








































Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
This is the summary of chapter 4 for Boylestad's Electronics Devices and Circuits book.
Typology: Slides
1 / 94

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!























































































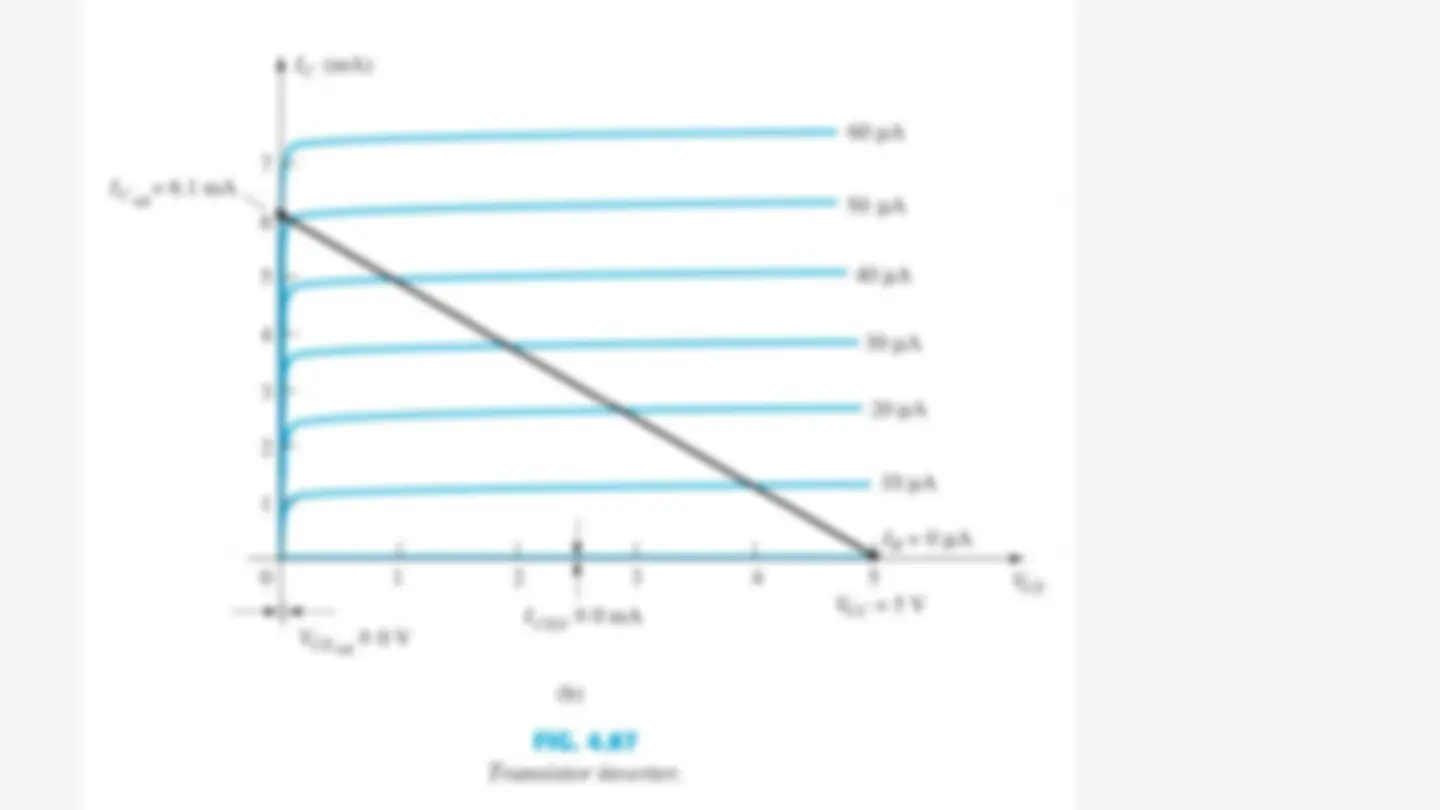
Region of the BJT Characteristic Linear- Region Operation Cut-off Region Operation Saturation Region Operation
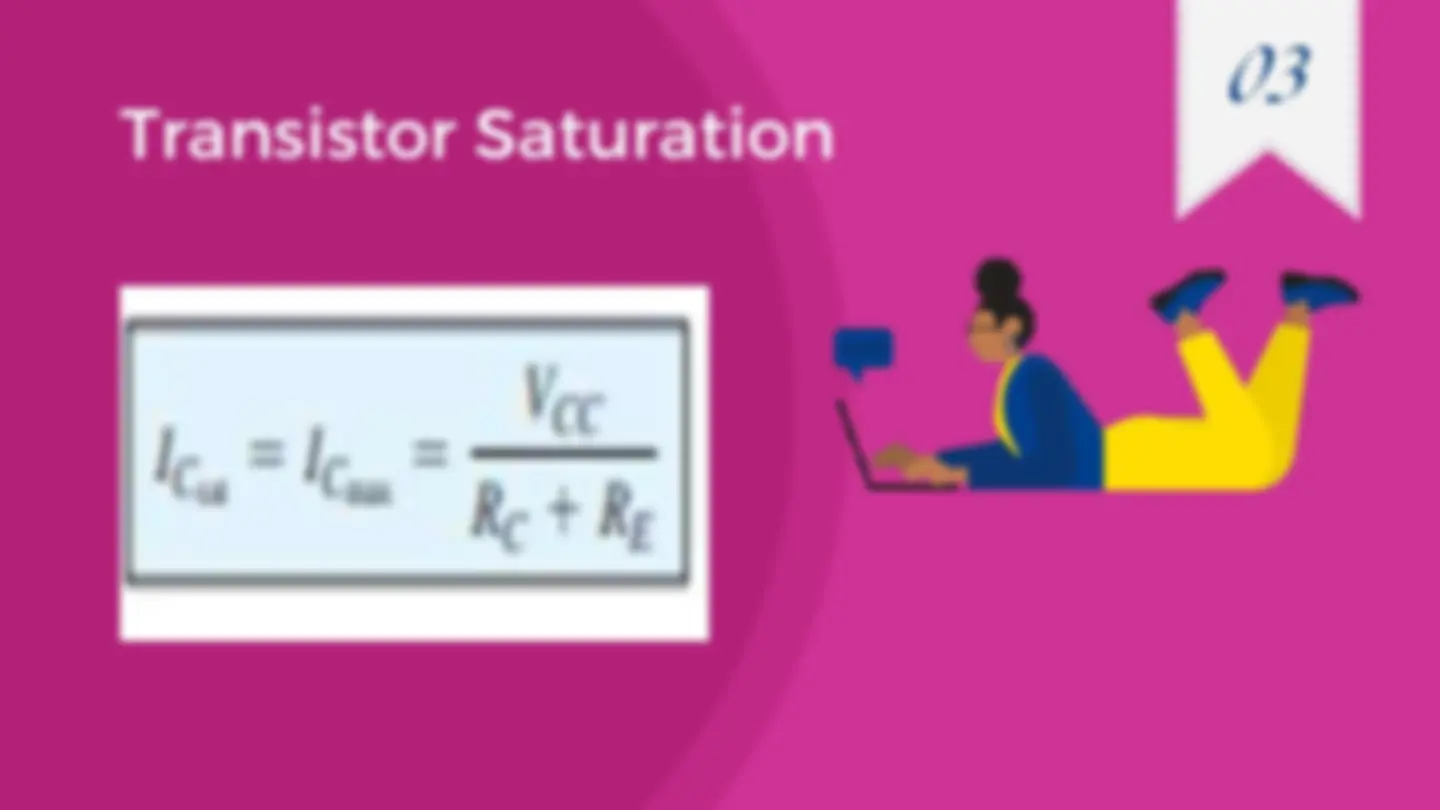
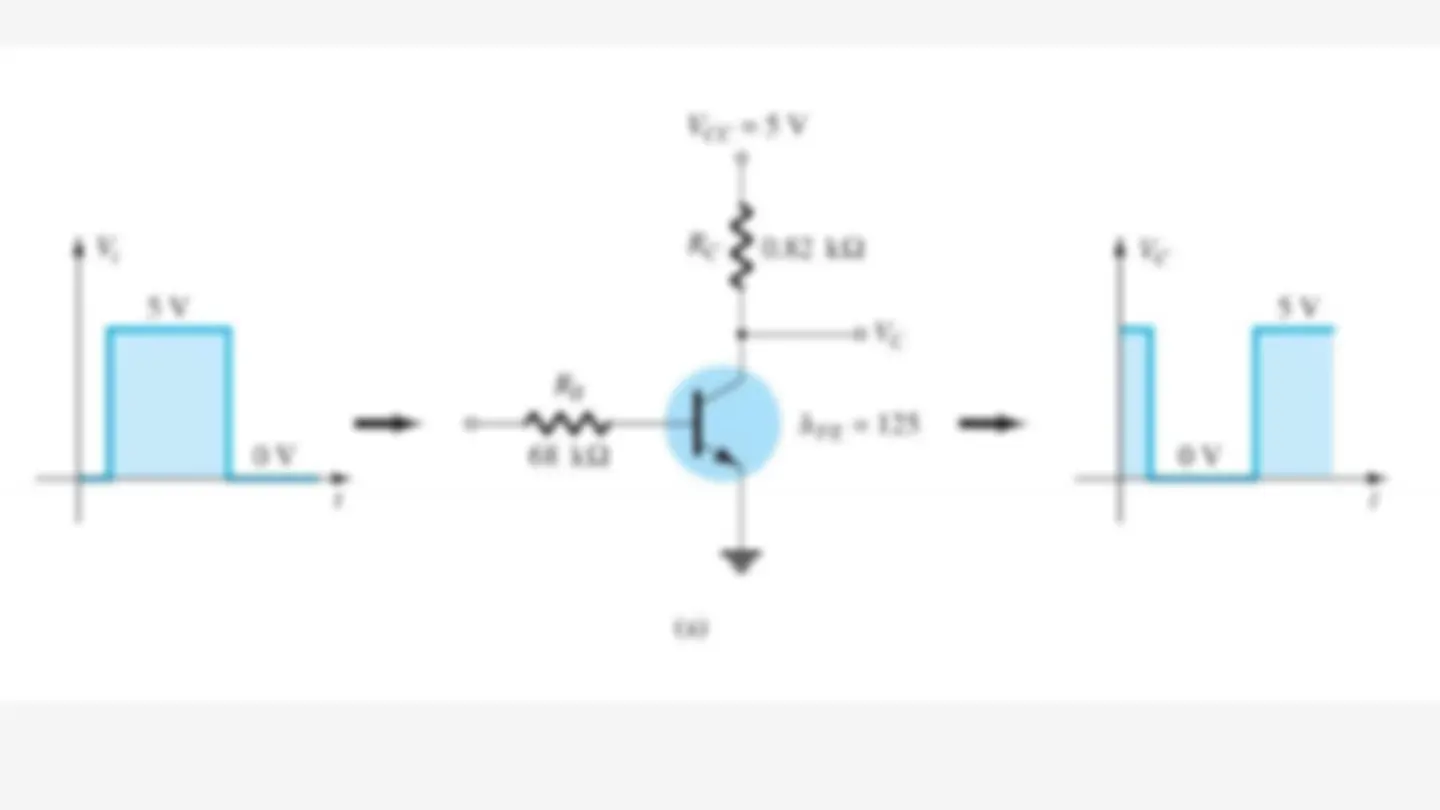
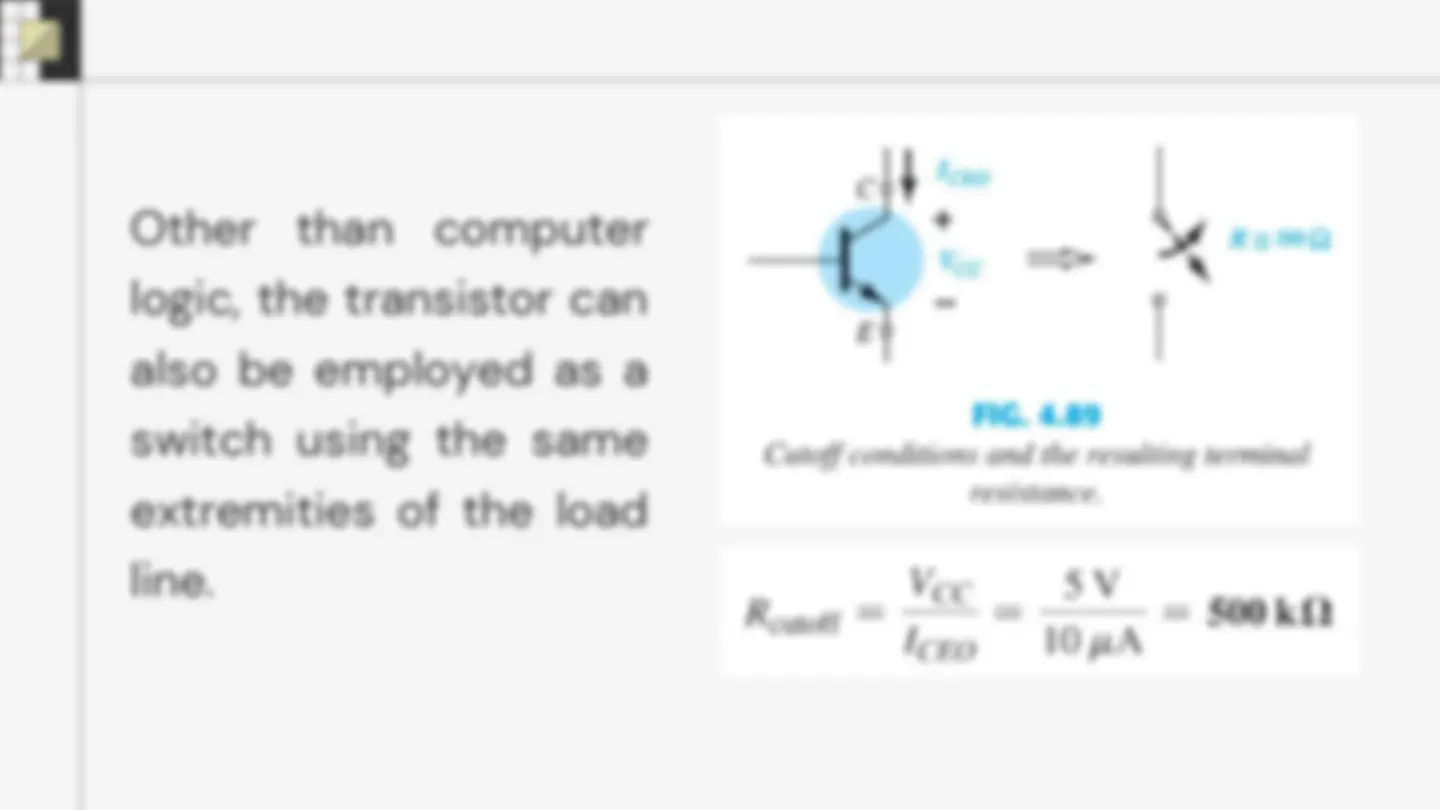
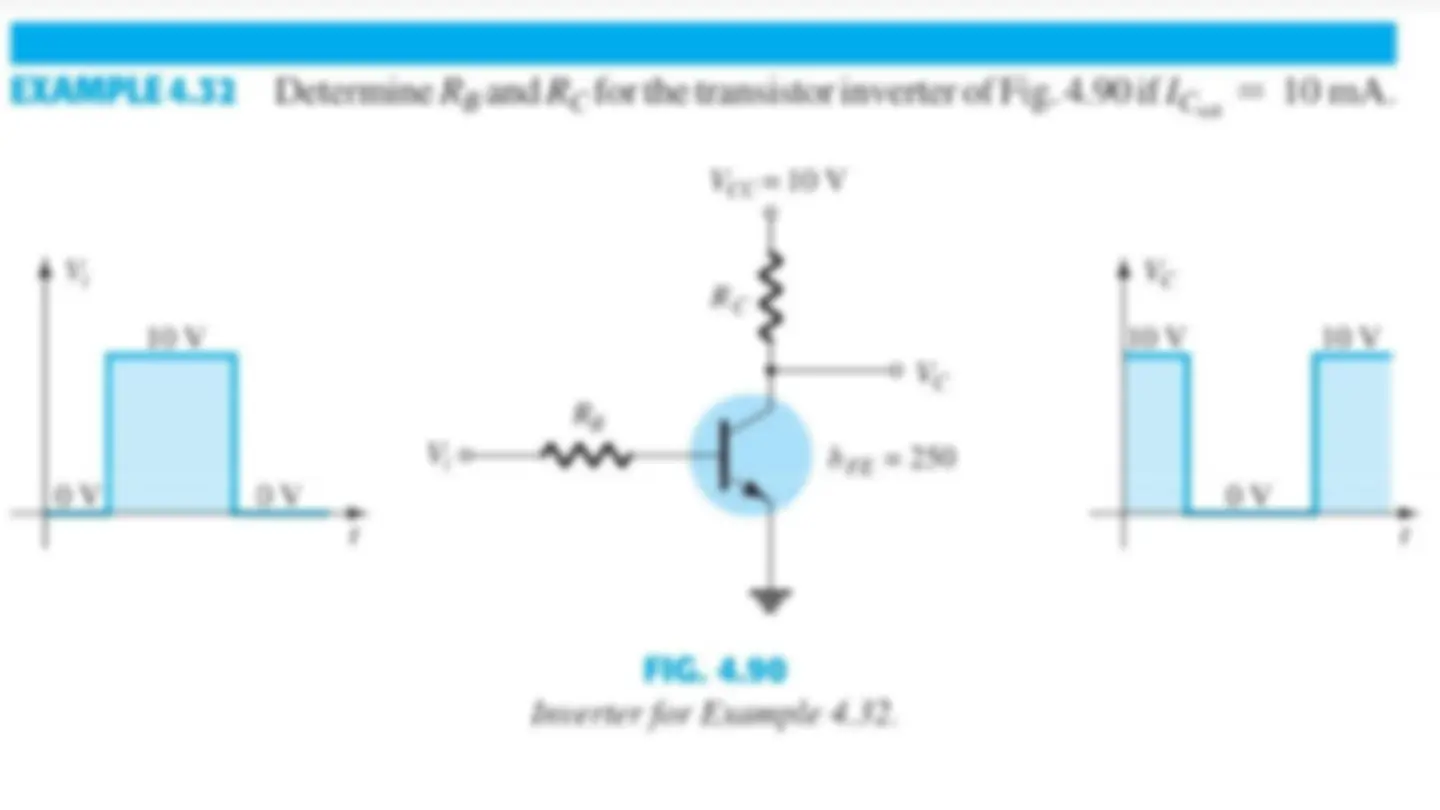
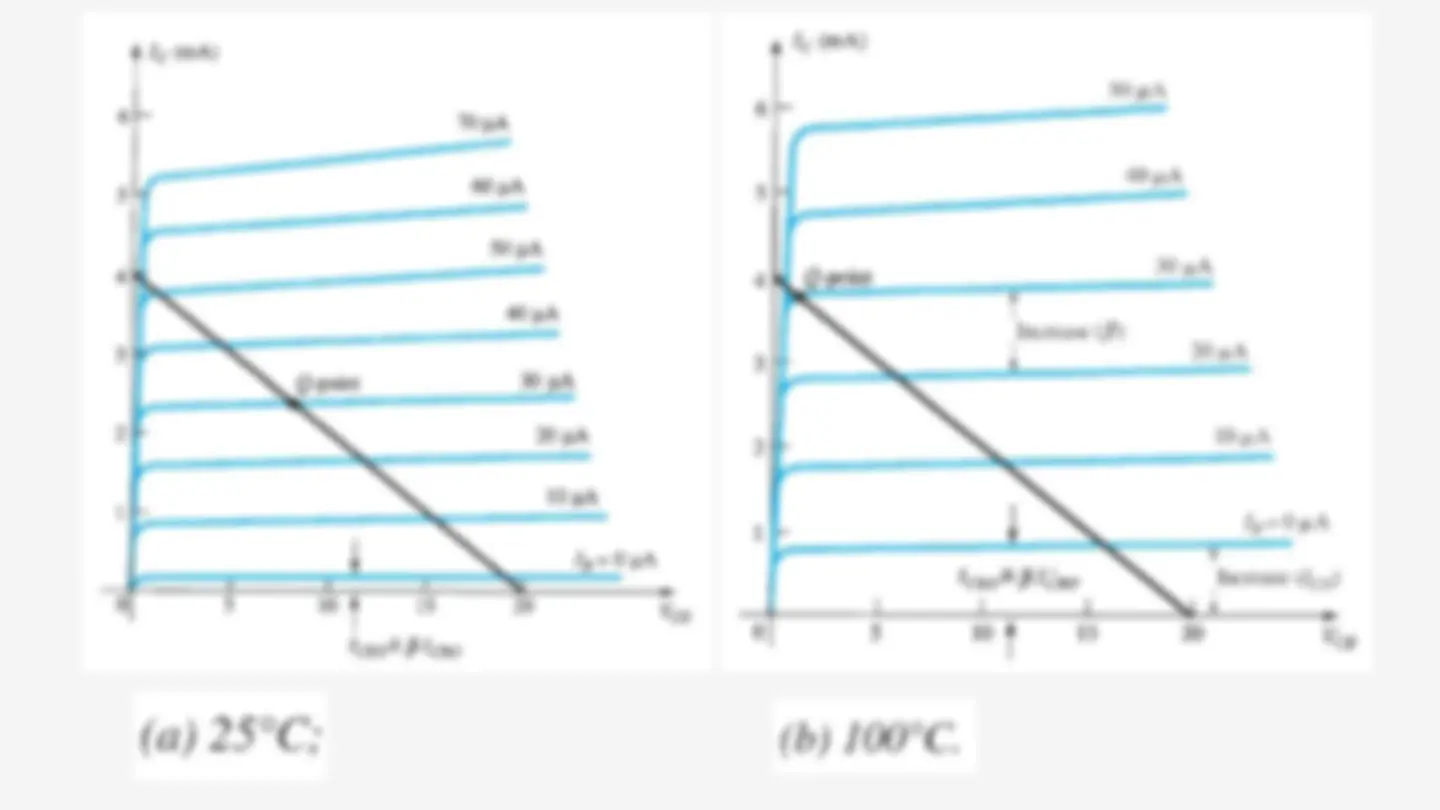
Transistor Saturation is used to describe any system in which levels have reached their maximum values.
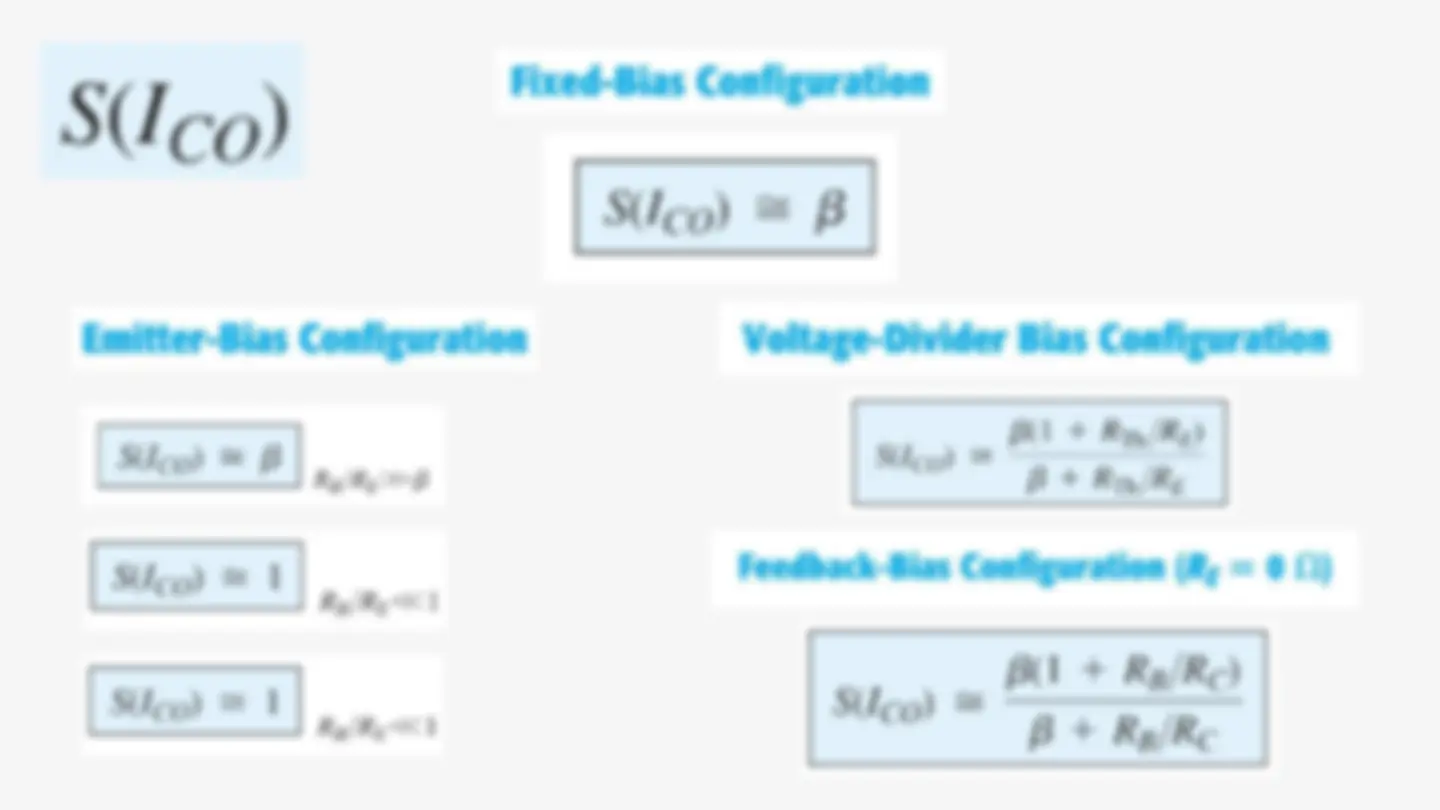
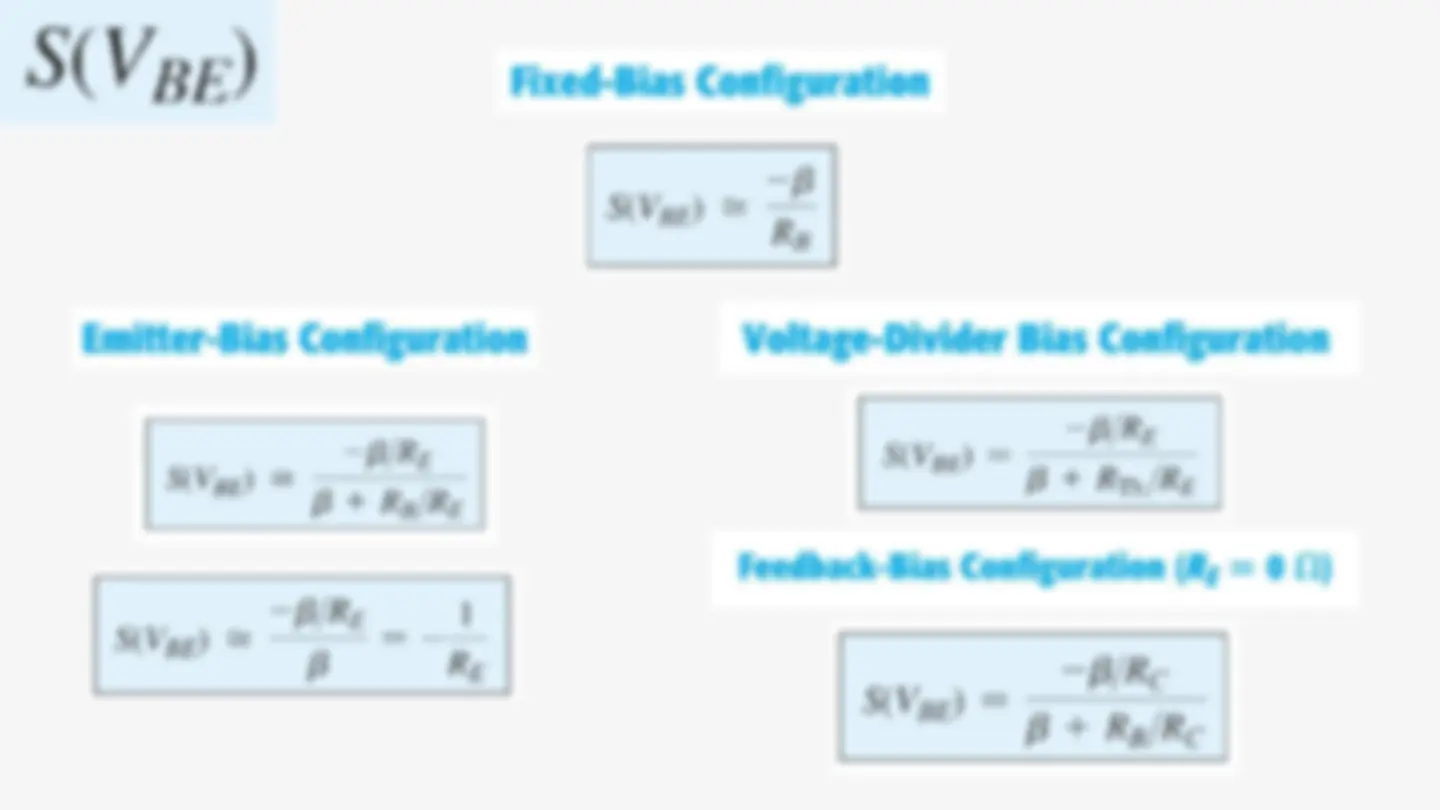
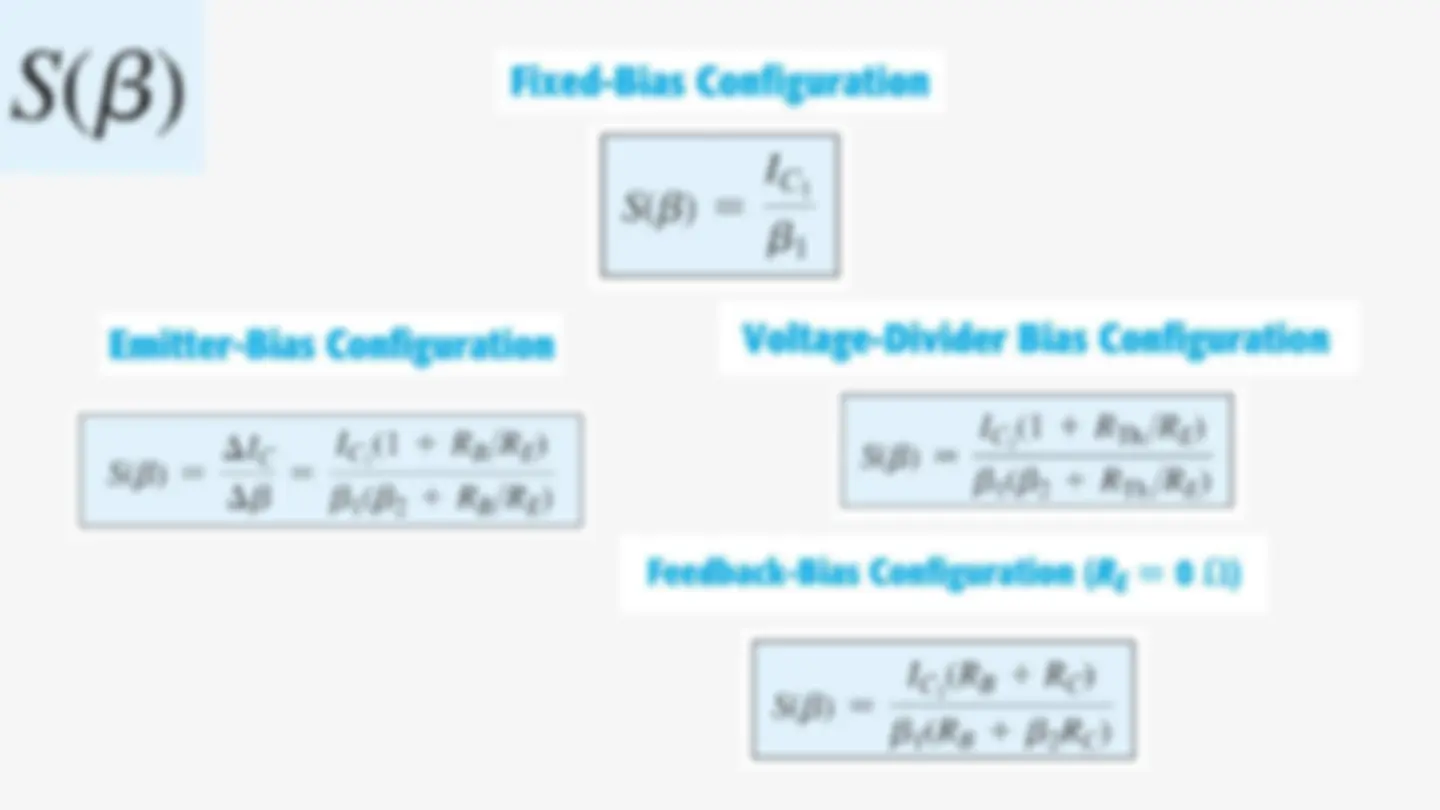
Emitter-Bias The dc bias network includes an emitter resistor to improve the stability of the fixed- bias configuration. The more stable the configuration, the less responsive it is to unwanted changes in temperature and parameter variations.
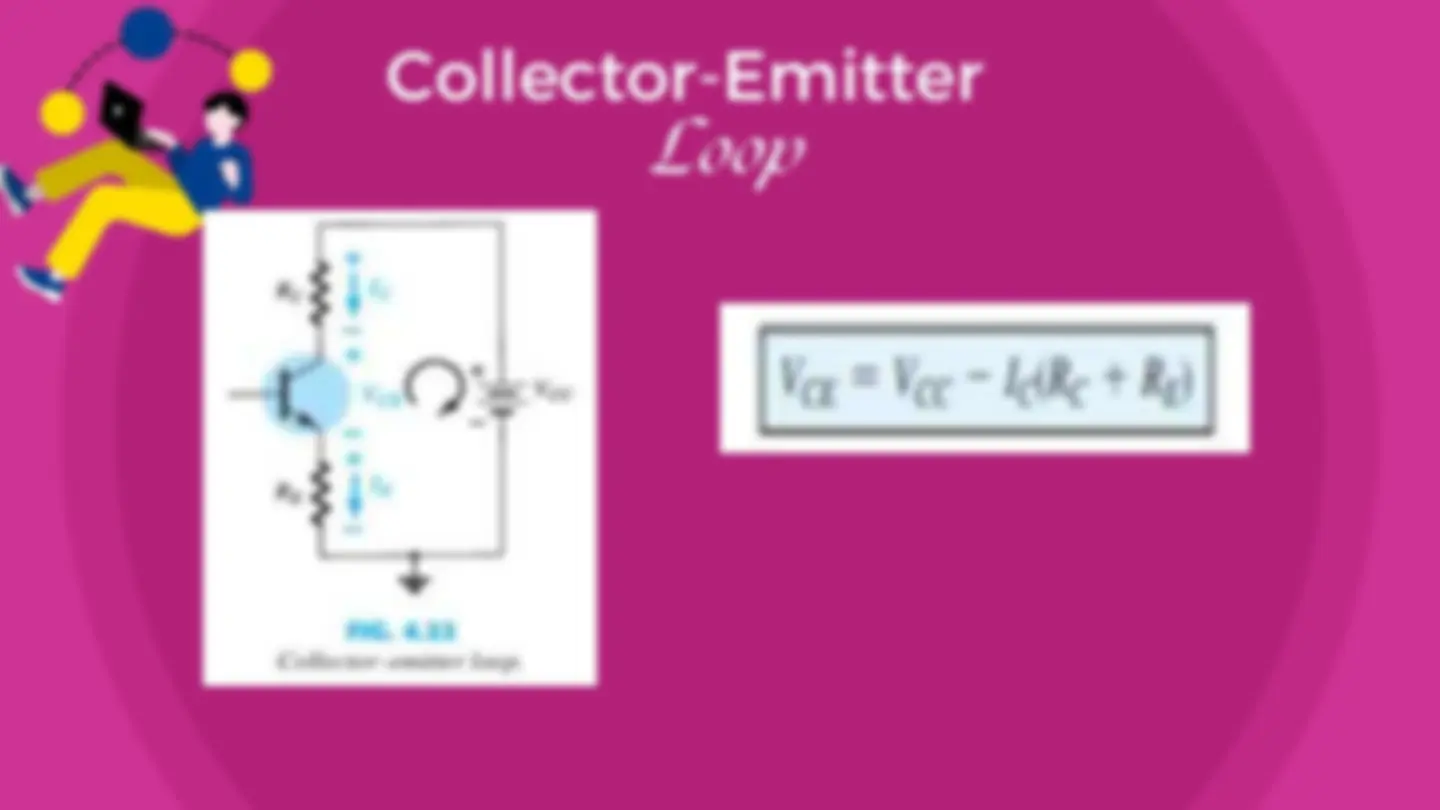
Collector-Emitter
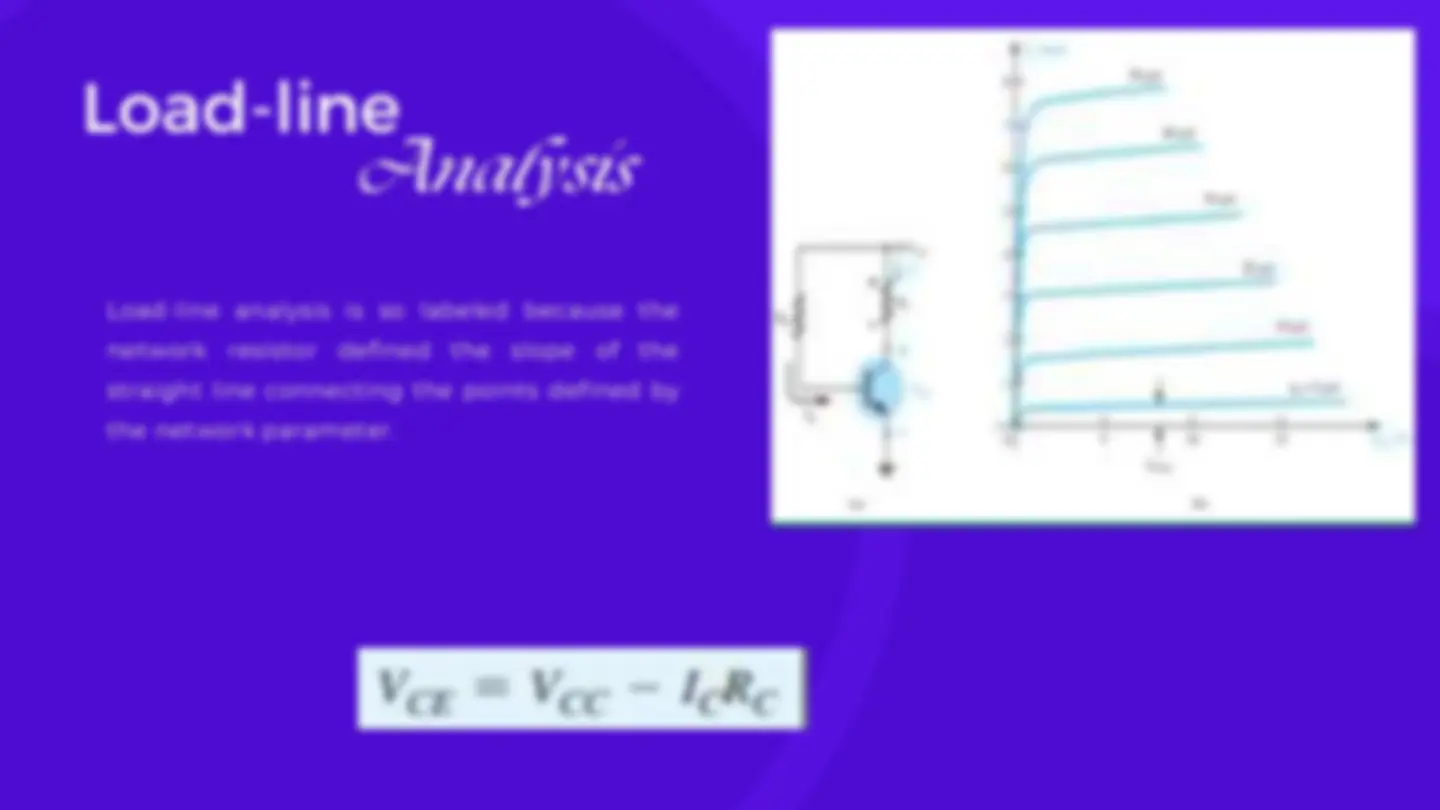
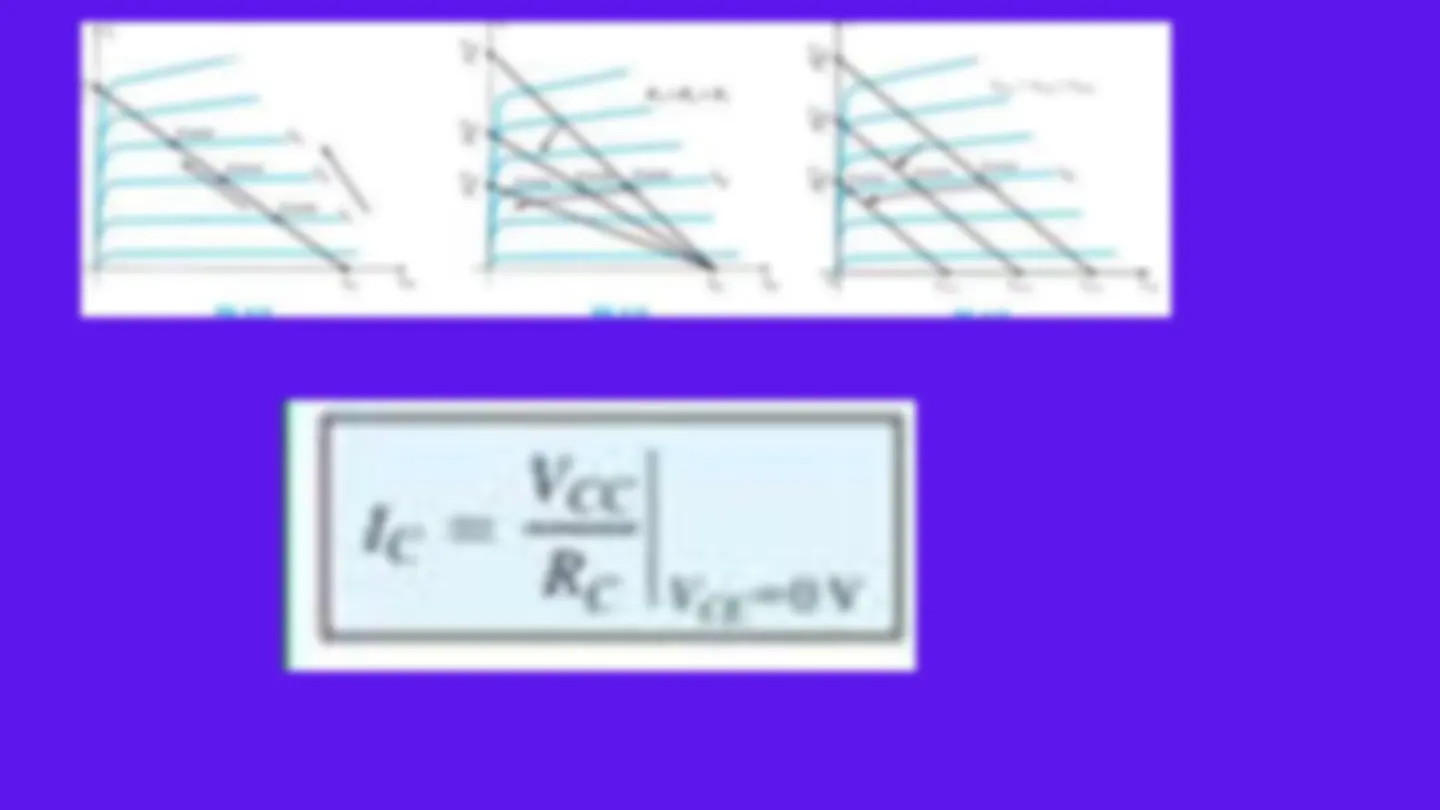
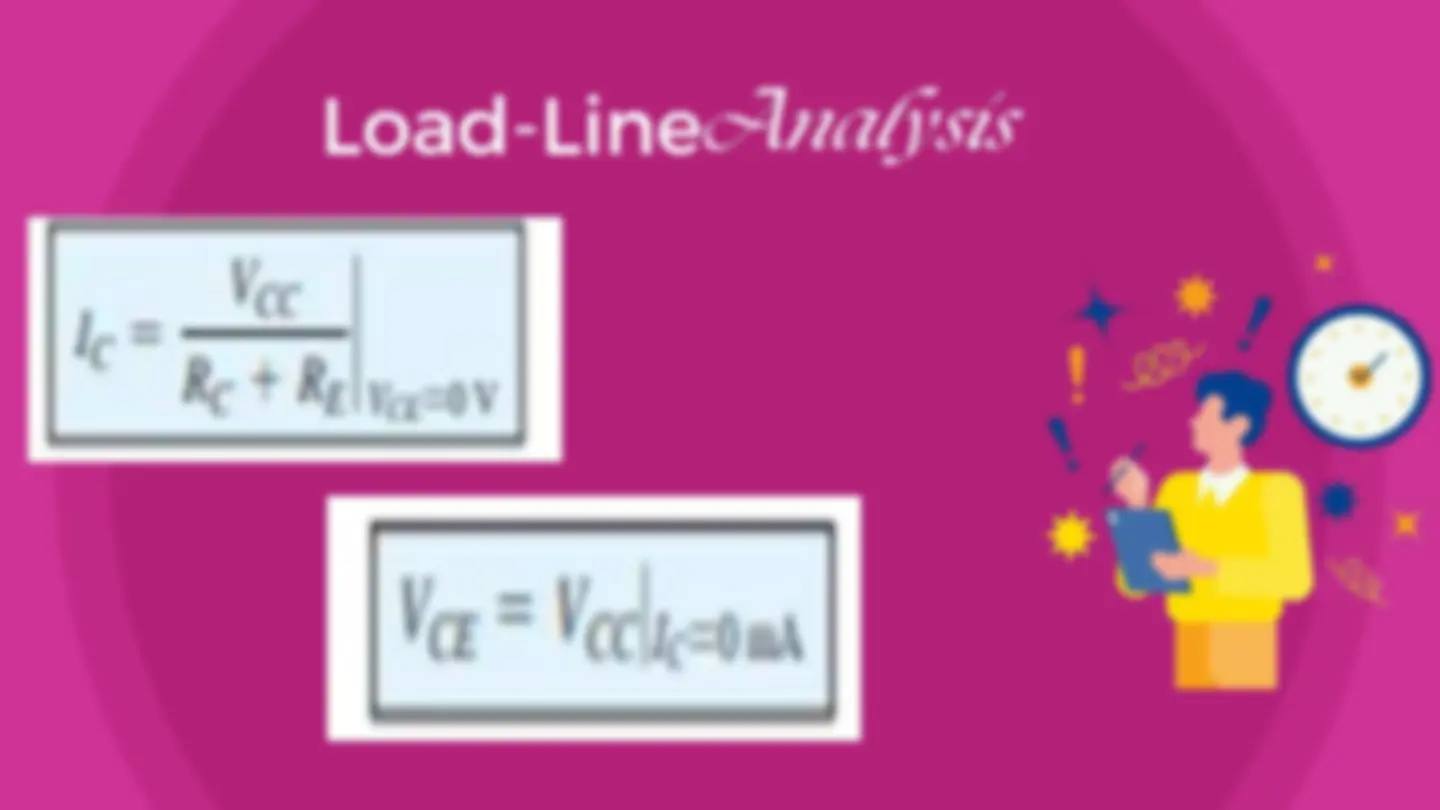
Load-Line The maximum collector current or collector saturation level for an emitter-bias design can be determined using the same method as for a fixed- bias configuration: Apply a short circuit between the collector-emitter terminals and calculate the resulting collector current:
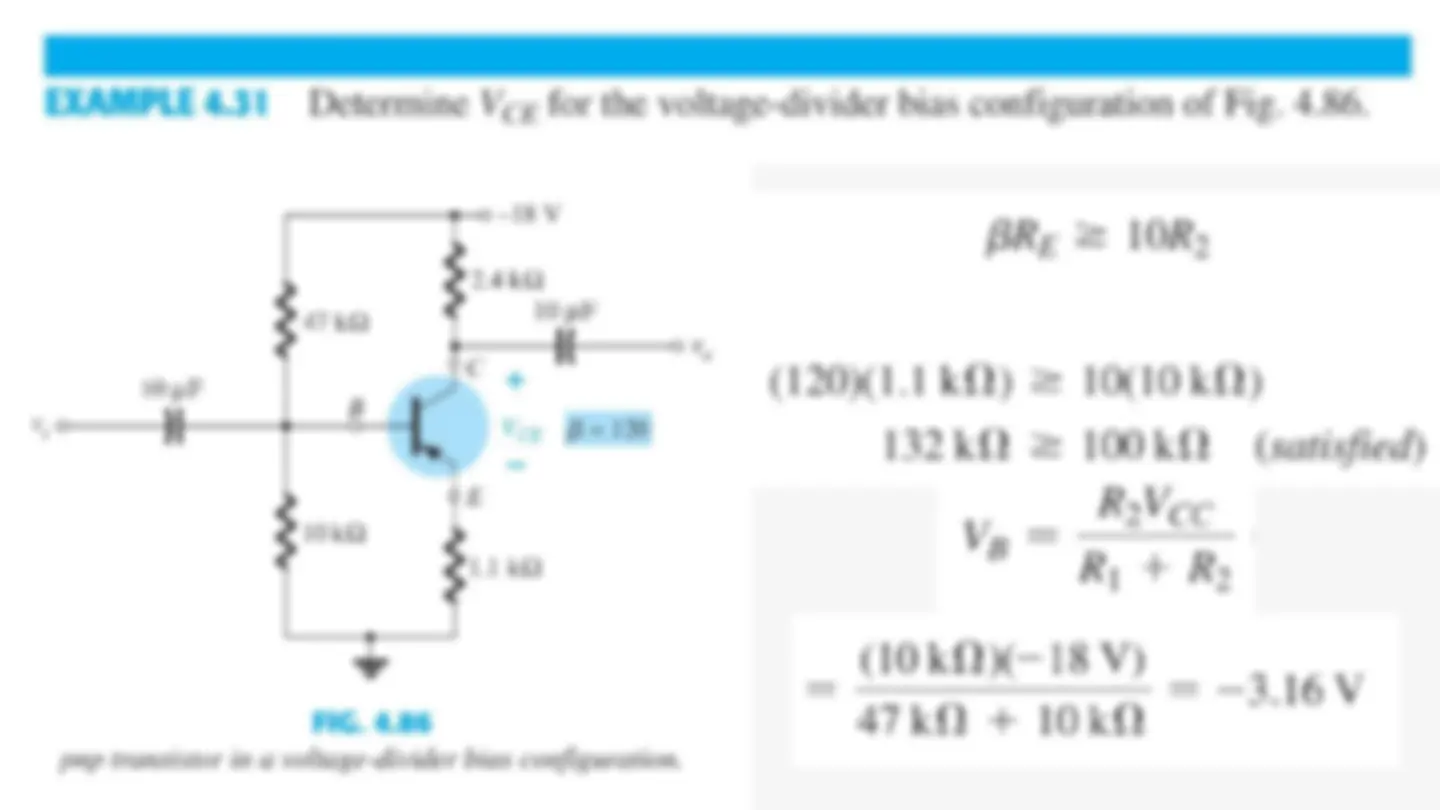
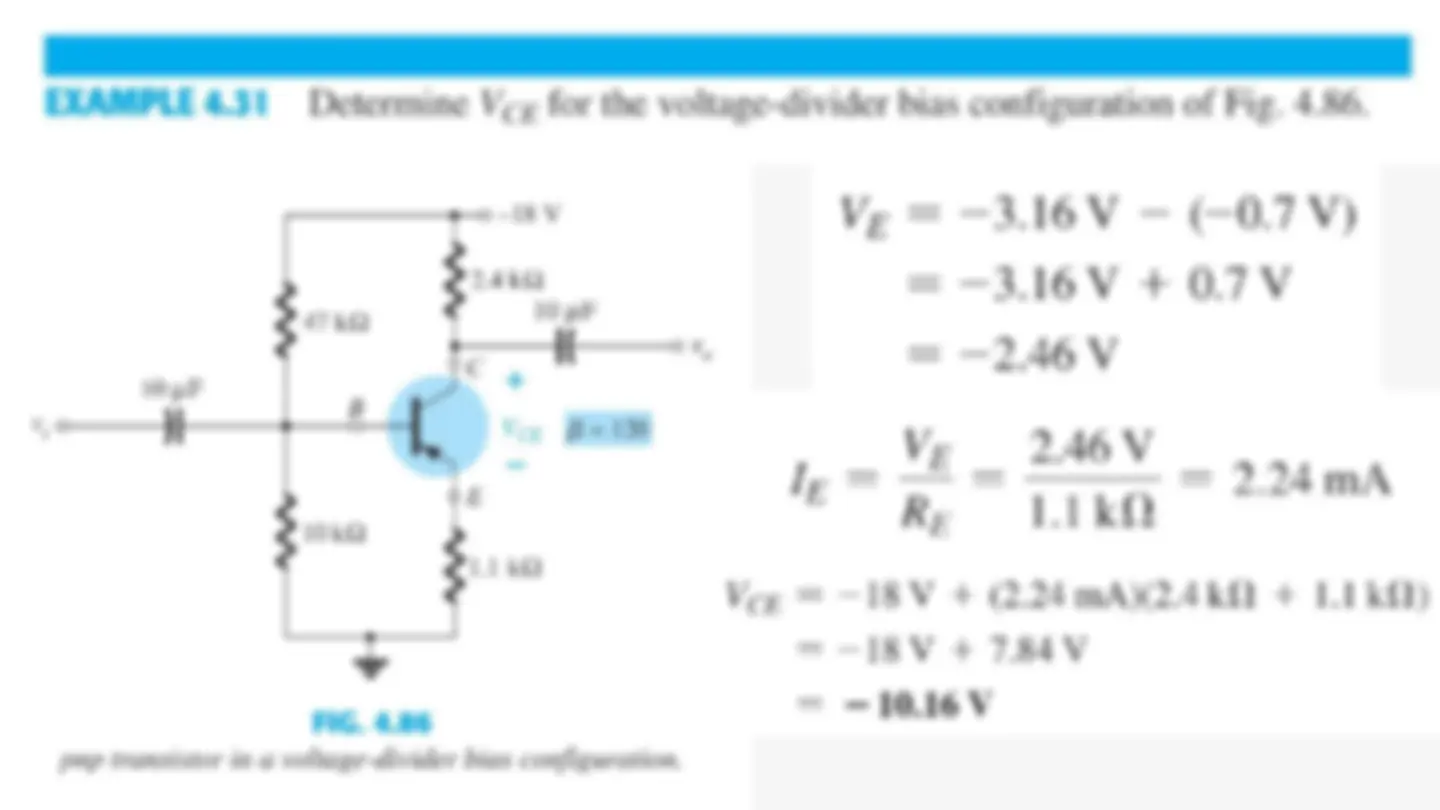
Voltage-Divider Bias