











Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
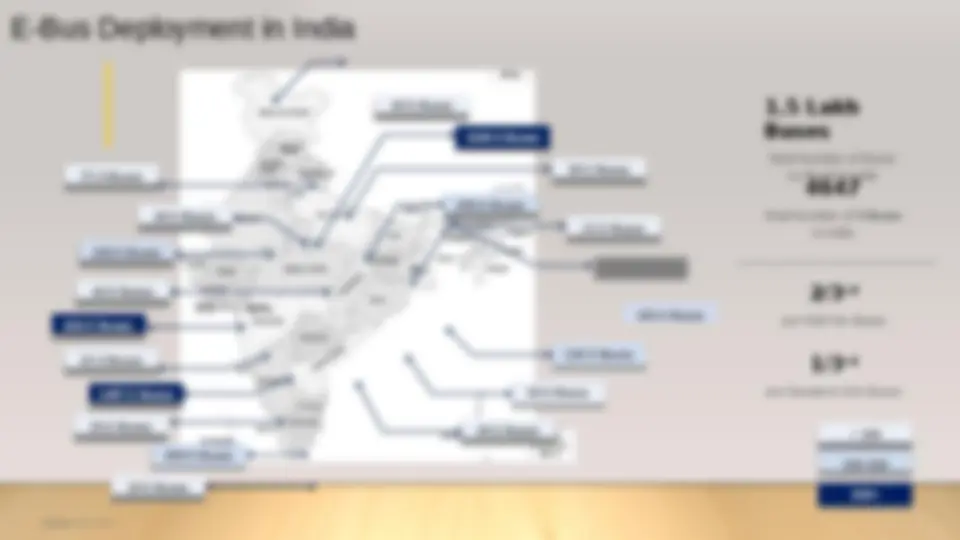
An overview of the different types of electric vehicle (ev) charging stations for buses in india. It covers the introduction to ev charging stations, the various types of charging infrastructures such as plug-in, on-board, pantograph, inductive, and battery swapping charging stations. The benefits and challenges of each charging technology, including factors like charging time, capital cost, passenger capacity, and operating efficiency. It also highlights the current deployment of electric buses across different cities in india and the importance of charging infrastructure in the adoption of electric buses. The document aims to educate readers on the current state of ev charging infrastructure for buses in the indian context, which is crucial for the successful transition to sustainable public transportation.
Typology: Cheat Sheet
1 / 18

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!











PRESENTED BY: NAME: SANIKA. A .SHIRKE ROLL.NO.:23EL PRESENTATION ON EV CHARGING STATIONS- BUS
INDEX (^) Introduction (^) Types of EV charging stations (^) Infrastructures of buses charging stations
Introduction
Types of charging stations (^) SLOW CHARGING STATIONS (^) Most common type of charging station for electric buses in India. (^) Use a three-phase ac supply. (^) Ideal for overnight charging.
(^) Shorter amount of time than slow charging. (^) Ideal for bus fleets with unpredictable schedules and high usage. (^) Fast charging can lead to battery degradation if used too frequently. (^) Ultra-fast charging stations (^) Charge the bus's battery in a matter of minutes. (^) New to India and are not yet widely available. (^) Ideal for Hightraffic bus routes (^) Reduce the time
(^) Plug in charging stations (^) On board charging stations (^) Pantograph charging stations (^) Inductive charging (^) Battery swapping charging stations
ON BOARD BATTERY CHARGER (^) The on-board battery of BEBs needs to be charged regularly. (^) Equipped with a charging interface that can be connected to the appropriate charging infrastructure to charge the battery with power from the grid. (^) Most convenient type of charging. (^) Cost effective. .
(^) Includes DC charging via pantograph with on-board (^) Minimum voltage :415 V in the Indian context. (^) Technology is expensive. (^) Requires auxiliary infrastructure including distribution transformer, protection system, SCADA system. (^) Charging time is short and buses get charged while they are in traffic. DC PANTOGRAPH
INDUCTIVE CHARGING (^) Includes all charging technologies which achieve wireless transfer of electricity. (^) Either by static or dynamic induction. (^) Minimum voltage : 415 v in the Indian context. (^) Bus battery gets charged through charging pads. (^) Ideal when buses are parked at bus stops.
How Its Beneficial Reduce investment costs You can save on grid usage charges every month by reducing load peaks. Save on energy costs
Conclusion