


Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
An introduction to flowcharts, their significance, and how to create one. Intended for students in grades 2-8, this 45-minute activity uses household items and paper to design a flowchart for decision-making processes or identifying items. The document also includes background information on flowcharts, their symbols, and real-life applications in engineering and programming.
What you will learn
Typology: Assignments
1 / 2

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!


Property of Iowa State University Engineering Community Outreach: No duplication without permission. Version 5/7/
Grades: 2-
Length: 45 minutes
Concepts: Flowcharts, flow, sequences, data Materials : household items, pencil, paper
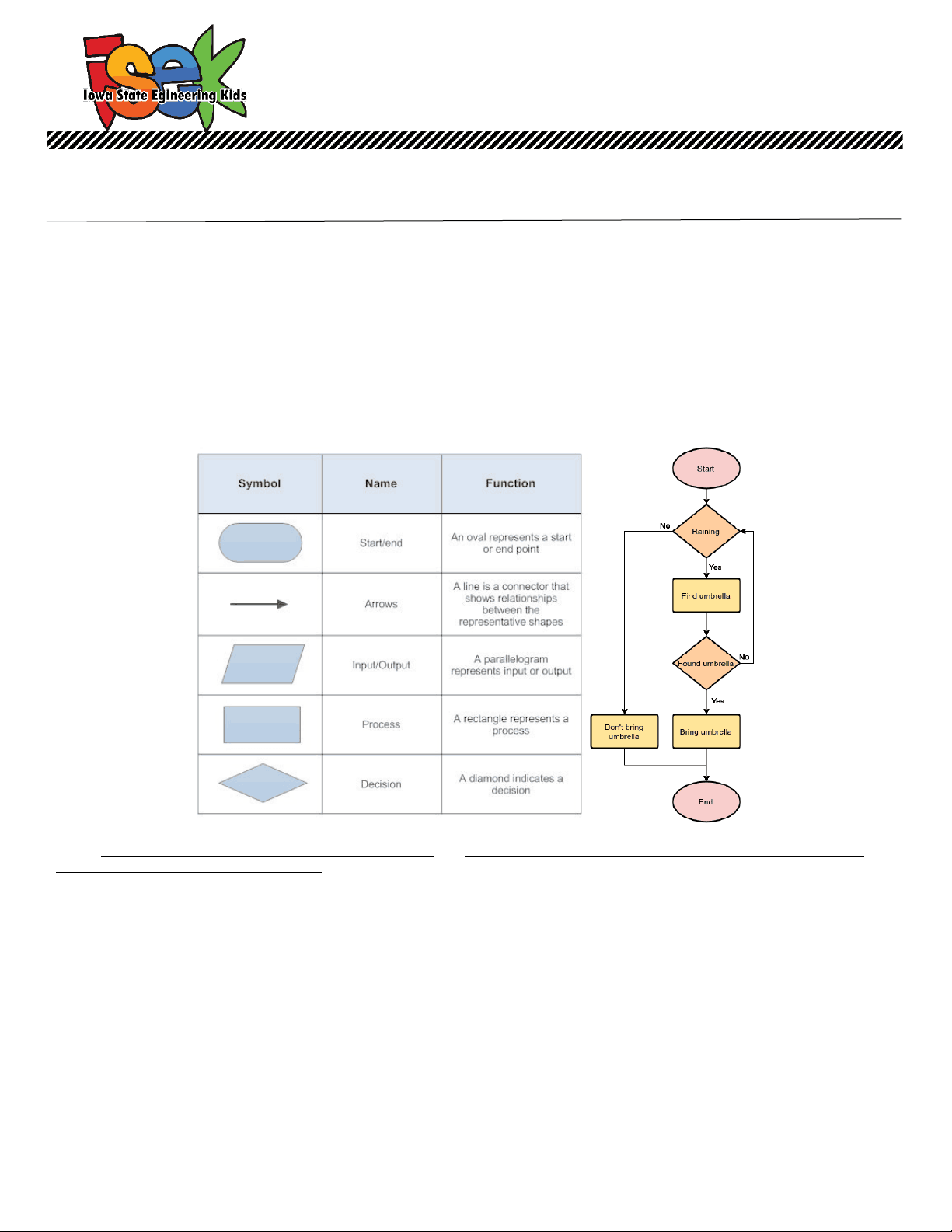
A flowchart is a diagram that depicts a process, system, or computer algorithm for just about anything you can imagine. They are used in multiple fields to document, study, plan, and communicate complex processes in a clear, easy manner. They use different shapes, such as rectangles, ovals and diamonds to define each step along with arrows pointing to define the flow and sequence. It is a fun and easy way to visualize, or see, your information known as data.
Here is an example of a simple flow chart and what each symbol means:
Credit: www.smartdraw.com/flowchart/flowchart-symbols.htm and https://medium.com/@warren2lynch/a-comprehensive-guide-for- flowchart-over-50-examples-785d6dfdc
You probably use this type of thinking every day. For example if you found a sock on the floor, what would you do? First you might ask yourself whether it was a clean sock or a dirty sock. Depending on that information, you then decide what to do with it. If it was dirty, you might put it with the rest of the laundry. If it is clean, you may need to ask another question: whom does the sock belong to? Depending on that answer, you may need to put it in different places.
Engineers and other STEM professionals use flowcharts to help organize their ideas and communicate to their peers. This type of thinking is also used in programming. In order to tell a computer exactly what to do, a computer programmer needs to provide the computer a set of instructions with great detail. For example, depending on the air temperature in the room, a computer (like in a thermostat) may need to tell the air conditioner or heater to turn on or do nothing. A flowchart can help layout the necessary steps in the programmer’s thinking to make sure the computer has all the steps in the process.
Property of Iowa State University Engineering Community Outreach: No duplication without permission. Version 5/7/
Learn more about flow charts at https://kids.kiddle.co/Flow_chart.
Think about what other kinds of data (information) exist? How do we use data and flowcharts to improve our lives every day? How else can we sort data effectively?
Activity: Start by reading through the Background Information.
What’s the Problem: Today you are going to make your own flowchart. You can make a process
showing your decision making for an activity (like getting dressed) or to identify items inside your own
home (similar to I-Spy).
Be creative and detailed: Since flowcharts are used to communicate your thinking to others, think
through all the steps. If your example is getting dressed, does your outfit depend on the season? Does it
depend on the activity that you will be doing?
Design your Solution: Brainstorm, plan, and draw out your flowchart! If you need ideas of what kind of
flowchart to make, look at the example below. What do you need to consider? What changes your
decision?
Try it Out: Once you have your flow chart, try it out with someone!
Expand Upon your Design. What else needs to be considered? Did you get to the end of your
flowchart? Does anything need to be in a different sequence (order)?
Credit: https://teachersworkstation.files.wordpress.com/2014/06/solid-liquid-gas-flowchart.png
Definitions:
Reading and Resources:
Books and Articles
from the Wonderfully Weird Brains of Children by David Vienna
Videos
Check out more great resources at www.isek.iastate.edu!