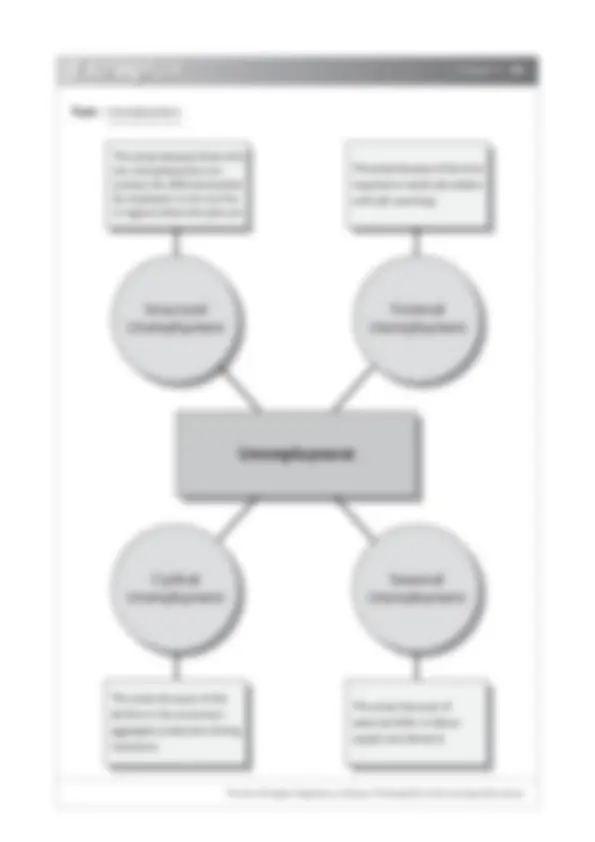
A
lthough there are many variations and possible combinations of graphic organizers used in the classrooms, most of them fall into four basic categories, namely cyclical organizers, conceptual organizers, sequential organizers and hierarchical organizers.
Chapter 3 • 5
Cyclical Organizers
Sequential Organizers
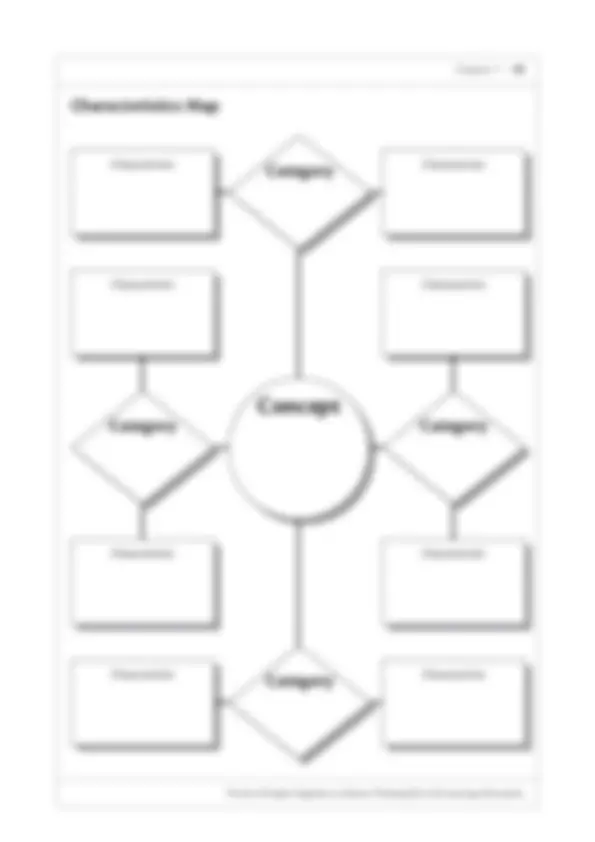
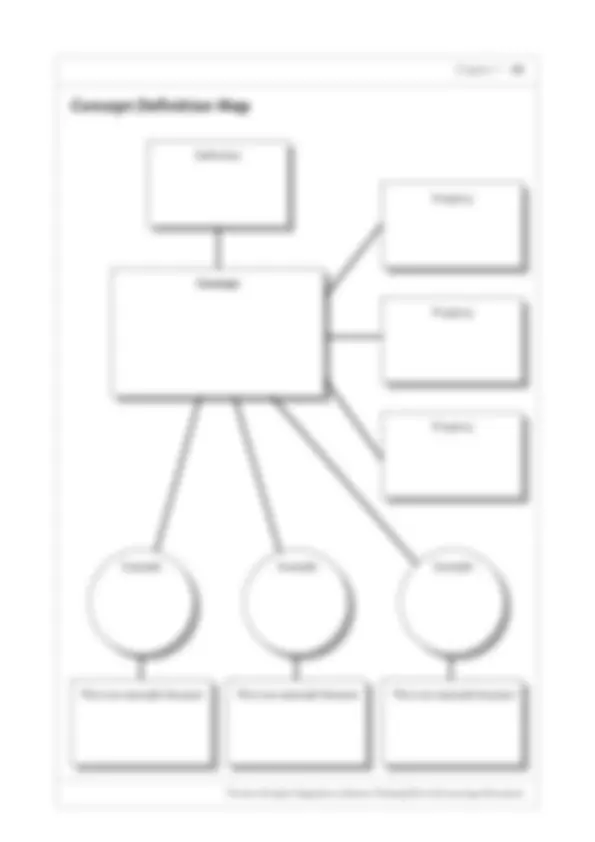
Definition Organizers showing how a main concept is supported by facts, evidence and characteristics
Definition Organizers showing the relation between a concept and its subordinate levels of characteristics
Example Concept Definition Map
Example Hierarchy Diagram
Definition Organizers showing the sequence of events in a process
Example Circle organizer
Definition Organizers showing events in chronological order
Example Multiple Timeline
Hierarchical Organizers
Conceptual Organizers
Graphic Organizers
The Use of Graphic Organizers to Enhance Thinking Skills in the Learning of Economics
G
raphic organizers enable teachers to show and explain relationships between content and subcontent and how they in turn relate to other content areas. On the other hand, through the use of the organizers, students can make more abstract comparisons, evaluations, and conclusions. In short, graphic organizers allow students an active role in their learning. For easy understanding, specific benefits to students and teachers are presented in the following organizer.
Chapter 4 • 7
Assess what students know
Recognize and assimilate different points of view
Assist students in prewriting techniques
Motivate students
Help visual learners to acquire information more easily
Make your lessons interactive
Show and explain relationships between and among content
Record relationships
Clarify and organize ideas
Improve memory
Comprehend texts
The Use of Graphic Organizers
Understand the concept of part to whole
The Use of Graphic Organizers to Enhance Thinking Skills in the Learning of Economics
A
mong the brain’s many functions is the ability to think (Parry and Gregory, 1998), but many students do not have the skills necessary for the more “higher-order” creative and critical thinking needed to thrive both within and beyond the economics lessons.
Generally speaking, there are five different ways in which thinking skills can be used to enhance classroom instruction in economics lessons. First, thinking skills can be used to enhance students’ learning by generating ideas and activating relevant diagrams of economic concepts. This makes it more likely that they can connect new knowledge to their prior knowledge. Second, thinking skills help students organize ideas and components of economic concepts by searching for meaningful patterns, organizing information, and putting things in groups or categories in order to understand. Third, thinking skills help students understand the parts of an economic idea to the whole by seeing the structure of a concept or an event. Fourth, by focusing on similarities and differences, thinking skills can be used to help students establish relationships between two or more ideas, concepts and events. Finally, knowing how to use thinking skills in teaching economics will provide teachers with a vast repertoire of activities to use with any unit or lesson. (Johnson, 2000)
Graphic organizers have a number of attributes that enhance students’ thinking skills. They allow students to make connections among pieces of information and make information easier to recall. Furthermore, they also allow students to break information into manageable chunks, so that they can easily see the relationships among the separate ideas.
Chapter 6 • 11
The Use of Graphic Organizers to Enhance Thinking Skills in the Learning of Economics
Chapter 7 • 13
I
n this chapter, we’ve included a variety of graphic organizers that can be used in many areas of economics learning. They are accompanied by brief descriptions, step-by-step procedures and exemplars. However, teachers are reminded to modify the ideas to meet their own needs. The modification should depend on students’ developmental level and their experience with graphic organizers. Certainly, the modification itself is a valuable opportunity for critical thinking.
14 • Graphic Organizers: Description, Procedures and Exemplars
The Use of Graphic Organizers to Enhance Thinking Skills in the Learning of Economics
This organizer can be used to help students improve their research and problem-solving skills. Students are trained to plan their research and investigation of a topic and thus promote their ability to learn and think independently.
The Use of Graphic Organizers to Enhance Thinking Skills in the Learning of Economics
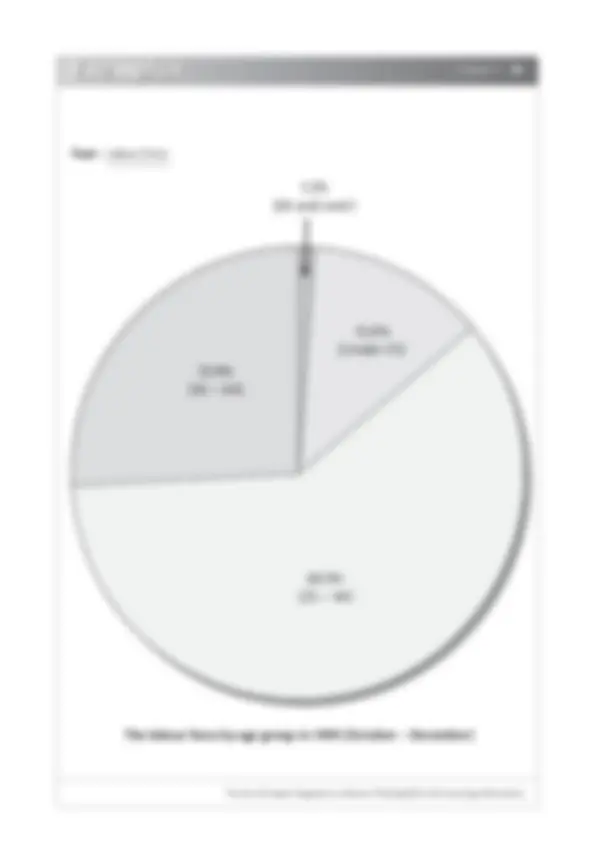
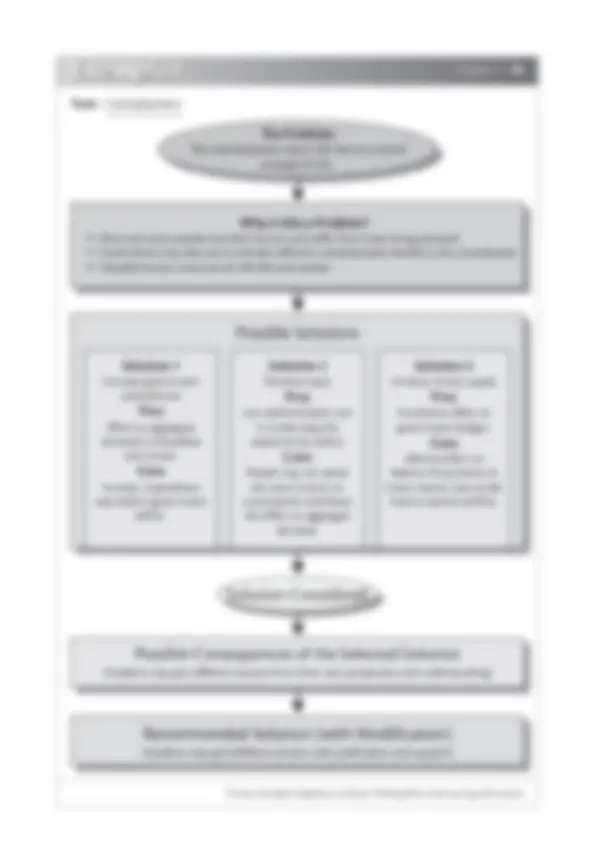
Occupational Mobility of Labour
The Use of Graphic Organizers to Enhance Thinking Skills in the Learning of Economics
What are the factors leading to high occupational mobility of labour and how it can be minimized?
The problem has been existing for a long time. It becomes more serious when employees strongly feel that they are unfairly treated by their employers.
What are the factors leading to high occupational mobility of labour and how it can be minimized?
The problem has been existing for a long time. It becomes more serious when employees strongly feel that they are unfairly treated by their employers.
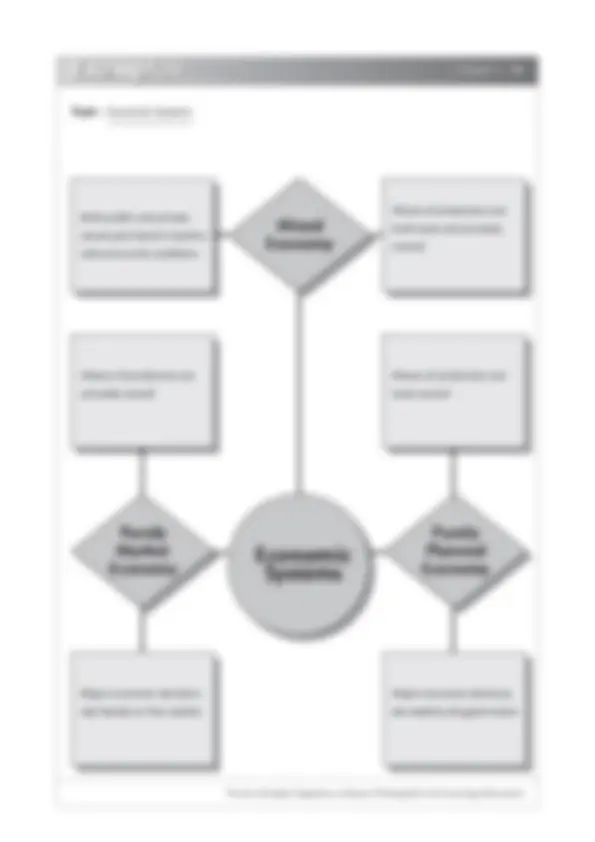
Topic :
Occupational Mobility
of Labour