






Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
An overview of vehicle emission standards in the us and europe, focusing on light duty vehicles and heavy duty engines. It covers the history of emission regulations, emission standards for different vehicle types, and the evolution of these standards over the years. The document also mentions motorcycle emission standards in asia.
Typology: Study notes
1 / 14

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!









The vehicle emission standards were implemented for the first time in 1965 when control of crankcase hydrocarbon emissions from gasoline passenger cars was required as per the law. Use of positive crankcase ventilation (PCV) system on the gasoline passenger cars became necessary to prevent emission of hydrocarbon rich crankcase blow by gases into atmosphere. At the same time, the exhaust gas emission standards for new cars were also established in the state of California and in 1968, US enacted legislation to implement nationwide vehicle emission regulations. In Europe , vehicle emission standards were implemented beginning from the year 1970. Over the years, the emission standards have become more and more stringent and have driven the development of advanced engine designs and emission control technology. Now, nearly all the countries all over the world have enforced vehicle emission regulations of varying severity following largely either the US or the European regulations.The emission limits that are in force in the US and Europe and the trends thereof over the years are discussed below.
US Standards
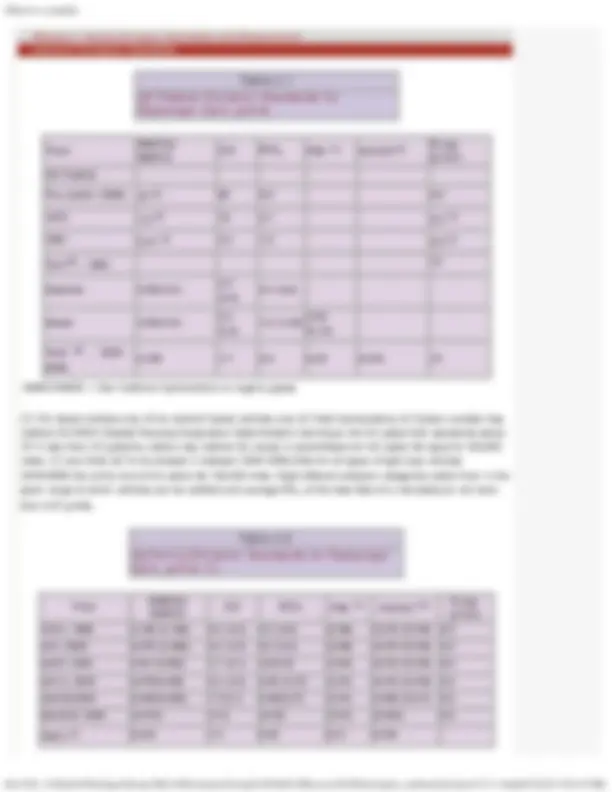
The US emission standards for passenger cars are given in Table 4.1 since the limits were set for the first time under the Clean Air Act of 1968. The standards set for 1975 were rather stringent such that the oxidation catalytic converters were required on most cars. Amendments to Clean Air Act in 1977 resulted in the standards that required in 1980/1981 reduction of 90% in HC and CO, and 75% in NO (^) x.
The 1980-81 standards resulted in widespread use of 3-way catalyst technology.
During 1990s, the 1977 amendments were found inadequate as 9 US cities had higher ozone levels and 41 cities higher CO levels than the air quality standards. The 1990 Clean Air Act Amendments (CAAA) followed resulting in further tightening of the emission standards besides other measures like introduction of better quality fuels such as the reformulated gasoline. The new emission regulations known as Tier 1 were implemented from 1994 and Tier 2 standards from 2004 through to 2009. It is seen that the current production vehicles emit less than 1% of emissions of pre-control era vehicles.
In the mean time California introduced a new set of emission regulations (Table 4.2) and called the vehicles meeting these regulations by the name of different grades of low emission vehicles (LEV) such as TLEV ( Transitional), LEV, ULEV (Ultra), SULEV (Super Ultra) and PZEV ( Partial zero emission vehicles).
(1) Limits in parentheses at the end of durability run for 100,000 miles and from the year 2004 at 120,000 miles. (2) Partial zero emission vehicles (PZEV) limits are for 150,000 miles durability.
European Standards
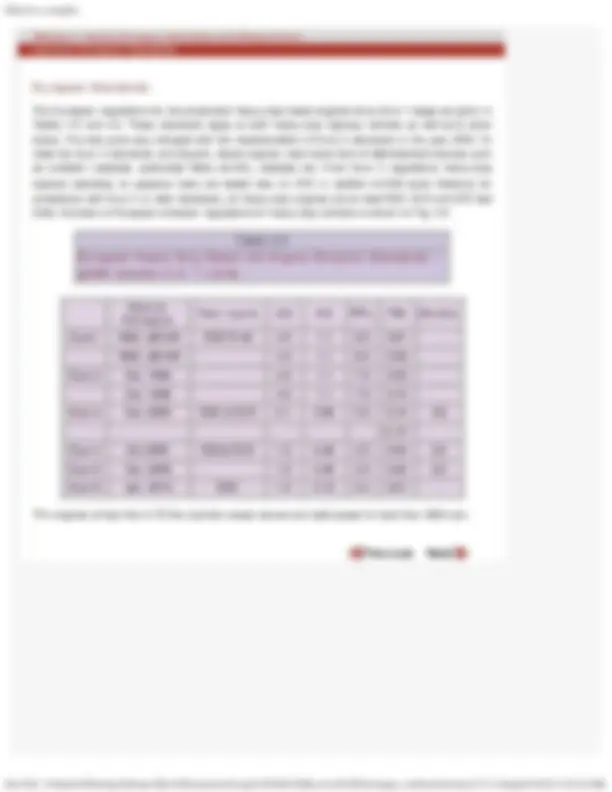
European emission standards for the light duty vehicles are given in the Table 4.3. Before1992 i.e. prior to Euro 1 standards, emission limits were based on ECE-15 cycle and varied with vehicle reference weight, the higher emissions were permitted for the heavier passenger cars. From 1992 however, the same limits for all the passenger cars irrespective of vehicle weight as in the US were introduced. EU standards up to Euro 3 stage require durability demonstration for 80,000 km or 5 years, whichever occurs first. In lieu of actual durability test, the manufacturers may use the following deterioration factors:
Gasoline cars: 1.2 for CO, HC and NO (^) x Diesel cars: 1.1 for CO, NO x and HC+ NO (^) x , 1.2 for PM
Euro 5 stage requires durability of 160,000 km or 5 years, whichever occurs first. The emission standards for the light duty trucks and medium duty vehicles also, have been laid down and can be found in the European regulations.
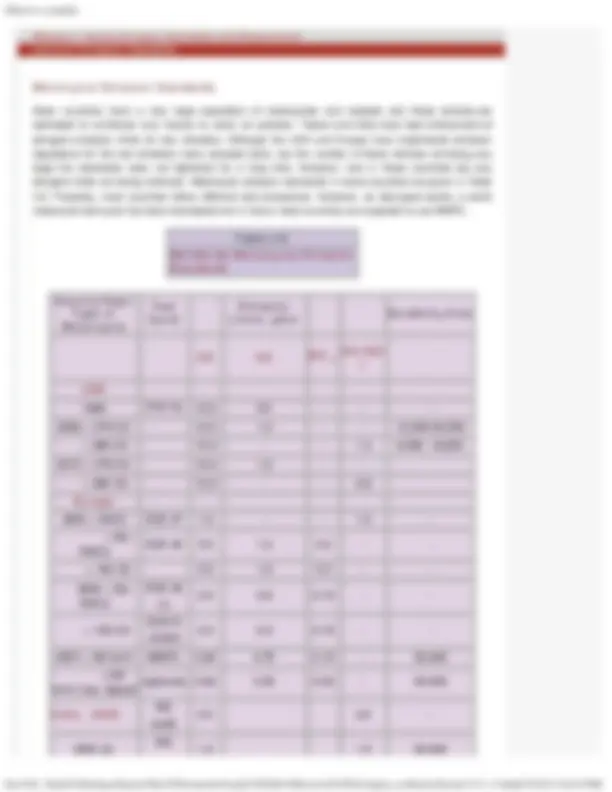
Most heavy-duty vehicles are powered by the diesel engines. Hence, the heavy duty engine emission regulations have been directed more towards reduction in NO (^) x and PM emissions.
US Standards
The US emission standards for the engines of heavy-duty vehicles (GVW >3855 kg) are given in Table 4.4. The emission limits applicable from the model year 2007 specify a drastic reduction over the year 2004 standards. The PM standards will be fully effective from the year 2007. The NO (^) x and NMHC
standards are to be phased-in for the diesel engines between 2007 and 2010.
Emission durability is to be demonstrated over the useful life of the vehicles that varies from 8 years or 176,000 km for light heavy-duty engine vehicles (>8,860 kg <15000 GVW) to 8 years or 465,300 km for heavy heavy-duty vehicles (> 15000 kg GVW).To make the year 2007 standards effective, diesel fuel sulphur is to be reduced to 15 ppm maximum down from the earlier limit of 500 ppm.
Option 1 15.5 - 2.4 - 0.10 (0.05) Option 2 15.5 0.5 (3)^ 2.5 - 0.10 (0.05)
2007 15.5 0. (3)
Note: values in parentheses apply to urban buses
Euro3 Oct. 2000 ETC 5.45 0.78 1.6 5.
Euro 4 Oct. 2005 4.0 0.55 1.1 1.1 0. Euro 5 Oct. 2008 4.0 0.55 1.1 2.0 0. Euro 6 Jan. 2013 4.0 0.16 (4) 0.5 0.4 (^) 0.01 (5)
(1) for natural gas engines only; (2) not applicable for gas fuelled engines for approval to Euro 3 and Euro 4 standards; (3) for engines of less than 0.75 litre/cylinder swept volume and rated speed above 3000 rpm; .(4) THC (total hydrocarbons) limits apply for diesel; (5) particle number limit may apply to prevent ultra fine particles from flow through ( or partial flow) filters.
file:///C|/...20and%20Settings/iitkrana1/My%20Documents/Google%20Talk%20Received%20Files/engine_combustion/lecture17/17_11.htm[6/15/2012 3:02:45 PM]
Asian countries have a very large population of motorcycles and mopeds and these vehicles are estimated to contribute very heavily to urban air pollution. Taiwan and India have lead enforcement of stringent emission limits for two wheelers. Although the USA and Europe have implementd emission regulations for the two wheelers many decades back, but the number of these vehicles not being very large the standards were not tightened for a long time. However, now in these countries too very stringent limits are being enforced. Motorcycle emission standards in some countries are given in Table 4.8. Presently, most countries follow different test procedures. However, as discussed earlier, a world motorcycle test cycle has been developed and in future most countries are expected to use WMTC.
file:///C|/...20and%20Settings/iitkrana1/My%20Documents/Google%20Talk%20Received%20Files/engine_combustion/lecture17/17_11.htm[6/15/2012 3:02:45 PM]