







Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
Lesson 2 of Electronic Circuits
Typology: Lecture notes
Uploaded on 11/28/2020
5
(1)4 documents
1 / 11

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!







The output of one amplifier is the input to the next amplifier
The overall voltage gain is determined by the product of gains of the
individual stages
The DC bias circuits are isolated from each other by the coupling
capacitors
The DC calculations are independent of the cascading
The AC calculations for gain and impedance are interdependent
This example is a CE – CB
combination. This arrangement
provides high input impedance
but a low voltage gain.
The low voltage gain of the
input stage reduces the Miller
input capacitance, making this
combination suitable for high-
frequency applications.
B D E
CC BE B R R
Base current:
Emitter current:
Emitter voltage:
Base voltage:
VB = VE +VBE
This is a two-transistor circuit that operates like a
Darlington pair, but it is not a Darlington pair****.
It has similar characteristics:
The difference is that a Darlington
uses a pair of like transistors,
whereas the feedback-pair
configuration uses complementary
transistors.
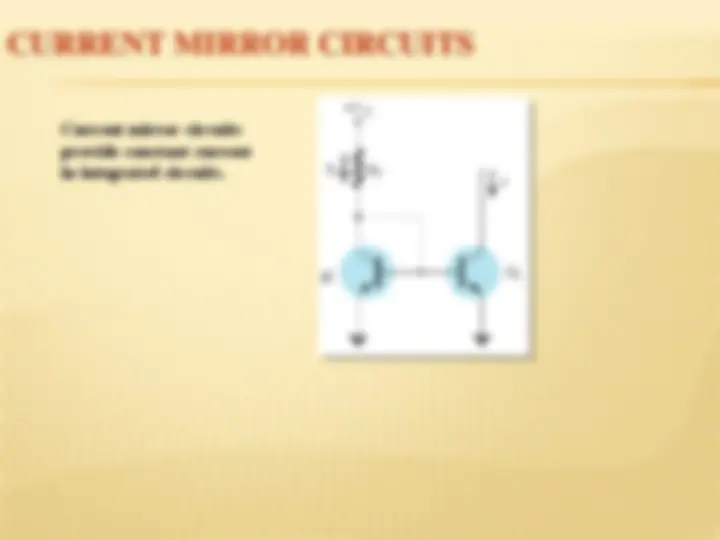
Constant-current sources can be built using FETs, BJTs, and
combinations of these devices.
E
Z BE E R
V V I I
− =
more…
ID = IDSS = 10 mA