
















Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
The brachial plexus is the network of nerves that sends signals from the spinal cord to the shoulder, arm and hand. A brachial plexus injury occurs when these nerves are stretched, compressed, or in the most serious cases, ripped apart or torn away from the spinal cord.
Typology: Slides
1 / 42

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!



































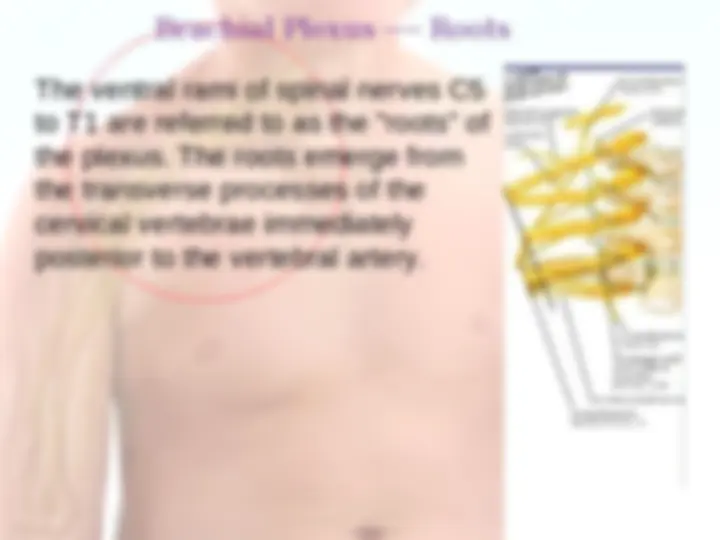
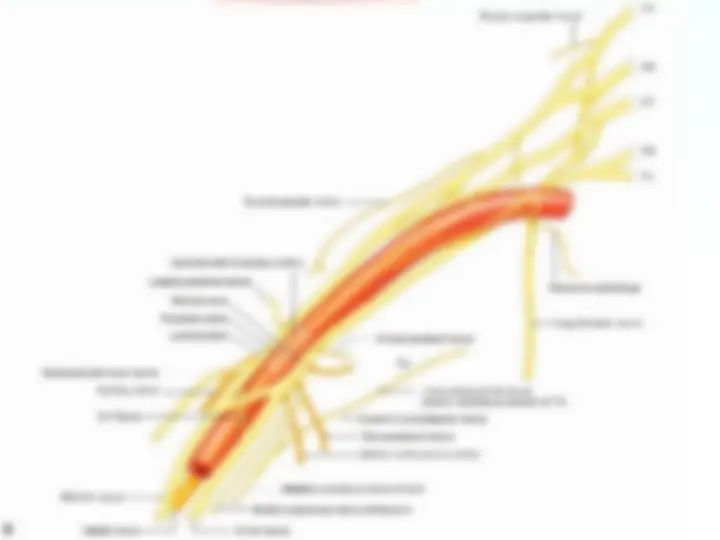
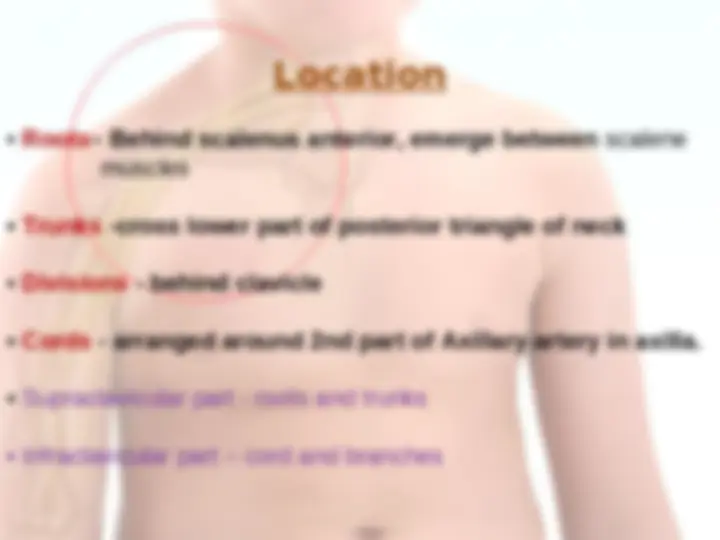
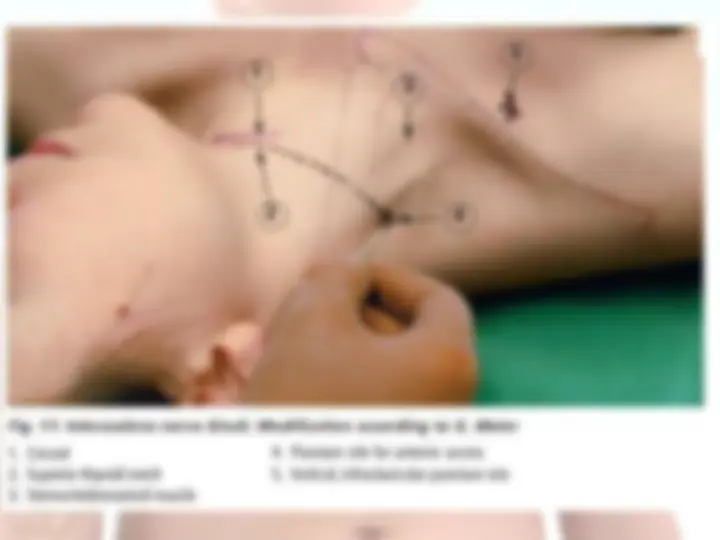
The brachial plexus is a network ( plexus ) of nerves (formed by the ventral rami of the lower four cervical nerves and first thoracic nerve (C5, C6, C7, C8, and T1). This plexus extends from the spinal cord, through the cervicoaxillary canal in the neck, over the first rib, and into the armpit.
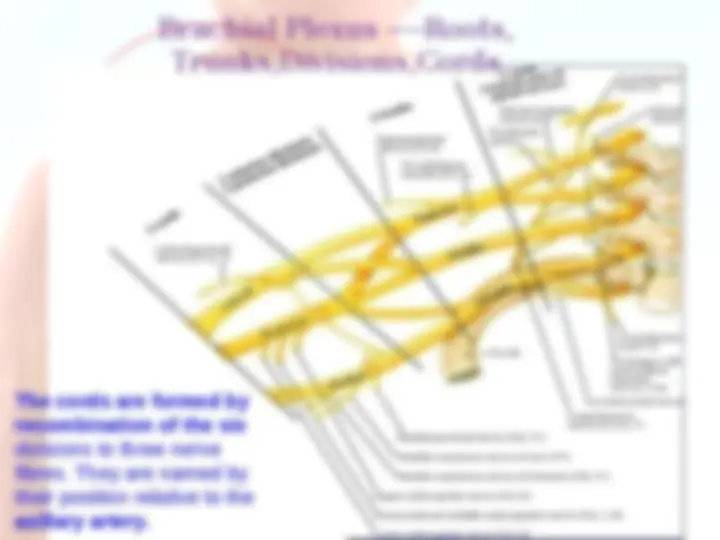
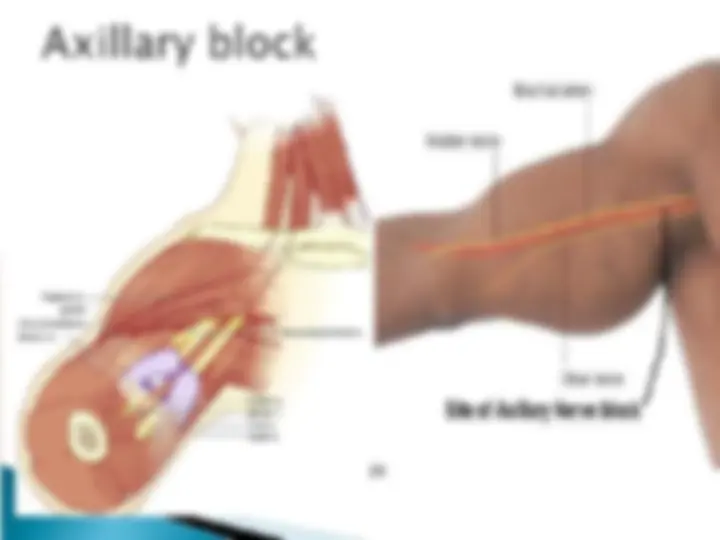
The cords are formed by recombination of the six divisions to three nerve fibres. They are named by their position relative to the axillary artery.
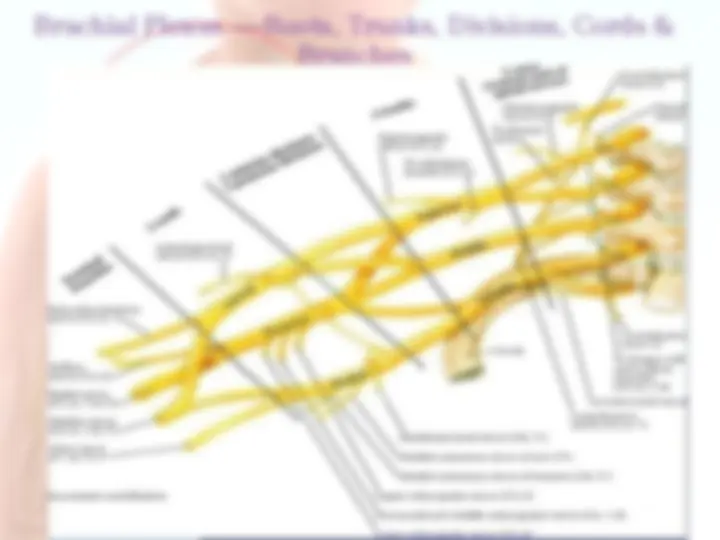
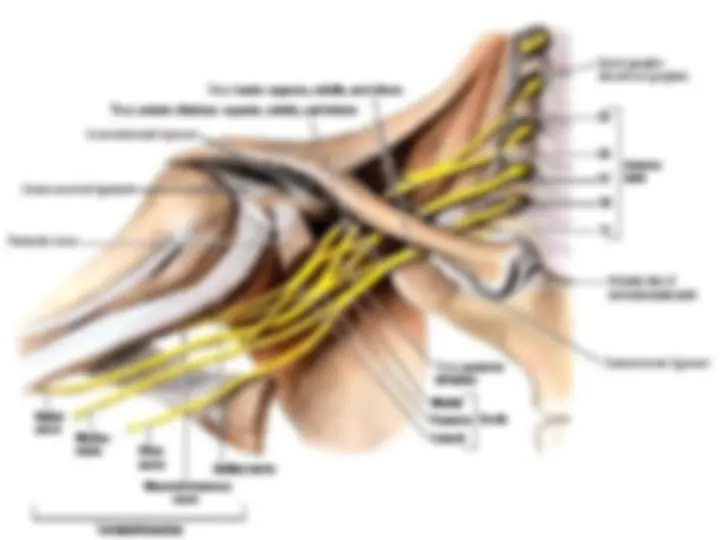
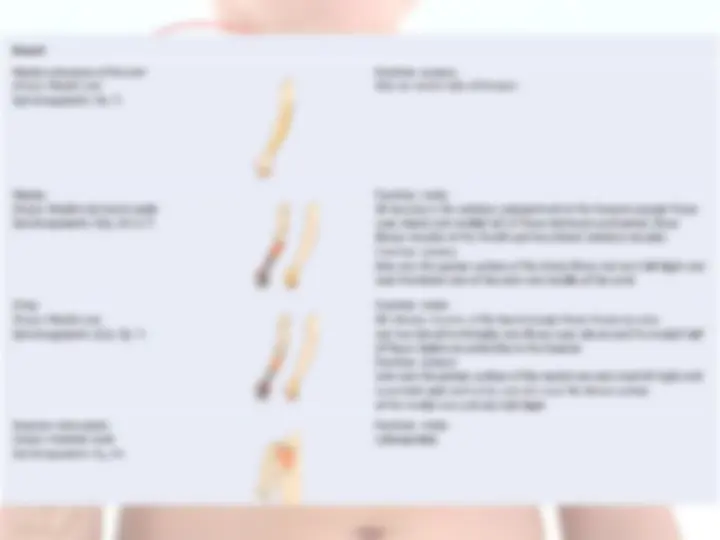
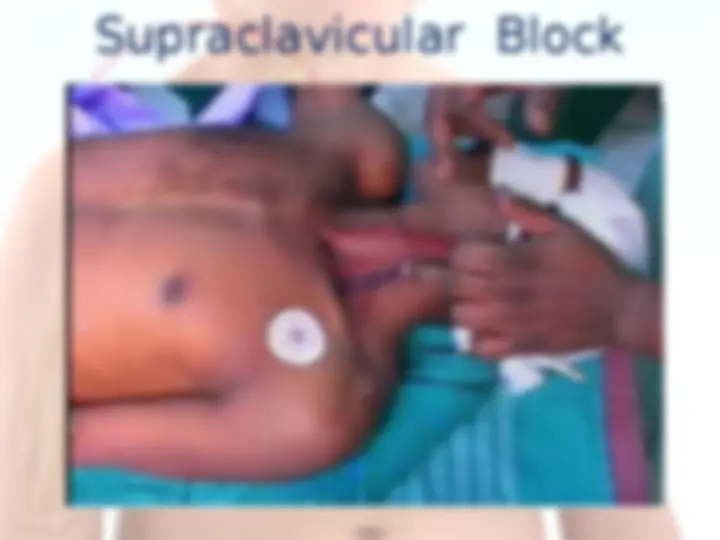
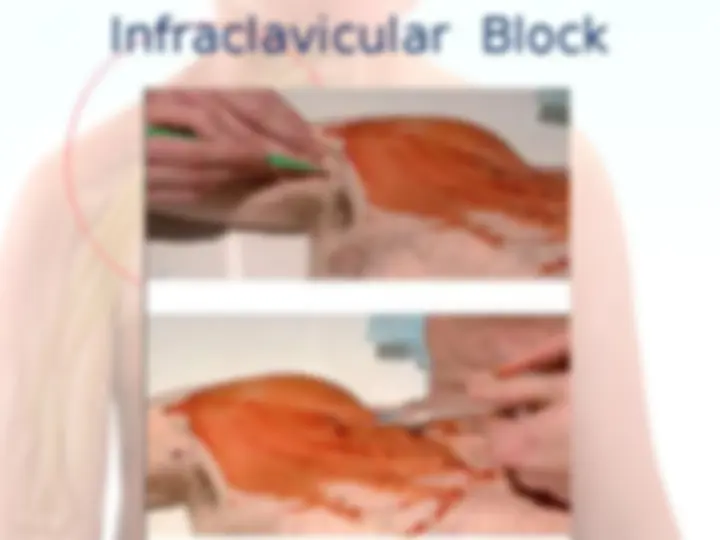
Branches of Brachial Plexus Supraclavicular Infraclavicular From the roots : 1.Dorsal scapular Nv (C5) – Rhomboideus Maj & minor 2.Br to join Phrenic Nv 3.Long thoracic Nv (C5-C7) – Serratus anterior. 4.Muscular branches to Longus colli & Scalenii. From the trunk : 1.Nv to subclavius 2.Suprascapular nv (C5-C6)- Supra & Infra spinatus.
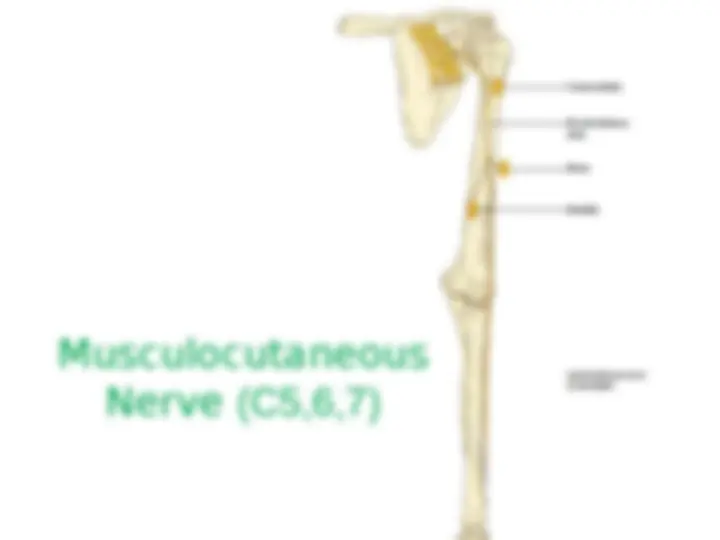
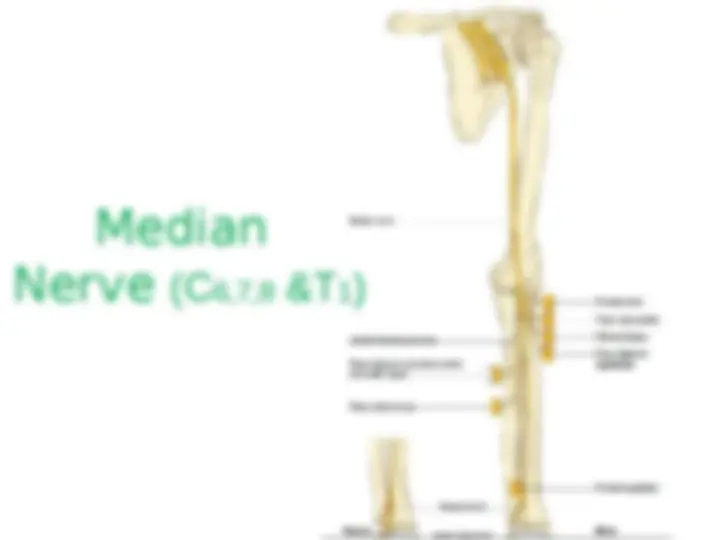
Lateral Cord branches: (LML) 1.Lateral Pectoral Nv (C5-C7) – Supplies Pectoralis Maj & minor 2.Musculo cutaneous Nv (C5-C7) – Supplies Choracobrachialis, Biceps brachi (both head) and medial part of Brachialis. 3.Lateral root of Median Nv (C5-C7). Medial Cord branches: (M 4
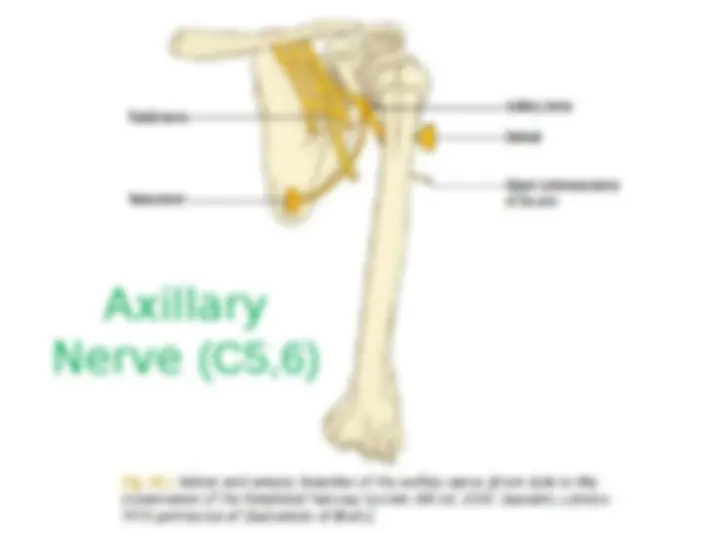
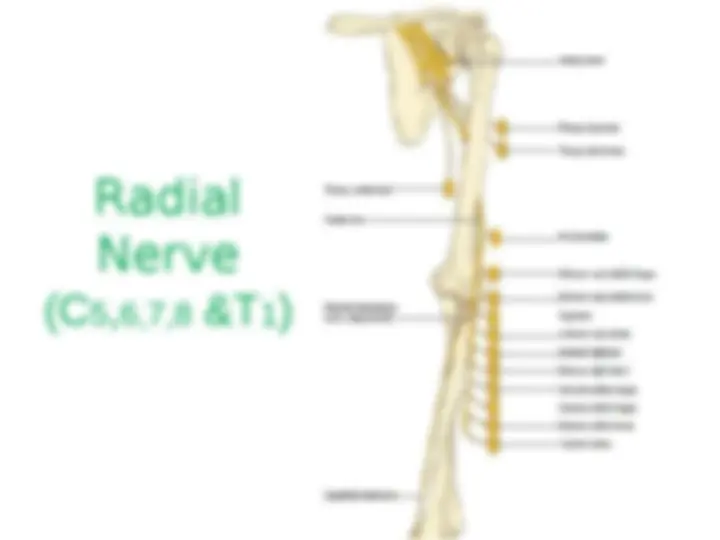
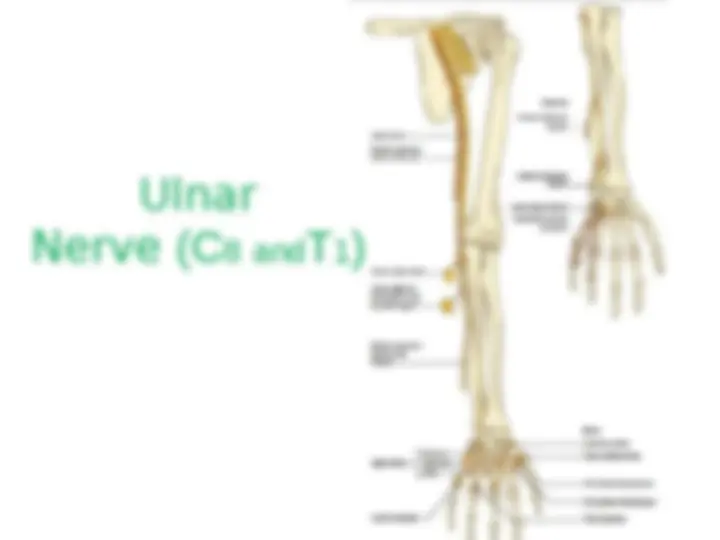
1.Medial Pectoral Nv (C5-C7) – Supplies Pectoralis Maj & minor 2.Medial cutaneous Nv of forearm 3.Medial cutaneous Nv of arm 4.Medial root of Median Nv (C8-T1). 5.Ulnar Nv (C8-T1). Postreior Cord branches: (ULMAR) 1.Upper subscapular Nv (C5-C6) – Upper part of subscapularis. 2.Lower subscapular Nv (C5-C6) – Lower part of subscapularis & Teres major. 3.Middle subscapular (Thoracodorsal) Nv – Latissimus dorsi. 4.Axillary Nv (C5-C6) – Supplies Deltoid and Teres minor 5.Radial Nv (C5,C6,C7,C8 & T1)) – Triceps, Anconeus, Brachioradialis and all the