








Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
Vertical Analysis about financial statement analysis techniques
Typology: Lecture notes
1 / 15

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!










4- 1
4- 2
4- 4 VERTICAL ANALYSIS OF A BALANCE SHEET VERTICAL ANALYSIS OF A BALANCE SHEET Presented on the right is the 2-year comparative balance sheet of Quality Department Store Inc. for 1996 and 1995. 1 Current assets increased $75,000 from 1995 to 1996, they decreased from 59.2% to 55.6% of total assets. 2 Plant assets (net) increased from 39.7% to 43.6% of total assets, and 3 Retained earnings increased from 32.9% to 39.7% of total liabilities and stockholders’ equity. These results reinforce earlier observations that Quality is financing its growth through retention of earnings. Presented on the right is the 2-year comparative balance sheet of Quality Department Store Inc. for 1996 and 1995. 1 Current assets increased $75,000 from 1995 to 1996, they decreased from 59.2% to 55.6% of total assets. 2 Plant assets (net) increased from 39.7% to 43.6% of total assets, and 3 Retained earnings increased from 32.9% to 39.7% of total liabilities and stockholders’ equity. These results reinforce earlier observations that Quality is financing its growth through retention of earnings.
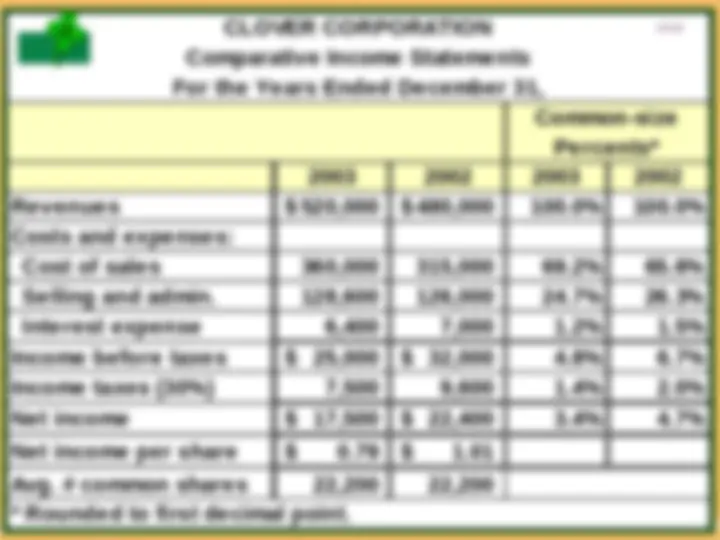
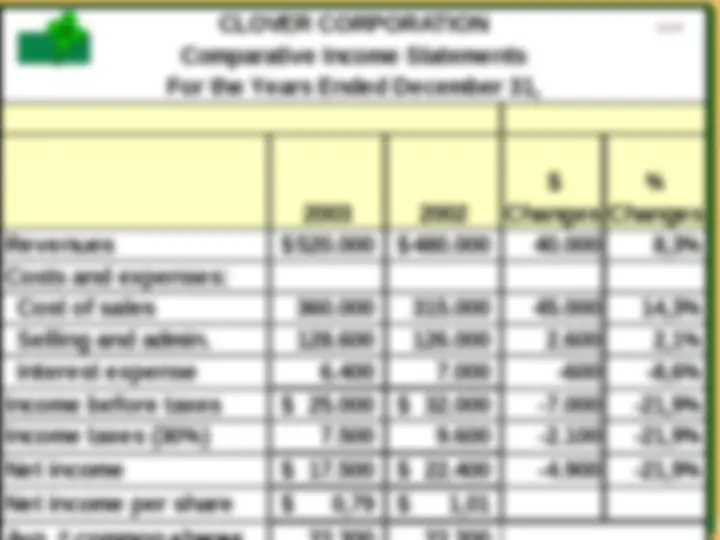
4- 5 VERTICAL ANALYSIS OF AN INCOME STATEMENT VERTICAL ANALYSIS OF AN INCOME STATEMENT Vertical analysis of the 2- year comparative income statement of Quality Department Store Inc. for 1996 and 1995 is shown on the right. 1 Cost of goods sold as a percentage of net sales declined 1% (62.1% versus 61.1%). 2 Total operating expenses declined 0.4% (17.4% versus 17.0%). 3 Net income as a percent of net sales therefore increased from 11.4% to 12.6%. Quality appears to be a profitable enterprise that is becoming more successful. Vertical analysis of the 2- year comparative income statement of Quality Department Store Inc. for 1996 and 1995 is shown on the right. 1 Cost of goods sold as a percentage of net sales declined 1% (62.1% versus 61.1%). 2 Total operating expenses declined 0.4% (17.4% versus 17.0%). 3 Net income as a percent of net sales therefore increased from 11.4% to 12.6%. Quality appears to be a profitable enterprise that is becoming more successful.
4- 8
13- 10
4- 11
McGraw-Hill/Irwin © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 20 4- 13
Comparative Balance Sheets December 31, Common-size Percents* 2003 2002 2003 2002 Liabilities and Shareholders' Equity Current liabilities: Accounts payable $ 67,000 $ 44, Notes payable 3,000 6, Total current liabilities $ 70,000 $ 50, Long-term liabilities: Bonds payable, 8% 75,000 80, Total liabilities $ 145,000 $130, Shareholders' equity: Preferred stock 20,000 20, Common stock 60,000 60, Additional paid-in capital 10,000 10, Total paid-in capital $ 90,000 $ 90, Retained earnings 80,000 69, Total shareholders' equity $ 170,000 $ 159, Total liabilities and shareholders' equity (^) $ 315,000 $ 289,
Comparative Balance Sheets December 31, Changes 2003 2002
Change
Change Liabilities and Shareholders' Equity Current liabilities: Accounts payable $ 67.000 $ 44.000 23.000 52,3% Notes payable 3.000 6.000 -3.000 -50,0% Total current liabilities $ 70.000 $ 50.000 20.000 40,0% Long-term liabilities: Bonds payable, 8% 75.000 80.000 -5.000 -6,3% Total liabilities $ 145.000 $ 130.000 15.000 11,5% Shareholders' equity: Preferred stock 20.000 20.000 0 0,0% Common stock 60.000 60.000 0 0,0% Additional paid-in capital 10.000 10.000 0 0,0% Total paid-in capital $ 90.000 $ 90.000 0 0,0% Retained earnings 80.000 69.700 10.300 14,8% Total shareholders' equity $ 170.000 $ 159.700 10.300 6,4% Total liabilities and shareholders' equity (^) $ 315.000 $ 289.700 25.300 8,7%
4- (^14) CLOVER CORPORATION Comparative Income Statements For the Years Ended December 31, Common-size Percents* 2003 2002 2003 2002 Revenues $ 520,000 $480, Costs and expenses: Cost of sales 360,000 315, Selling and admin. 128,600 126, Interest expense 6,400 7, Income before taxes $ 25,000 $ 32, Income taxes (30%) 7,500 9, Net income $ 17,500 $ 22, Net income per share $ 0.79 $ 1. Avg. # common shares 22,200 22,