


















































Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
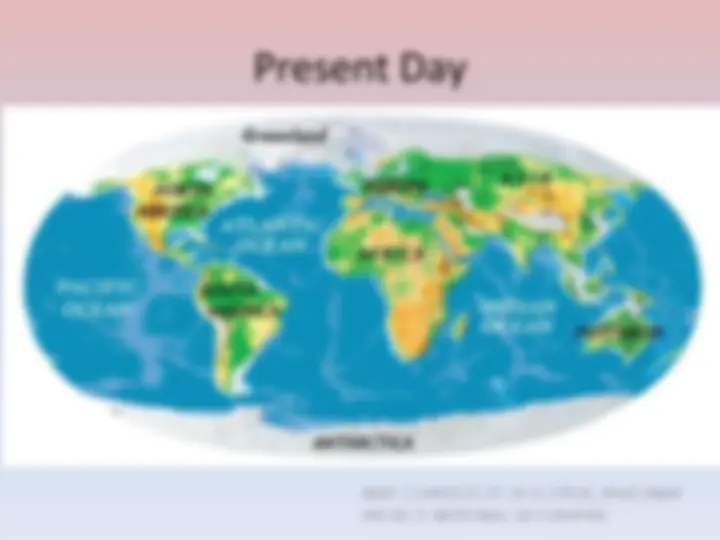
Explore Antarctica, the 7th largest continent and the coldest, driest, and windiest place on Earth. Learn about its unique history, formation, and the scientific research conducted there, including ice dynamics, drilling, and the Antarctic Treaty. Discover the significance of the South Pole and its research stations, as well as the impact of climate change and tourism.
What you will learn
Typology: Study notes
1 / 87

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!
















































































th
John Gunton Mar 27, 2021
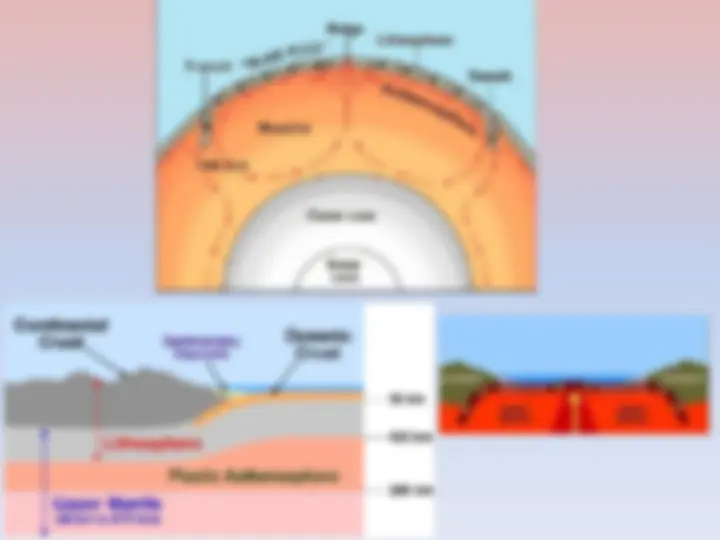
Why the 7 th Continent? What defines a continent? Convention: World’s main continuous expanses of land? Historical: Last to be discovered Geological: “Lands accreted to a core of ancient cratonic rock (2.4 Gya)”
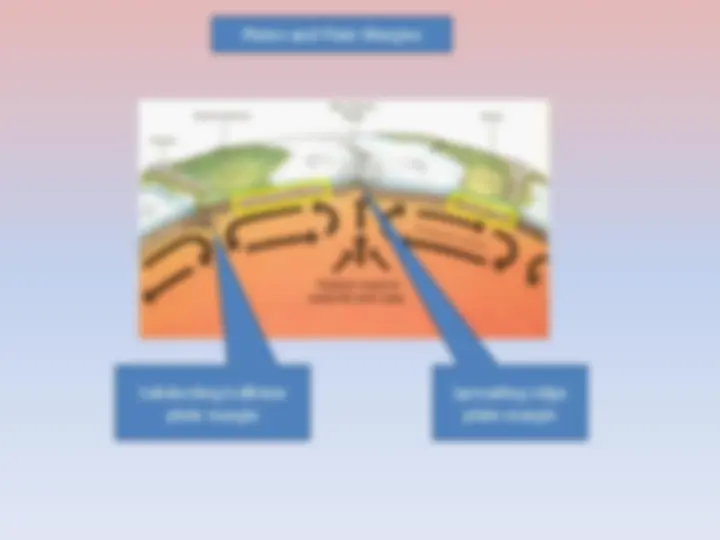
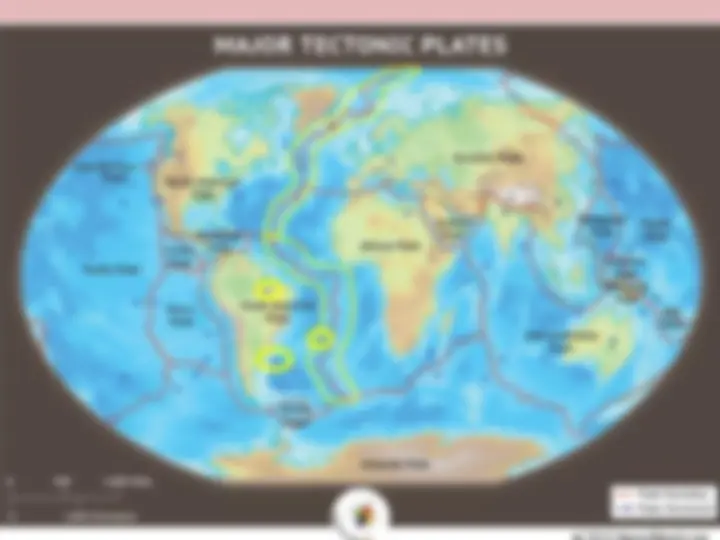
Subducting/collision plate margin Plates and Plate Margins Spreading ridge plate margin
J. Tuzo Wilson CC OBE FRS FRSE FRSC (1908-1993) Continental Drift: A precursor concept to Plate Tectonics
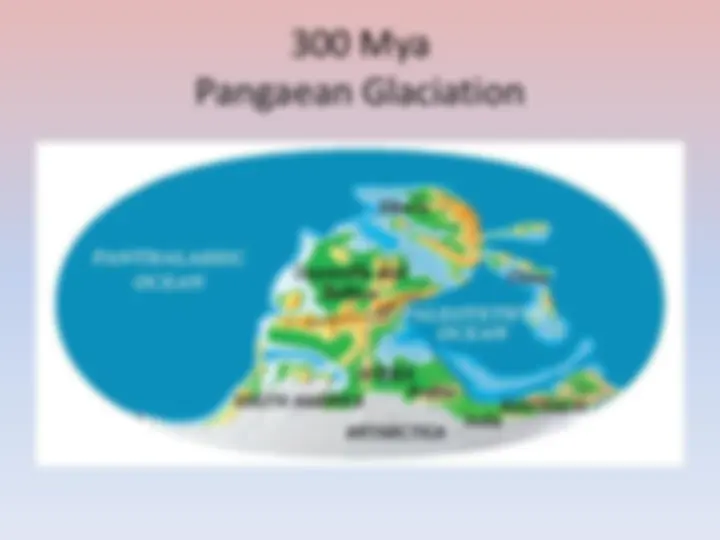
300 Mya Pangaean Glaciation
300 My of Temperature Fluctuation Global Average Wikimedia 1 8 C Snowball Earth # Drake Passage Forms & Antarctica is isolated in polar position 40 mya East Antarctica Ice Sheet West Antarctica Ice Sheet North Hemisphere Ice TODAY Time zero Snowball Earth # TODAY’s Temp Scale change Scale change Scale change Scale change
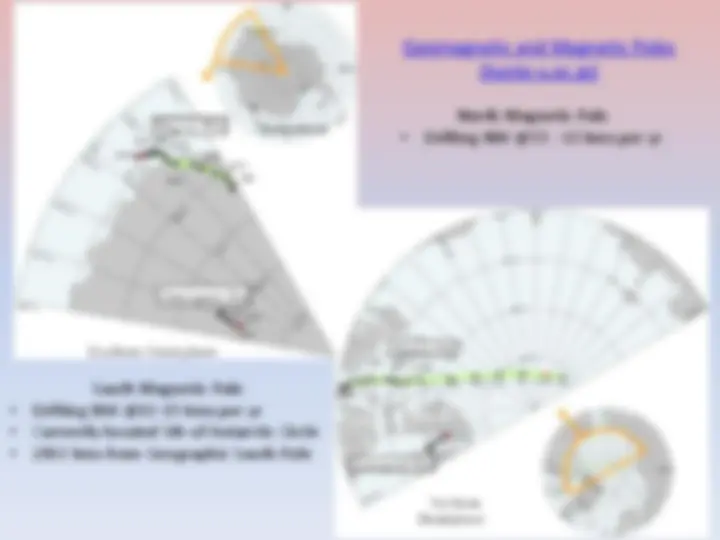
South Magnetic Pole
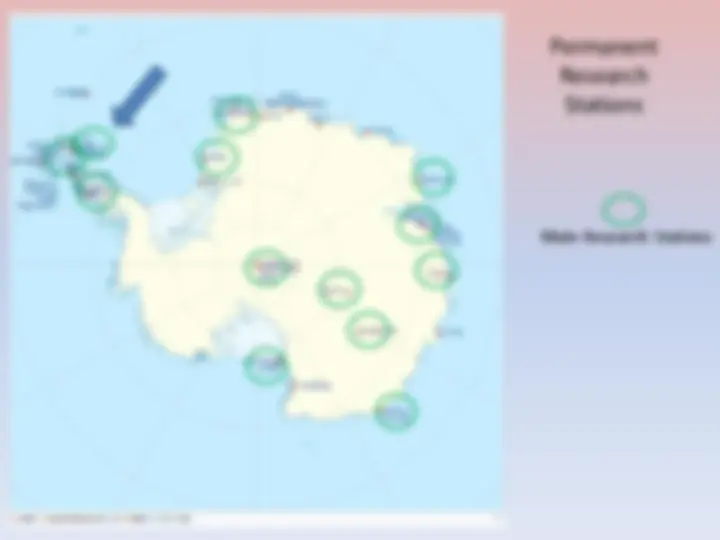
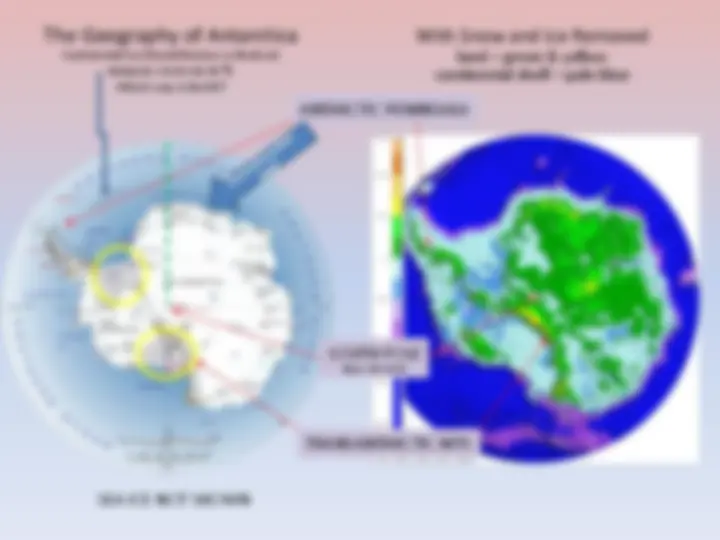
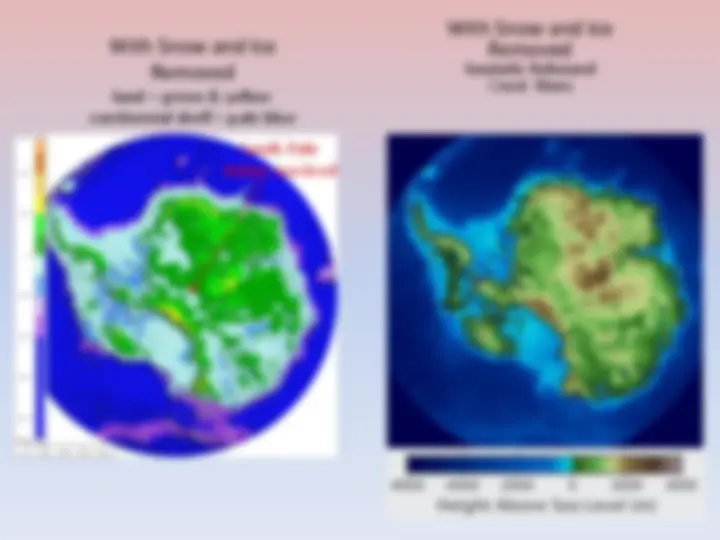
ANTARCTICA First sighted 1820 (Russians - Lazarev) First landing 1821 (Americans - Davis) 7 th Continent 1839 (Americans – Wilkes) 5 th largest continent Twice size of Australia Coldest, driest, windiest, highest continent Highest Point 4 , 892 m ( 16 , 050 ft) Vinson Massif 98 % covered by a continuous ice sheet called land ice to distinguish it from sea ice The land ice holds approx. 70 % of world`s fresh water Predicted sea level rise of 60 m if melted No permanent human residents